Slides 4 – 9: What are the types of glaciers?
advertisement
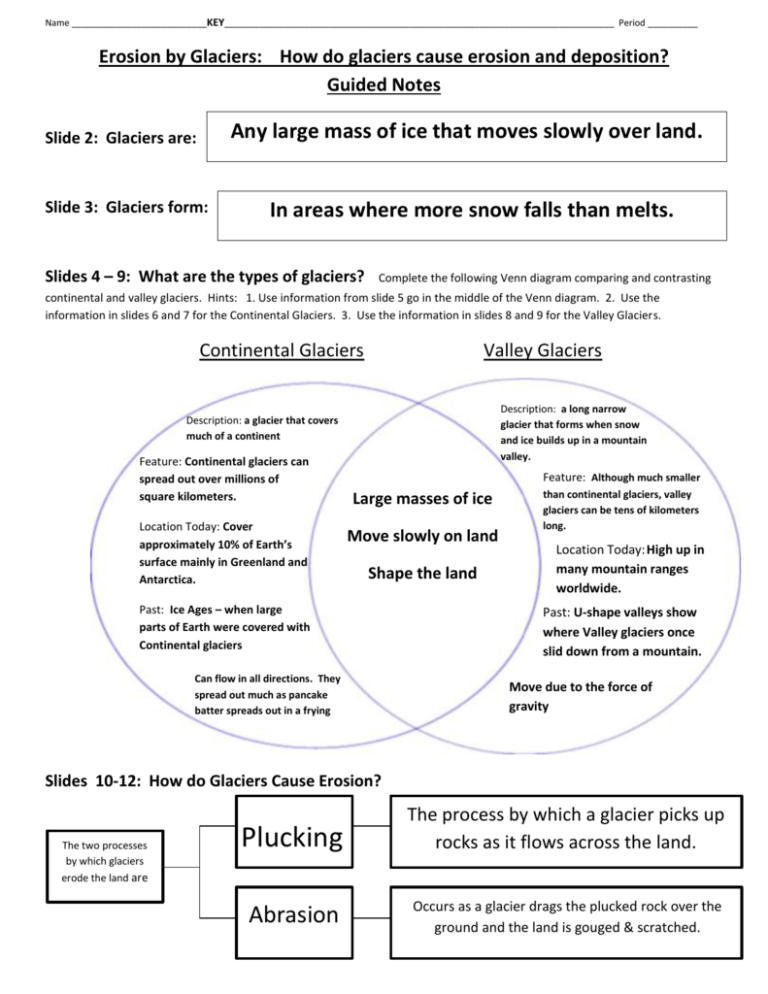
Name ___________________________KEY______________________________________________________________________________ Period __________ Erosion by Glaciers: How do glaciers cause erosion and deposition? Guided Notes Any large mass of ice that moves slowly over land. Slide 2: Glaciers are: Slide 3: Glaciers form: In areas where more snow falls than melts. Slides 4 – 9: What are the types of glaciers? Complete the following Venn diagram comparing and contrasting continental and valley glaciers. Hints: 1. Use information from slide 5 go in the middle of the Venn diagram. 2. Use the information in slides 6 and 7 for the Continental Glaciers. 3. Use the information in slides 8 and 9 for the Valley Glaciers. Continental Glaciers Valley Glaciers Description: a long narrow glacier that forms when snow and ice builds up in a mountain valley. Description: a glacier that covers much of a continent Feature: Continental glaciers can spread out over millions of square kilometers. Location Today: Cover approximately 10% of Earth’s surface mainly in Greenland and Antarctica. Feature: Although much smaller Large masses of ice Move slowly on land Shape the land Past: Ice Ages – when large parts of Earth were covered with Continental glaciers . Can flow in all directions. They spread out much as pancake batter spreads out in a frying pan than continental glaciers, valley glaciers can be tens of kilometers long. Location Today: High up in many mountain ranges worldwide. Past: U-shape valleys show where Valley glaciers once slid down from a mountain. Move due to the force of gravity Slides 10-12: How do Glaciers Cause Erosion? The two processes by which glaciers Plucking The process by which a glacier picks up rocks as it flows across the land. Abrasion Occurs as a glacier drags the plucked rock over the ground and the land is gouged & scratched. erode the land are Slide 14: What Landforms are created by Glacial Erosion? Horn When glaciers carve away the sides of a mountain, the result is a sharpened peak. Cirque Complete the following table Fiord Arête U-Shaped Valley Form when A bowlA sharp Slowly the level of moving shaped ridge the sea rises valley hollow separating filling a glaciers eroded by valley once two carve or cut by a a glacier. cirques. Slide 15: Glacial Till is: glacier. scoop out U-shaped valleys. The sediment deposited as a glacier melts and recedes. Glacial till is of various sizes, and can be in the size of clay, silt, sand, gravel, or boulders. Slide 16: What Landforms are created by Glacial Deposition? Complete the following table Drumlin A long mound of till that is smoothed in the direction of the glaciers flow. Kettle Lake Forms when a depression left in till by melting ice fills with water. Moraine Forms at the edge of a glacier where the glacier deposits till and are usually in the form of a mound or ridge.







