Notes
advertisement

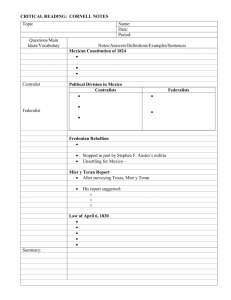
____________________________________ 7 Grade Social Studies Canada, Mexico, & U.S. History from the Revolution to Reconstruction th Class 20—Mexican Independence September 28, 2015 Focus: Why would Colonial New Spain feel inspired by the American Revolution? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------Student Objectives: 1. I will identify the following events that help push Mexico to achieve its own independence: Bourbon Reform The Enlightenment The American Revolution The French Revolution The Haitian Revolution 2. I will identify the leaders of Mexican independence. Homework: -Read and outline Chapter2, Section 2, pgs. 15-16-start @ Iturbide Takes Power (due 9/29) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 3, pgs. 17-18 (due 9/30) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4, pgs. 19 (due 10/2) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4 & 5, pgs. 20-21 (due 10/5) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 6, pgs. 22-24 (due 10/6) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 7, pgs. 25-26 (due 10/7) -Chapter 2 Test Thursday 10/8 -Current Events (“The Confederate Flag: Heritage or Hate?”) due 10/5 Handouts: None I. Revolutionary Movements II. Independence leaders Key terms/ideas/people/places: Bourbon Reform Enlightnement American Revolution French Revolution Haitian Revolution Social Revolution mexicanidad mexicanos John Locke Agustìn de Iturbide Father Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla José María Morelos y Pavón grito de Dolores Virgin of Guadalupe Guerrilla Plan of Iguala Vicente Guerrero Three Guarantees Mexican Flag coup d'état By the end of class today, I will be able to answer the following: What were the political beliefs of the Enlightenment? Who became a unifying force in Mexico? Who is considered the father of Mexican independence? What became a symbol of the revolution? What is the Plan of Iguala ? What is a coup d'état? How do guerrillas fight? Notes Class 20—Mexican Independence September 28, 2015 Bourbon Reforms 1780s Maximize revenue collection Make sure colony demands Spanish goods New tax system-collected by Peninsulares Mixed bag for Criollos o Get high paying jobs in the military o Pay higher taxes and losing government jobs o they were the true Mexicans, descendants of the conquistadors but linked to the Aztec past by their birth in New Spain National conscious emerges-a sense of Mexico as a geographical and cultural space different from Spain Start celebrating their native culture or their mexicanidad Don’t call themselves criollos, but instead mexicanos Virgin of Guadalupe gave criollos, mestizos, and Indians a shared sense of identity Enlightenment John Locke-government exists to protect life, liberty, and property Liberty and citizenship Freedom and Equality American Revolution Model for all Latin American countries Attacked divine right of king and the idea of colonial empires Showed criollos that people could take history into their own hands French Revolution Toppled one of Europe’s most powerful monarchies based on liberty, equality and fraternity Haitian Revolution Inspired by the French Revolution Non-whites seek freedom Shows criollos the social dangers of independence Criollos recognized that revolution was destructive and involved international wars with immense loss of life. That was ok, as long as their revolution would be like the American Revolution which left the social hierarchy intact, unlike the French and Haitian Revolutions. Both the American Revolution and the Haitian Revolt were done by colonial populations smaller than Mexico’s and had over thrown imperial powers greater than Spain Father Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla-criollo Considered the father of the independence movement o Early on September 16, 1810 Hidalgo rings the church bells to summon his flock to mass o About to be arrested as a conspirator o grito de Dolores or Cry of Dolores-inaugurated a long series of wars that ultimately freed Mexico from Spain “My children: a new dispensation comes to us today. Will you receive it? Will you free yourselves? Will you recover the lands stolen three hundred years ago from your forefathers by the hated Spaniards? We must act at once….Will you not defend your religion and your rights as true patriots? Long live our Lady of Guadalupe! Death to bad government! Death to the Peninsulares!” Hidalgo picks up a banner of the Virgin of Guadalupe and proclaimed her the symbol of his rebellion-unifying force No military training Captured, executed, and decapitated José María Morelos y Pavón Mestizo Guerrilla tactics Brilliant military strategist The peninsulares and criollos become afraid of mob violence (social revolution) and preferred colonial rule to Morelos’ rebellion which they viewed as chaos. Placed in front of the firing squad and executed-head placed on same wall as Hidalgo’s One of the people to hunt down Morelos was Agustìn de Iturbide. Agustìn de Iturbide For a decade fought against the rebels on the side of the crown After he tracked down Morelos he was after a new leader, Vicente Guerrero Gets fired for a while because he is a cruel commander-wants to stick it to his boss Meets Guerrero and plans a coup d'état and they create the Plan of Iguala o Equal treatment under law for peninsulares and criollos o Catholicism is the official religion o Mexico would be a moderate monarchy-Invite a King Ferdinand or some prince Known as union, religion, and independencia or the Three Guarantees Mexican flag o Red-union of America and Europe-blood of Criollos and Peninsulares o White-purity of catholic faith o Green-hope of independence Iturbide’s plan is a compromise-instead of asking for death to Peninsulares he curried their favor. Brought liberals and conservatives together-liberals wanted a republic and conservatives wanted an absolute monarchy. Compromise because both groups want independence. Impact of the Revolution: Revolutionary movements are almost always preceded by a plan that outlines the principles in order to gain wider support For a century the military is very much involved in the political process and would bargain with opposing factions for a greater share of the nation’s wealth The idea of coup d'état ____________________________________ 7 Grade Social Studies Canada, Mexico, & U.S. History from the Revolution to Reconstruction th Class 21— Mexico under Agustìn de Iturbide September 29, 2015 Focus: Explain the Plan of Iguala and the three major points it makes. How is the plan incorporated into the Mexican flag? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------Student Objectives: 1. I will analyze Mexico under the leadership of Agustìn de Iturbide. Homework: -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 3, pgs. 17-18 (due 9/30) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4, pgs. 19 (due 10/2) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4 & 5, pgs. 20-21 (due 10/5) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 6, pgs. 22-24 (due 10/6) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 7, pgs. 25-26 (due 10/7) -Chapter 2 Test Thursday 10/8 -Current Events (“The Confederate Flag: Heritage or Hate?”) due 10/5 Handouts: None I. First Emperor of Mexico II. Antonio de Padua María Severino López de Santa Anna y Pérez de Lebrón A. Plan de Veracruz Key terms/ideas/ people/places: Antonio de Padua María Severino López de Santa Anna y Pérez de Lebrón Nepotism Generalìsimo de Tierra y mar caudillo By the end of class today, I will be able to answer the following: What did the Plan de Veracruz supposedly make Mexico? What is a caudillo? What precedent did Iturbide set that? Agustìn de Iturbide Precedent Notes Class 21— Mexico under Agustìn de Iturbide September 29, 2015 1821-Mexican Independence from Spain Agustìn de Iturbide Makes himself Generalìsimo de Tierra y mar (highest general of the earth and sea) pays himself 180,000 pesos a year Caudillo-a charismatic military leader with a personal following Becomes emperor of Mexico Here were some of the issues facing Iturbide as emperor: Silver mining destroyed-national currency had no support People who had money were investing outside of Mexico Agricultural production decreased and food prices rose He had a large army and had to pay the 40,000 officers Iturbide was also egotistical Nepotism-awarded noble titles to his family Birthdays of his immediate family became national holidays If you wanted to see him, you had to kneel and kiss his hand He became the first Mexican head of state to abolish/dissolve a legislative branch that opposed him-establishes a precedent Precedent-an example for others to follow Antonio de Padua María Severino López de Santa Anna y Pérez de Lebrón-Plan de Veracruz- coup d'état to overthrow Iturbide and make Mexico a republic Iturbide is arrested in executed ____________________________________ 7 Grade Social Studies Canada, Mexico, & U.S. History from the Revolution to Reconstruction th Class 22— Federalism vs. Centralism September 30, 2015 Focus: Place the following events in the correct chronological order from first to last: Father Hidalgo executed, grito de Dolores, Plan de Iguala, Agustìn de Iturbide becomes emperor of Mexico, José Morelos is executed, Vicente Guerrero leads the rebellion, and Agustìn de Iturbide is executed. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------Student Objectives: 1. I will define the following terms: Clientelism Federalism Centralism 2. I will identify the key components of the Mexican Constitution of 1824. 3. I will analyze the impact of outside influences upon Mexico. Homework: -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4, pgs. 19 (due 10/2) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4 & 5, pgs. 20-21 (due 10/5) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 6, pgs. 22-24 (due 10/6) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 7, pgs. 25-26 (due 10/7) -Chapter 2 Test Thursday 10/8 -Current Events (“The Confederate Flag: Heritage or Hate?”) due 10/5 Handouts: None I. Centralism vs. Federalism II. Clientelism III. Constitution of 1824 IV. Foreign Involvement A. Investment B. Monroe Doctrine Key terms/ideas/ people/places: Centralism Federalism Vicente Guerrero Santa Anna Clientelism Caudillo Guadalupe Victoria James Monroe Monroe Doctrine By the end of class today, I will be able to answer the following: Who was Mexico’s first president? How do caudillos use clientelism to stay in power? What is the difference between federalism and centralism? Who enforced the Monroe Doctrine in the 19th Century? Notes Class 22— Federalism vs. Centralism September 30, 2015 Centralism/Centralists o Strong central government o Catholic church-strong political role Federalism/Federalists o Weak central government o Independent, strong states o End privileges of the Church Constitution of 1824 o 3 branches-executive, legislative, & judicial Legislative 2 houses-Senate (2) & Chamber of Deputies (population) Federalism Executive-President Elected by state legislatures-4 year term o Catholic Church maintains its power o President-emergency powers = dictator Centralism Caudillos had military forces at their personal command and they thus vied for power after independence. Their power rested on charisma and personal alliances in which the caudillos promised a material benefit to their followers, or clients, who reciprocated by pledging loyalty. This practice is known as clientelism which is the practice of using family, marriage, and friendship to forge important economic and political networks. Caudillos viewed centralism and federalism as vehicles for their own ambition and thus many would change affiliations to benefit themselves. The first president of the republican Mexico-Guadalupe Victoria. He had a hard time dealing with the caudillos, especially Santa Anna his own Vice President tried to overthrow him, even though it was unsuccessful When it comes time for the second election, Santa Anna and others don’t like the result and imposed Vicente Guerrero as the second president. Just as Guerrero took office, Spain attempted to recapture its colony. They were repelled by Santa Anna. After the failed attempt at re-conquest, many Spaniards in Mexico left because they felt like they would be targeted. Because these Spaniards had money, they took it with them. What ends up happening is that the Spanish investors are replaced by British, French, and German merchants-this makes Mexico extremely dependent on European industrial powers. That is not a good thing for Mexico. With the Constitution the president can act like a dictator in times of emergency. An attempted re-colonization of Mexico is an emergency. When the Spanish were defeated, Guerrero refused to relinquish his power. Guerrero’s own vice president stages yet another coup and is successful. Guerrero tries to escape on a boat. However, the captain has already sold Guerrero out and once Guerrero boards the ship, he is tied hand and foot and take to be tried. Found guilty of treason, he too dies at the hands of a firing squad, just like Hidalgo, Morelos, and Iturbide. Monroe Doctrine-proclaimed the U.S. the protector of the Western Hemisphere ____________________________________ 7 Grade Social Studies Canada, Mexico, & U.S. History from the Revolution to Reconstruction th Class 23—Santa Anna October 1, 2015 Focus: If Santa Anna was able to become president/leader of Mexico 11 different times, do you think he was Centralist or a Federalist? Explain. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------Student Objectives: 1. I will analyze the role Santa Anna played in forming Mexican politics. Homework: -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4, pgs. 19 (due 10/2) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4 & 5, pgs. 20-21 (due 10/5) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 6, pgs. 22-24 (due 10/6) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 7, pgs. 25-26 (due 10/7) -Chapter 2 Test Thursday 10/8 -Current Events (“The Confederate Flag: Heritage or Hate?”) due 10/5 Handouts: None I. Santa Anna A. Background B. Impact III. French Revolution A. Haitian Revolution Key terms/ideas/ people/places: “His Most Serene Highness” Santa Anna Pastry War By the end of class today, I will be able to answer the following: What social class was Santa Anna? Why was Santa Anna always able to rise to power? Notes Class 23—Santa Anna October 1, 2015 Between 1821-1850 Mexico had 50 changes in government o 11 of those times were Santa Anna o average term-seven and half months o Caudillos-switched back and forth in their allegiance From until 1834, Santa Anna= Federalist After 1834, Santa Anna=Centralist Santa Anna o Born in 1794 o Criollo o Joined army at 16 o Followed Iturbide’s lead and switched sides o Helps overthrow Iturbide o Saves Mexico from Spain o As President, he gets bored and goes home-leaves country to vice president o Portrays himself as protector of fatherland-Spain, France, Texas, U.S. o Loses his leg in the “Pastry War” o Makes everyone call him “His Most Serene Highness” Pastry War (1838) o French Cannon hits Santa Anna’s horse and his left leg is badly wounded o Amputated just below knee o 1842-has leg dug up, transported to Mexico City, where it was paraded through the streets in a celebration to Santa Anna, he had given the leg to the fatherland. ____________________________________ 7 Grade Social Studies Canada, Mexico, & U.S. History from the Revolution to Reconstruction th Class 24—Texas Independence October 2, 2015 Focus: What did the Mexican government look like under the Constitution of 1824? Did it favor Centralists or Federalists? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------Student Objectives: 1. I will analyze why Mexico lost Texas. Homework: -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 4 & 5, pgs. 20-21 (due 10/5) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 6, pgs. 22-24 (due 10/6) -Read and outline Chapter 2, Section 7, pgs. 25-26 (due 10/7) -Chapter 2 Test Thursday 10/8 -Current Events (“The Confederate Flag: Heritage or Hate?”) due 10/5 Handouts: None I. Americans in Texas A. Regulations B. Reasons Texas are upset II. Battles A. Alamo B. Goliad C. San Jacinto Key terms/ideas/ people/places: Moses and Stephen Austin Goliad San Jacinto Santa Anna Lone Star Republic By the end of class today, I will be able to answer the following: Who were Moses and Stephen Austin? Why did Mexico invite Americans into Texas? Where was Santa Anna captured? What did Mexicans do to upset Texans? Alamo Notes Class 24—Texas Independence October 2, 2015 1836-Santa Anna-abolish the Constitution of 1824 and create the new Constitution of 1836 much more centralist states were downgraded to departments run by a governor appointed by the central government For Mexico, Texas was a distant frontier. In the year 1800, Texas only had about 7,000 people living in the area. Mexico gave permission to Moses Austin, and later his son Stephen Austin, to settle 300 American families in Texas as long as they met the following criteria: Catholic Good moral character Abide by Mexican law Land in Texas was almost free-it was only ten cents an acre compared to $1.25 in the U.S. The idea did work as by 1835, Mexico had 30,000 people but only 7,800 of those were Mexican. Well it didn’t take long for tension to mount as the Americans did not follow the Catholic faith and more than a number were actually fugitives. Why do the Texans start to get angry and move towards independence? 1829-Mexico abolished slavery 1830-Mexico closed all immigration from the United States 1835-Santa Anna annulled the Constitution of 1824-more centralist means less voice for Texans Santa Anna once again takes up arms and wins victories at the Alamo and Goliad. However, he is caught off guard by Sam Houston at San Jacinto and loses a decisive victory. Two days later he is captured and signs a treaty. Santa Anna was able to escape initially at San Jacinto as he was disguised as a common soldier. When he captured he was dirty and wet and was dressed as a common soldier. The search party did not recognize him until he was addressed as "el presidente" by other Mexican prisoners. Texas was an independent nation, the Lone Star Republic from 1836-1845. Mexico should have easily been able to re-take Texas but Mexico was so racked with internal issues it could never get Texas back.