IEMA
advertisement
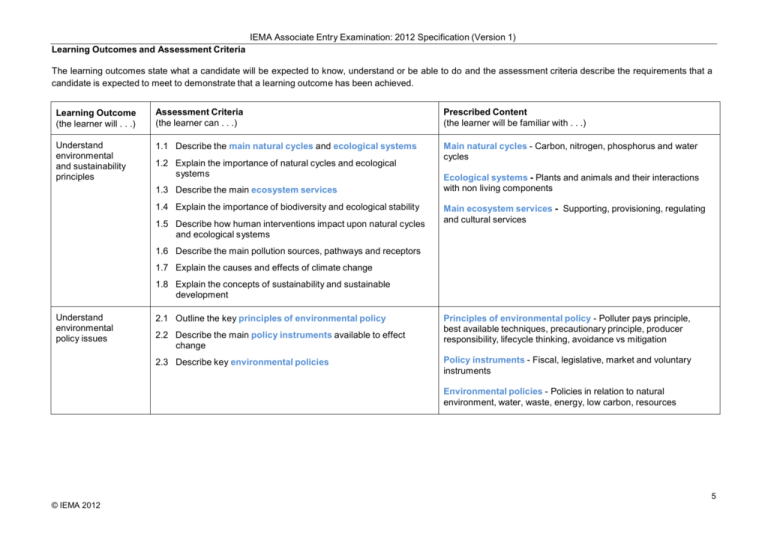
IEMA Associate Entry Examination: 2012 Specification (Version 1) Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes state what a candidate will be expected to know, understand or be able to do and the assessment criteria describe the requirements that a candidate is expected to meet to demonstrate that a learning outcome has been achieved. Learning Outcome (the learner will . . .) Assessment Criteria (the learner can . . .) Prescribed Content (the learner will be familiar with . . .) Understand environmental and sustainability principles 1.1 Describe the main natural cycles and ecological systems Main natural cycles - Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and water cycles 1.2 Explain the importance of natural cycles and ecological systems 1.3 Describe the main ecosystem services 1.4 Explain the importance of biodiversity and ecological stability 1.5 Describe how human interventions impact upon natural cycles and ecological systems Ecological systems - Plants and animals and their interactions with non living components Main ecosystem services - Supporting, provisioning, regulating and cultural services 1.6 Describe the main pollution sources, pathways and receptors 1.7 Explain the causes and effects of climate change 1.8 Explain the concepts of sustainability and sustainable development Understand environmental policy issues 2.1 Outline the key principles of environmental policy 2.2 Describe the main policy instruments available to effect change 2.3 Describe key environmental policies Principles of environmental policy - Polluter pays principle, best available techniques, precautionary principle, producer responsibility, lifecycle thinking, avoidance vs mitigation Policy instruments - Fiscal, legislative, market and voluntary instruments Environmental policies - Policies in relation to natural environment, water, waste, energy, low carbon, resources 5 © IEMA 2012 IEMA Associate Entry Examination: 2012 Specification (Version 1) Understand key environmental legislation and compliance measures 3.1 Describe the regulatory framework including the relationship between UK, EU and international law Types of law - Common and statute law, and civil and criminal law (in jurisdictions where they exist) 3.2 Outline the main types of Law Environmental legislation - Legislation in relation to natural environment, air, water, land, waste, energy, climate change, producer responsibility and planning 3.3 Describe key environmental legislation 3.4 Describe how organisations comply with environmental legislation 3.5 Outline the penalties for non-compliance with environmental legislation Penalties - Civil and criminal sanctions Environmental regulators - National regulators appropriate to country or region of operation/activity 3.6 Explain the roles of environmental regulators Understand environmental management and sustainable development in a business context 4.1 Outline how environmental issues present risks and opportunities for organisations Risks - At an operational and an organisational level, risks to the environment, and risks presented by a changing environment 4.2 Propose measures to manage environmental risks 4.3 Propose ways to take advantage of opportunities created 4.4 Describe the main components of an environmental business case 4.5 Explain the importance of corporate responsibility in relation to environmental management Measures to manage environmental risks - Operational, mechanical, technological, strategic and human (e.g. training/competencies) Environmental business case – Non financial and financial case Organisational value chain – Michael Porter definition 4.6 Explain the importance of environmental sustainability in value chain management 4.7 Explain the importance of effective resource use and recovery 6 © IEMA 2012 IEMA Associate Entry Examination: 2012 Specification (Version 1) Be able to collect, analyse and report on environmental information and data 5.1 Identify relevant sources of environmental information and data 5.2 Describe appropriate techniques to collect, process, store and retrieve information and data 5.3 Evaluate the accuracy and relevance of data 5.4 Analyse and interpret data This box is intentionally blank 5.5 Draw appropriate conclusions 5.6 Use appropriate techniques to disseminate findings 5.7 Describe the role of verification and assurance Be able to apply environmental management and assessment tools 6.1 Describe the application of environmental management and assessment tools 6.2 Outline the advantages and disadvantages of environmental management and assessment tools Be able to analyse problems and opportunities to deliver sustainable solutions 7.1 Recognise when environmental problems and opportunities exist Be able to develop and implement programmes to deliver environmental performance improvement 8.1 Identify ways to improve environmental performance 7.2 Determine the nature of the risk or the scope of the opportunity Environmental management and assessment tools - Risk assessment, environmental management systems, environmental audit, life cycle assessment, environmental impact assessment , strategic environmental assessment, cost benefit analysis, footprinting This box is intentionally blank 7.3 Propose sustainable solutions and programmes to address environmental problems and opportunities 8.2 Describe how to develop a programme to improve environmental performance 8.3 Describe how to implement a programme to improve environmental performance This box is intentionally blank 8.4 Describe methods to monitor a programme to improve environmental performance 7 © IEMA 2012 IEMA Associate Entry Examination: 2012 Specification (Version 1) Be able to communicate effectively with internal and external stakeholders 9.1 Identify internal and external stakeholders 9.2 Describe the needs of stakeholders 9.3 Explain the importance of effective communication to stakeholders 9.4 Describe appropriate communication methods for stakeholders 9.5 Evaluate the effectiveness of communication with stakeholders Stakeholders - stakeholder groups, e.g. employees, suppliers, shareholders, regulators, local community, Needs - environmental information needs of stakeholders and why Guidelines for environmental reporting and green claims e.g. Global Reporting Index, DEFRA and DECC Guidance on how to measure and report greenhouse gas emissions, DEFRA Green Claims Guidance 9.6 Outline guidelines for environmental reporting and green claims Be able to influence behaviour and implement change to improve sustainability 10.1 Outline the principles of change management 10.2 Describe how to create a positive environmental culture and a move to sustainability 10.3 Describe the barriers to creating a positive environmental culture and a move to sustainability This box is intentionally blank 10.4 Constructively challenge behaviour that may cause environmental harm 10.5 Outline the implications and consequences of decisions 8 © IEMA 2012