external internal Respiration
advertisement

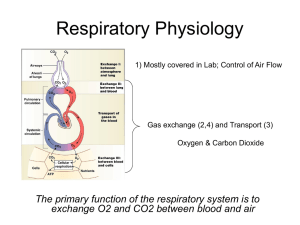
Respiration Gases move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. They will always try and balance out. Moving from one area to another is called diffusion. The gases will diffuse through structures. In this instance the structures will be the walls of the alveoli, capillaries and muscle. The concentration of gas within a mixture of gases is known as the partial pressure of the gas e.g. O2 within air. As described above gases will diffuse from areas of high partial pressure to areas of low partial pressure. External respiration - This refers to the exchange of gases between the Alveoli (lungs) and the Capillaries (blood).The partial pressure of O2 within the alveoli is high compared with the partial pressure of O2 in the blood, which has come from the heart to be oxygenated. The O2 diffuses across through the walls of the alveoli and capillaries and into the blood. (see transport of O2 and CO2) Meanwhile the partial pressure of CO2 is relatively high in the blood compared to the partial pressure of CO2 within the alveoli. Therefore the CO2 diffuses through the walls of the capillaries and alveoli and into the lungs (then breathed out). Remember that this is both O2 and CO2. The O2 from the alveoli to the blood. The CO2 from the blood to the alveoli. Internal respiration – This refers to the exchange of gases between the blood and the muscle tissue. The partial pressure of O2 in the blood is high in comparison to the partial pressure of O2 within the muscle tissue. The O2 diffuses across into the muscle tissue from the blood, bonding with the myoglobin. The partial pressure of CO2 is higher within the muscle tissue (as a result of energy production) than the blood, where the Partial pressure is low. The CO2, therefore moves from high concentration to low, diffusing from the muscle tissue into the blood. (See O2 and CO2 transport) The difference between the Partial pressures of O2 and CO2 within two areas i.e. lungs and blood is called the diffusion gradient. The bigger the difference - the bigger the diffusion gradient. The bigger the diffusion gradient – the more readily the gases diffuse. (as during exercise) The O2 from the Blood to the muscle tissue. The CO2 from the muscle tissue to the blood. Key words Internal respiration External respiration O2 and CO2 Diffusion Partial pressure Diffusion gradient Note -Questions could ask that you describe Internal or External respiration, or both – If both, then how the O2 and CO2 was transported between the two points of respiration could be included.