PE-Summer-Preparation
advertisement
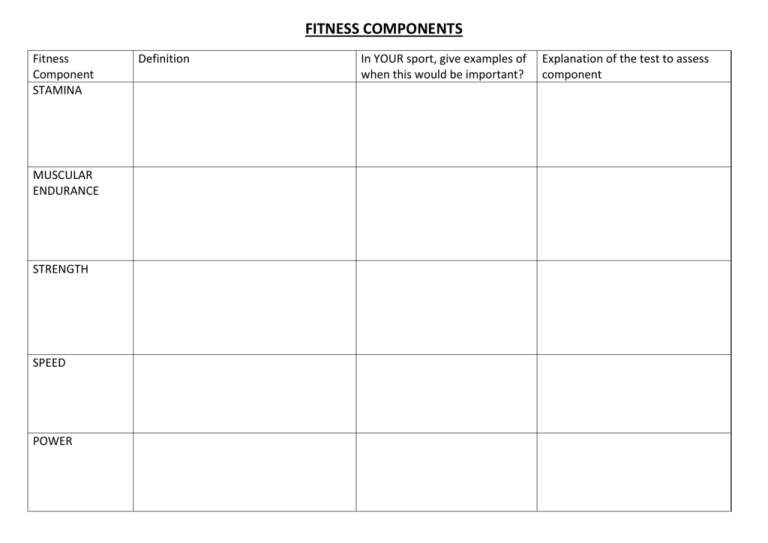
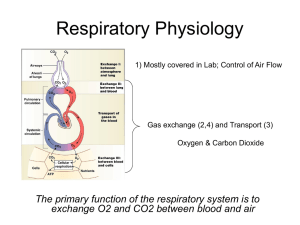
FITNESS COMPONENTS Fitness Component STAMINA MUSCULAR ENDURANCE STRENGTH SPEED POWER Definition In YOUR sport, give examples of when this would be important? Explanation of the test to assess component FLEXIBILITY REACTION TIME AGILITY BALANCE CO-ORDINATION The Circulatory System Heart structure & function Aerobic work refers to exercise that ................................................................................................ Examples Anaerobic work refers to exercise that ............................................................................................ Examples The aerobic system refers to three systems in order to ensure constant distribution of oxygen to the muscles during exercise, the heart, the vascular and the respiratory systems. Heart’s conduction system linked to the cardiac cycle The heart has a dual-pump action with two separate pumps that work simultaneously to pump blood to two different destinations. The right side pumps _______________________ blood towards the lungs The left side pumps ________________________ blood towards the rest of the body Label the heart Relationship between and resting values of Heart Rate, Stroke Volume & Cardiac Output Heart Rate (HR) The number of times the heart beats per _______________ Stroke Volume (SV) The volume of blood ejected from the heart per _________ The average resting heart rate is ____________ bpm The average resting SV is approx __________ml Cardiac Output (Q) This is the volume of blood ejected by heart ventricles in ______________ min Q = SV x HR EDV is volume of blood left in ventricles at end of filling stage ESV is volume of blood left in ventricles at end of contraction SV = EDV – ESV Work it out Using the calculations and information above, what would an average person’s cardiac output be at rest? What is your cardiac output? The heart’s response to exercise Exercise Intensity Resting SV 60/80 ml HR 70/72 bpm Q 5 L/min Complete the following table Sub-maximal (mod) 80/100 ml untrained 160/200 ml trained Up to 100/130 bpm Maximal 220 - age 20 – 40 L/min Gaseous Exchange External Respiration (NB: sometimes called pulmonary diffusion) Where? Movement Why? 02 Why? CO2 Internal Respiration Where? Between alveoli air and blood in the alveolar capillaries Between the blood in the capillaries and the tissue (muscle) cell walls Movement O2 diffuses into tissues; CO2 diffuses into blood O2 in alveoli diffuses into blood; CO2 in blood diffuses into alveoli Why? – 02 PP of O2 in alveoli is higher than the PP of O2 in the blood so O2 diffuses into the blood PP of O2 in blood is higher than PP of O2 in the tissues so O2 diffuses into the myoglobin within the tissues Why? – CO2 PP of CO2 in the tissues is higher than the PP of CO2 in the blood so CO2 diffuses from the tissues into the capillary blood PP of CO2 in the blood is higher than the PP of CO2 in the alveoli so CO2 diffuses into the alveoli