Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activities of Some 6-Methyl-3
advertisement

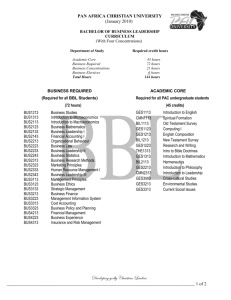
S1 Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activities of Some 6-Methyl-3-Thioxo-2,3-Dihydro1,2,4-Triazine Derivatives Ahmed A. El-Barbary,[a] Ashraf A. El-Shehawy,[b] and Nabiha I. Abdo[a] [a] Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta 31527, Egypt [b] Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Kafr El-Sheikh University, Kafr El-Sheikh 33516, Egypt Email: elshehawy2@yahoo.com Supplemental Materials Biological Activities TESTED ORGANISMS The microorganisms used in this study included Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Aeromonas sp and Klebsiella sp), Gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) in addition to the non- filamentous fungus (Candida albicans). The strains under study were obtained from the culture collection of Bacteriology laboratory (Microbiology Unit, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt). Bacteria were maintained on nutrient agar and the fungus was maintained on sabaroud agar slopes. ANTIMICROBIAL SCREENING Antibacterial and antifungal activities of the synthesized compounds were tested in vitro against six different types of bacteria and one fungi strain by the cut plug method. The assay plates were seeded with the test bacteria or fungus and inoculated with 100 μL containing the diluted inoculum (107 CFU/mL) of each tested organism that were spread on the corresponding media. After solidification, the wells were made and 1 mg of the synthesized chemicals were dissolved in DMSO and inserted in the wells. The plates were incubated at 30οC for 24 h, after which the diameters of inhibition zones were evaluated. The compounds that produced promising inhibition zones were taken for further antimicrobial assay in liquid broth media using different concentrations in order to determine their minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC). S2 The growth of each tested organism on a slant was placed in 50 mL of the corresponding broth and incubated overnight at 30οC. The growth of the test bacteria and fungus was adjusted to 107 CFU/mL. The synthesized compounds were dissolved in DMSO to make different concentrations. The chemicals were pipetted and added to flaks containing broth media to give the final concentrations (0.2-16 mg/mL). The flaks containing the different concentrations of the chemicals were each inoculated with the test organism at 107 CFU/mL. The flaks were incubated at 30οC for 24 h or 48 h, then decimal dilutions were prepared and the resulted surviving bacteria or fungi after 24 h or 48 h were enumerated by the spread-plate method. The counts were carried out in triplicate for each sample. The number of colonies for the media containing the concentration of the chemicals (M) and for the media without the chemical compounds or their concentrations (C) were taken on the surviving cell number (CFU) and the ratio between M and C (M/C) was taken as indication of surviving cells and with this value, the antimicrobial activity of different chemicals and their concentrations were evaluated (Figures S 1, S 2 and Table S 1) Figure S 1: Inhibition growth of different concentrations of compound 1 against E. coli. S3 Figure S 2: Inhibition growth of different concentrations of compound 1 against C. albicans. S4 Table S 1: Diameter of the inhibition zone (mm) produced by 1 mg of compounds 4a,b, 5a, 11a, 12, 14 and 16. Organism Candida albicans Aeromonas sp. Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Staphylococcus aureus Bacillus subtilis Klebsiella sp. Compound 27± 2.9 ND ND ND ND 28± 3.3 21±1.3 4a ND ND 20± 1.7 ND ND 23± 2.6 ND 4b 25± 0.8 ND ND ND ND 24± 1.5 ND 5a ND 13± 2.4 ND ND 31± 1.0 ND ND 11a ND 18± 2.4 ND ND 26± 4.3 ND ND 12 33± 2.8 ND 18± 2.4 ND 26± 2.4 16± 2.4 30± 1.0 14 ND 11± 1 30± 3.7 ND ND ND 16± 1.5 16 ND: Not detected under the experimental condition