Signal processing in GSM
advertisement

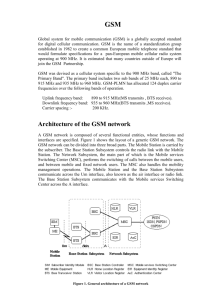
Signal processing in GSM Block diagram for signal processing in GSM is shown in figure. It is done in six steps as given below. (1) Speech coding (GSM speech coder). As we know that in GSM we have limited available frequency spectrum, so it is necessary to efficiently use the available spectrum. So here first preprocessing is performed on analog speech, where the analog speech is first pre emphasized. The pre emphasized speech is then passed through segmentation block where 160 samples for every 20ms speech is made. The samples are then passed through hamming window to reduce the noise interference. The speech coder used in GSM is RPE-LPC (Residual Pulse Excited-Linear Predictive Coder). Here first short term prediction is performed on speech for 16 samples. After the short term prediction 8 STP coefficients are derived and coded using 36 bits. Then long term prediction is performed for 20 to 120 samples. After the long term prediction 8 LTP co efficient are derived which are coded using 36 bits. Then RPE computation step is performed and RPE coefficient are derived which are coded using 32 bits. Then only 52 pulses are used which are encoded using 3 bits so total bits are 156 for pulses. So after complete process of speech coding there will be total 260 bits for 20 ms. So it is possible to obtain bit rate of 13 kbps. (2) Channel coding. Channel coding step is performed to detect and sometimes correct error introduced in the signal. In channel coding of speech signal extra 196 bits are added so there will be total 456 bits. So it is also possible to have bit rate of 22.8 kbps after channel coding. (3) Interleaving Here whole 456 bits are spreaded over different time slots of TDMA channel. The whole 456 bits are arranged in matrix in the form of 8 column and 57 rows. Then bits of each column are combined and first column having number(0,8,16…448), the second column having number(1,9,17…..449) and so on. So after interleaving there will be 8 blocks of 57 bits. (4) Burst formatting In burst formatting step any two block of 57 bits are placed in the one time slot (burst) of the TDMA channel. (5) Ciphering. This step adds security to the speech by adding cipher key to the original data. Here when mobile wants to make a call randomly generated number of 128 bits are transmitted to mobile station. The mobile station then combines that number with authentication key Ki having also 128 bits in A3 algorithm. The output signal is called cipher key Kc which is then mixed with the signal in A5 algorithm. The signal is then transmitted to base station. (6) Modulation In the last step of signal processing the speech signal is modulated by GMSK modulation. At the receiving side inverse process is done such as demodulation, deciphering, burst deformatting,de interleaving, channel decoding and speech decoding. Frame stracture for GSM As we know that in GSM time division multiplexing technique is used in which one complete channel of 200 KHz is assigned to 8 different users in time division manner. So each user transmits a burst of data during a time slot assigned to it. Each of the burst assigned is of 576.92us and of 156.25 bits having specific format The format for single burst is shown in figure(for figure see book) It consists of first 3 tail bits, after that block of 57 encrypted data bits are placed. Then 1 bit of stealing flag is used with 26 bits of midamble. Again 1 bit is used as a stealing flag and one more block of 57 encrypted data bits are placed. Then after 3 tail bits are placed with 8.25 bits for guardband. A TDMA frame contains 8*156.25=1250 bits with total time of 576.25us*8=4.615ms. Total 26 frames are combined to form a Multiframe. Out of total 26 frames 2 frames are used for control purpose. So only 24 frames carries traffic. So total time required for one multiframe is 120 ms. Similar 51 frames are combined to form one super frame and time for the one super frame is 6.12 ms. So total data of the a single user transmitted after speech coding is 13 kbps and that after channel coding is 22.8 kbps. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM The block diagram of air conditioning system is shown in figure. Air conditioning system are mainly two types 1) split ac and 2) window ac. In window ac both indoor and outdoor units are combined together at the same place while in split ac both the units are separated with copper ducts. Here the block diagram for split ac system is shown. The inlet copper duct consists of cooling agent at low temperature. It is then arranged in the zig zag pattern in the indoor unit where over it flow of air is passed through fan. As a result cooling of the coolant agent is transferred through filter into the room. Similarly other side of the indoor unit receives hot air and it is also passed over the duct with cooling agent. Finally the cooling from the duct is transferred into the room and heat from the room is received by the duct. So cooling liquid in the duct now becomes somewhat hot and results inot vapour. It is then transferred to the outdoor unit using outlet duct. The outlet unit consists of compressor which compresses the vapour at high pressure. As a result the temperature increases and cooling agent becomes gas with high pressure. This high pressure is then passed through the zig zag pattern of the pipes, where flow of air is passed over it. So it transfer its heat into the atmosphere and becomes cool again. These cooling pipes are then fed towards indoor units. Air filter Piping subsystem compressor Hot air fan system duct cool liquid duct fan system Inlet ducts Cooling pipes Outlet ducts Air filter Air from room Cool air