File
advertisement

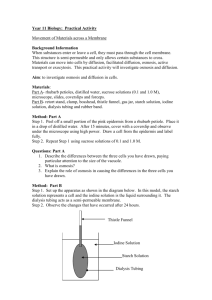
BIOLOGY Lab2 – Organic molecules Date: 19/12/13 Thaksaporn (May) Warattaya (Mook) Kanyapat (Nuey) Kantisa (Milk) Parima (Kaew) Natarpakul (Tammy) Purpose: To test different organic molecules of foods by using various chemicals such as Benedict’s reagent, iodine solution, Biuret’s reagent, and absolute ethanol to find sugars, starch, protein, and lipids in each sample and identify what are positive and negative controls and the content of three unknown samples. Hypothesis: I think if we put Benedict’s reagent, iodine solution and Biuret’s reagent in each test tube of water, the color will not change. But if we put Benedict’s reagent in other test tubes, the test tubes that contain sugars will change color from blue to green, yellow, orange or red. If we put iodine solution in other test tubes, the test tubes that contain starch will change color from brown to black-blue. If we put Biuret’s reagent in other test tubes, the test tubes that contain protein will change color from blue to purple. And if we put absolute ethanol in the tube that contains lipids, it will turn the solution white with homogenous mixture. Procedure: Procedures (Carbohydrates and proteins) 1) Fill 300ml of water into the 500ml beaker with a magnetic stirrer. Place the beaker on the hot plate. 2) Turn on the hot plate and the stirrer to the instructed levels. 3) Make labels on provided marking tape to be placed on the outside of each test tube. Use the chart below for abbreviation. 4) Apply the label on each test tube. And arrange the test tube on the rack according the Table. 5) Put on protective gloves and a goggle. 6) Adding approximately 1cm of each sample according to the label. 6.1In total you should have 3 tubes of each of the following samples - Water >>> negative controls - Glucose solution (Monosaccharide) >>> positive controls for Benedict’s solution - Starch solution (Polysaccharide) >>> positive controls for Iodine solution - Gelatin solution - ---(Protein) >>> positive controls for Biuret solution - Diluted milk - 3-4 pieces of diced onion + water - 3-4 pieces of diced potato + water - Unknown1 - Unknown2 - Unknown3 7) In ROW1: Add 5 drops of Biuret solution into each of the sample. 7.1 Gently swirls the test tube around. 7.2 Observe and take note any the color changes in the result section. 8) In ROW2: Add 5 drops of Iodine solution into each of the sample. 8.1 Gently swirls the test tube around. 8.2 Observe and take note any the color changes in the result section. 9) In ROW3: Add 5 drops of Benedict’s solution into each of the sample. 9.1 Gently swirls the test tube around. 9.2 Use the beaker tong to transfer the test tube one at a time into the boiling water in the beaker for around 3-5 minutes. 9.3 Observe and take note any the color changes in the result section. 10) Turn of the hot plate and stirrer. 11) Continue to the next part of the experiment. Procedures (Oils) 1) Collect two test tubes labeled A&B from your instructor. 2) Unscrew the cap of the tube 3) Add approximately the same amount of absolute ethanol into each tube. 4) Screw the cap back on tightly. 5) Shake each tube vigorously. Observe the change and record the findings in the results section. 6) Call your instructor to show you the brown-paper test and record the findings in the results section. Result: Organic Molecules Test Data Table Contents Abbreviation Testing Reagents Water Glucose solution Starch solution Gelation solution Diluted milk Onion+ water Potato+ water Unknown 1 Unknown 2 Unknown 3 W GL ST GE DM ON PO U1 U2 U3 Row1 Benedict’s solution No Change Orange + No Change Light purple Yellow + Light yellow + Light yellow + Light purple Orange + No Change Row2 Iodine solution No Change No Change Black blue + No Change No Change No Change Black in potato stuff + No Change No Change No Change Row3 Biuret solution No Change No Change No Change Light purple + Cloudy purple + Light yellow Light gray Light purple + No Change No Change “+” is positive result Emulsification Test Data Table Emulsification Test Tube With Ethanol Without Ethanol A (oil) White opaque + Yellow (No change) B (water) No change No change “+” is positive result Conclusion: The negative and the positive controls display the correct color. For testing sugars, the contents which contain sugar will show the positive controls and the color of that samples will turn from blue color to display green, yellow, orange, and red color such as glucose solution displays orange color, diluted milk displays yellow color, onion water displays light yellow color, potato water displays translucent yellow color, and the unknown2 tube displays orange color. The other samples display light blue color (no change) and light purple color. For testing starch, the contents which contain starch will show the positive controls and the color of that samples will turn from yellowishbrown to display blue-black color such as starch solution and potato stuff. The other samples display light yellow color (no change). For testing protein, the contents which contain protein will show the positive controls and the color of that samples will turn from blue to display purple color such as gelation solution, diluted milk, and the unknown1 tube. The other samples display blue color (no change), light yellow, and light gray. For testing lipids, the tube which contains lipids will show the positive control and turn the solution white with homogenous mixture when absolute ethanol is added such as the test tube A with ethanol that displays white opaque color. Meanwhile, the others display yellow color (no change) and no changed color. Questions: 1. Does potato store glucose as starch? How do you know from your results? Yes, it does because when plants synthesize they will produce glucoses, which plants will use them as energy. Potato has to store these energies to use for next time so they will store them as polysaccharide such the starch. Potato stores these glucoses as starch. According to the results, potato displays the changing color in only the potato stuff. When we dropped iodine into the test tube the color of only the potato stuff turns to black, it shows that potato contains starch and the starch was stored in the potato obviously so potato is a good source of energy for human. 2. Does onion store glucose as starch? How do you know from your results? No, it doesn’t. Onion does not contain starch because when we dropped iodine for test starch in an onion, the onion has no any change that shows us onion doesn’t contain any starch but from the results the onion contains sugar instead of starch. To explain this, I have to search in google and find that mostly plants will store the energy as starch but there are some types of plants that will store the energy as sugar and oil. So I think that onion is the type of plants that stores energy as sugar instead of starch. 3. What sugar is most likely present in the diluted milk? The sugar that is most likely present in the diluted milk is lactose, a disaccharide sugar. Milk is probably the most nutritionally complete food that can be found in nature. Whole milk contains vitamins (principally thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, and vitamins A, D, and K), minerals (calcium, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, and trace metals), proteins (which include all the essential amino acids), carbohydrates (chiefly lactose), and lipids (fats). When the fats and the proteins have been removed from milk, the carbohydrates remain, the main carbohydrate in milk is lactose. 4. Even though, gelatin is made from protein, it changed color to purple after heating with Benedict’s solution? Gelatin is made from protein, but contains high amounts of sugar so if you test it with Benedict, the results will be positive. 5. A test tube contains starch, a digestive enzyme for starch, and water. The biuret test is negative showing no change. However, after 30 minutes, the Benedict’s test is positive. What substance is present? How do you know? At first when it is tested, starch is only present so the results will be negative. However, when time passed the digestive enzyme will digest the starch, which gives you sugar, so the test will become positive after about 30 minutes. 6. How would you test an unknown solution for each of the following: a. Sugars: It can be tested use Benedict’s reagent. Boil the solution and the color will change in a range of green to red depending on the concentration. b. Fat: You can test fat by dropping the substance with an eye-dropper on any kind of paper, if the paper doesn’t get crinkled and doesn’t evaporate, it means that the substance contains fat. c. Starch: You need iodine to test for starch. Drop around drops in to the substance, if it contains starch the color will turn to dark blue. d. Protein: Biuret reagent is used to test for the presence of proteins and will change for blue to purple if the test is positive.