Pre-Calculus
advertisement

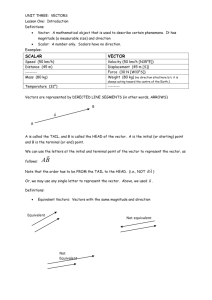
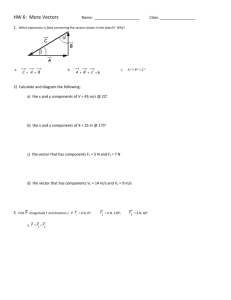
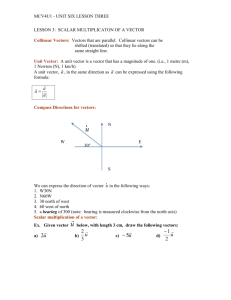
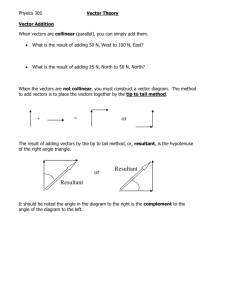
Chapter 6 Pre-Calculus Assignment Guide Chapter six finishes off our exploration of trigonometry with some final thoughts on some very useful applications. Some of this will be review but the final section is quite challenging. We begin by demonstrating how to solve any triangles by using the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines. We will also learn a couple of unique methods to find the area of triangles without knowing the altitude. Then we will examine vectors and some of the most common vector operations. And we will finish by covering complex numbers in trig form and how we can use DeMoivre’s Theorem to find powers and roots of complex numbers. Please ask questions regularly in class or stop by to see me or go to the Math Resource Center in room C117 for extra help. 1. 6.1 Law of Sines Pg. 398 # 3-19 odd # 21-35 odd 2. 6.1 Pg 398 3. 6.2 Law of Cosines Pg. 405-407 # 1-13 odd, 21-25 odd, 26, 27-35 odd 4. 6.2 Worksheet on determining how many triangles are possible with the given information 5. 6.3 Vectors in the Plane Pg. 417-418 # 1-11 odd, 13-18 all, 19-23 odd 6. 6.3 Pg. 418-419 # 29-65 odd 7. 6.3 Pg. 418-420 # 69-81 odd 8. 6.3 Vector Application Additional Practice Worksheet & Targets 9ab, 10a-d 9. 6.4 Vectors and the Dot Product Pg. 429-430 # 1-37 odd 10. 6.4 Pg. 430 11. 6.5 Trig Form of a Complex Number Pg. 440 # 7- 43 odd 12. 6.5 Pg. 441 13 Pg. 443 Pg. 444-447 # 39- 42 all, 47, 51, 56, 57 # 55, 57, 63-71 odd, 75, 79, 81, 91, 93, 95, 97, 105, 111, 113 FEB 17-21 President’s Day No School #1 #2 #3 #4 FEB 24 -28 #5 6.1-6.2 Quiz #6 start #7 finish #7 MAR 3-7 #8 #9 #10 More Applications 6.3-6.4 Quiz MAR 10-14 Read through Chapter Summary for sections 6.1-6.5. What did you learn? # 7, 11, 17, 18, 27, 31, 33, 39, 49, 55, 57, 61, 65, 67, 71, 87, 91, 93, 98, 107, 113, 123 #11 #12 WP Review #13 Review Ch 6 Test Part I Ch 6 Test Part II Even Answers to Chapter 6 Section 6-2 Pg: 405 26. Bearing a B: N43.03°E Bearing at C: S66.95°E Section 6-3 Pg: 417 14. Graph 16. Graph 18. Graph Section 6-4 Pg: 429 40. w1 = <0,0> w2 = <4,2> u = <4,2> + <0,0> 42. w1 = 2<-1,1> w2 = 3<-1,-1> u = <-3,-3> + <-2,2> 56. 937.7 pounds 5318 pounds Chapter Review Pg: 444 18. a = 634.7 ft w= 586.4 ft 98. 104 pounds H-Pre Calculus 6.3 Vector Applications Additional Practice Name___________________________ 1. Three forces with magnitudes of 65 pounds, 34 pounds, and 50 pounds act on an object at angles of -20˚, 60˚, and 135˚, respectively, with the positive x axis. Find the direction and magnitude of the resultant of these vectors. 2. A ball is thrown with an initial velocity of 65 feet per second at an angle of 43˚ with the horizontal (xaxis). Find the vertical and horizontal components of the velocity. 3. Two cranes are lifting an object that weighs 19,080 pounds. Find the tension in the cable of each crane. 4. A commercial jet is flying from Miami to Seattle. The jet’s velocity with respect to the air is 580 miles per hour and its bearing is N28˚W. The wind is blowing from the southwest with a velocity of 60 mph. a. Draw a picture. b. Write the velocity of the wind as a vector in component form. c. Write the velocity of the jet as a vector in component form. d. What is the speed of the jet with respect to the ground? What is the direction of the jet? Name ____________________________ H-Pre-Calculus Chapter 6 Word Problems 1. An airplane is traveling at a speed of 500 mph with a bearing of N40oW at a fixed altitude and no wind. As the plane crosses the Mississippi river, it encounters a wind blowing with a velocity of 50 mph in the direction of N20oE. What is the resultant speed and direction of the plane? 2. Sally is playing tug of war with two friends. She is pulling with a force of 50N at 250º Allison exerts a force of 40N at 65º. Maria exerts a force as well. To achieve equilibrium and thus, not lose the game, what is the force Maria must exert and at what angle? 3. A 10,000 pound object is suspended on a wire tied to two poles. The angle between the horizontal and the wire to the shorter pole is 22o. The angle between the horizontal and the wire to the taller pole is 49o. Find the tension in the cable to each pole. 22o 49o 10000 lbs 4. A 300 pound cart sits on a ramp inclined at 25o. Assume the only fore to overcome is the force of gravity. What is the force required to keep the cart from rolling down the ramp? 5. A truck with a gross weight of 40,000 pounds is parked on a slope of 12o. Assume the only fore to overcome is the force of gravity. Find the force required to keep the truck from rolling down the hill. 6. A mover exerts a horizontal force of 35 pounds on a crate as it is pushed up the ramp that is 20 feet long and inclined at an angle of 23o above the horizontal. Find the work done on the crate. 7. Two lighthouses are 30 miles apart along a straight shore. The ship is to the NE of one lighthouse and NW of the other lighthouse. The ship is 20 miles from one lighthouse and 15 miles from the other. How far is the ship from the shore? 8. The lengths of two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 4.5 yards and 6.8 yards. Find the area of the parallelogram is the angle between the two sides is 25˚. 9. Sara is in a boat traveling due west parallel to the shore. At one point Sara sees her friend Ashley on the shore at a bearing of S35˚W. Sara continues west for 400 more yards, where now she sees her friend at a bearing of S27˚E. How far is Sara from Ashley at both points? How far is Sara from the shore? 10. Two forces act on an object with magnitudes of 37 pounds and 42 pounds at angles of -40˚ and 91˚, respectively, with the positive x-axis. Find the direction and magnitude of the resultant of these forces. H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry Major Objective: Apply trigonometry to solve triangles, represent vectors and perform operations with complex numbers. Detailed Unit Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Section 6.1 1. Use the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines to solve oblique triangles. Find areas of oblique triangles. Represent vectors as directed line segments and perform mathematical operations on vectors. Find direction angles of vectors. Find the dot product of two vectors and use properties of the dot product . Multiply and divide complex numbers written in trigonometric form. Find powers and nth roots of complex numbers. Law of Sines I can use the Law of Sines to solve oblique triangles (AAS, ASA, or SSA). Solve the following triangles. a. c. 2. a = 7.5, b = 9, C = 100o b. A = 60o, a = 12, B = 75o a. The bearing from a fire tower to Station A is N53 oE and are 45 kilometers apart. A fire is spotted from the fire tower has a bearing of N75oE from the tower and N 120oE from Station A. Find the distance of the fire from the tower and the distance of the fire from StationA. b. A boat is sailing due east parallel to the shoreline at a speed of 10 miles per hour. At a given time the bearing to the lighthouse is S70oE, and 15 minutes later the bearing is S63 oE. The lighthouse is located at the shoreline. Find the distance from the boat to the shoreline. c. A 10-meter telephone pole casts a 17-meter shadow directly down a slope when the angle of elevation of the sun is 42o. Find the angle of elevation of the ground. Law of Cosines I can use the Law of Cosines to solve oblique triangles (SSS or SAS). Solve the following triangles. a. A = 52o, b = 6, c = 8 5. A = 63o, a = 17, b = 18 d. A = 42o, B = 55o, a = 15 I can use the Law of Sines to model and solve real-life problems. Section 6.2 4. b. I can find the areas of oblique triangles. a. 3. A = 29o, B = 62o, c =11.5 C = 17o, a = 15, c = 11 b. a = 21, b = 16.7, c = 10.3 I can use the Law of Cosines to model and solve real-life problems. a. A parallelogram has sides of 55 cm and 71 cm. Find the length of each diagonal of the parallelogram if the largest angle measures 106o. b. Two ships leave port at 9 A.M. One travels at a bearing of N53 oW at 12 miles per hour and the other travels at a bearing of S67oW at 16 miles per hour. Approximate how far apart the ships are at noon. 6. c. A ship travels 60 miles due east, then adjusts its course “north-eastward.” After traveling 80 miles in the new direction, the ship is 139 miles from its point of departure. What is the bearing of the “north-eastward” direction. d. A corner of Adam’s Park occupies a triangular area that faces two streets that meet at an angle measuring 85 o. The sides of the area facing the streets are each 60 feet in length. The park’s landscaper wants to plant shrubs around the edges of the triangular area. Find the perimeter of the triangular area I can use Heron’s (Hero’s) Area Formula to find areas of triangles. a. a = 14, b = 17, c = 7 c. A parking lot has the shape of a parallelogram. The lengths of two adjacent sides are 70 meters and 100 meters. The angle between the two sides is 70o. What is the area of the parking lot? Section 6.3 7. a = 4.45, b = 18.5, c = 3.1 Vectors in the Plane Write the component form of vectors. a. 8. b. Write the component form of the vector with initial point: (5, 7) and terminal point: (12, -1) Perform basic vector operations and represent vectors graphically. Given: u = <-3, 5>, v = <4, 10> find each of the following: a. 9. b. 3u - v Write vectors as linear combinations of unit vectors. a. b. 10. 2u + 3v Find a unit vector in the direction of the given vector: <3, 7> Find a unit vector in the direction of the given vector: 2i – 5j I can use vectors to model and solve real-life problems. a.. An airplane is traveling at a speed of 800 mph with a bearing of S40oE at a fixed altitude. Because of the wind, its groundspeed is 760 mph with a bearing of S43 oE. Find the direction and speed of the wind. b. Sally is playing tug of war with two friends. She is pulling with a force of 75N at 150º Allison exerts a force of 55N at 55º. Maria exerts a force as well. To achieve equilibrium and thus, not lose the game, what is the force Maria must exert and at what angle? c. A 500 pound object is suspended on a wire tied to two poles. The angle between the horizontal and the wire to the shorter pole is 29o. The angle between the horizontal and the wire to the taller pole is 38o. Find the tension in the cable to each pole. 29o 38o 500 lbs d. Use the figure below to determine the tension in each cable supporting the load. 22 ft. 8 ft. 25 feet 4000 lbs Section 6.4 11. Vectors and Dot Products I can find the dot product of two vectors and use properties of the dot product. Given u = 2, 5 and v = 4, 3 , find each of the following: 12. 13. 14. a. u·v b. u·u c. 3u · 7v d. v I can find angles between vectors and determine whether two vectors are orthogonal. a. u = 3, 7 v = 5, 7 c. u = 5i – 7j v = 7i – 5j a. Find the projection of v onto u if v = 3, 4 and u 5, 7 . b. Find the projection of u onto v if v = 3, 4 and u 5, 7 . v = 12, 9 I can use vectors to find forces and the work done by a force. a. A 700 pound cart sits on a ramp inclined at 28o. Assume the only force to overcome is the force of gravity. What is the force required to keep the cart from rolling down the ramp? b. A mover exerts a horizontal force of 50 pounds on a crate as it is pushed up the ramp that is 30 feet long and inclined at an angle of 19o above the horizontal. Find the work done on the crate. c. A mover exerts a force of 150 pounds (in a direction parallel to the ramp surface — 17o above the horizontal) on a crate in as it is pushed up the ramp that is 20 feet long and inclined at an angle of 17o above the horizontal. Find the work done on the crate. Trigonometric Form of a Complex Number I can find absolute values of complex numbers. a. b. 16. u = 3, 4 I can find the projection of a vector onto another vector. Section 6.5 15. b. Find the absolute value of -3 – 7i Find the absolute value of 4 – 9i I can convert between standard and trigonometric forms of complex numbers. a. Write 2 + 5i in trigonometric form. b. Write c. Write 8 cos 56 i sin 56 d. 17. 2 3 i in trigonometric form. in standard form. Write 5 cos 43 i sin 43 in standard form. I can multiply and divide complex numbers written in trigonometric form. a. 2 cos 6 i sin 6 5 cos 3 i sin 3 b. 73 cos10o i sin10o 54 cos130o i sin130o 2 cos 6 i sin 6 c. e. 18. 19. 7 cos50o i sin 50o 5 cos 3 i sin 3 (3 + 3i)(1 – i) d. 2 cos110o i sin110o f. 3 4 i 1 3 i I can use DeMoivre’s Theorem to find powers of complex numbers. a. (2 + 3i)5 c. 5 cos 40o i sin 40o 4 b. 4 1 3 i d. 2 cos 5 i sin 5 3 3 I can find the nth roots of complex numbers. Find the indicated roots of the complex number and write each of the roots in standard form. 1 a. 2 cos 60o i sin 60o 5 b. 3 cos 53 i sin 53 4 c. 81i d. 25 e. Find all solutions for x4 + 3i = 0 1 3 1 Chapter 6 1 6 Target – Answers 1a. 1b. 1c. 1d. C = 89o a = 5.576 b = 10.155 B = 70.634o C = 46.366o c = 13.809 B = 109.366o C = 7.634o c = 2.535 A = 23.496o B = 139.504o b = 24.432 A = 156.504o B = 6.496o b = 4.256 C = 83 b = 18.363 c = 22.250 33.237 units2 2b. 56.784 units2 3a. 23.840 km & 58.581 km 3c. 4a. 4b. 5a. 6, 40 8b. 13, 5 9a. 3 58 58 9b. 2 29 29 , 7 58 58 i 5 29 29 j 10a. N4.103oE, 57.153 mph 10b. 89.056N at 292.031o 10c. Fleft = 428.032 lbs Fright = 475.076 lbs 10d. Fleft = 1420.888 lbs Fright = 3079.856 lbs 11a. -23 11b. 29 11c. -483 11d. 5 12a. 58.736o 12b. 90o 12c. 18.925o o 2a. 3b. 8a. 3.185 miles o 16.078 a = 6.395 B = 47.675o C = 80.325o o A = 99.372 B = 51.686o C = 28.942o 101.088 cm & 76.898 cm 13a. 215 74 , 301 74 129 25 , 172 25 5b. 43.267 miles 5c. N76.153oE 13b. 5d. 201.071 ft. 14a. 328.630 lbs. 6a. 47.749 units2 14b. 1418.278 ft-lbs 6b. not a triangle 14c. 3000 ft-lbs 6c. 6577.848 15a. 58 7a. 7, 8 15b. 97 29 cis 68.199 16a. o 5 cis 50.768o 16b. 4 3 4i 16d. 52 17a. 10i 17b. 0.410 0.344i 17c. 3 5 17d. 7 4 17e. 6 17f. 7 3 4 34 3 4 i 4 3 3 4 i 122 597i 18b. 32 32 3 i 18c. 125 2 18d. 2.472 7.608i 19a. 1.124 0.239i 0.120 1.142i 1.049 0.467 i 0.769 0.854i 0.574 0.994i 19b. 0.341 1.271i 1.271 0.341i 0.341 1.271i 1.271 0.341i 19c. 3 3 3 i 3 6 35 2 125 3 2 33 3 2 33 3 2 i 3 5 2 i i 3 5 3 2 i 3 5 3 2 i 3 5 3 2 i 5 3 19e. i 5 2 5 2 18a. 3 6 35 2 5 3 3 15 i 3 16c. 5 3 2 19d. 3 5 2 3 5 3 2 i 0.504 1.216i 1.216 0.504i 0.504 1.216i 1.216 0.504i