Conversion to Newly Defined Core Learning Outcomes May 2012
advertisement

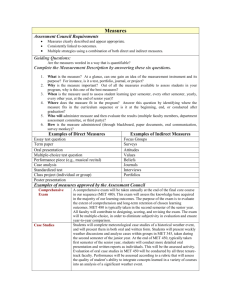
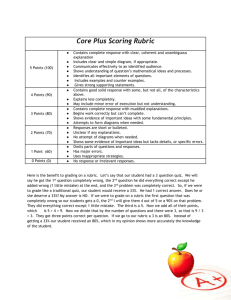
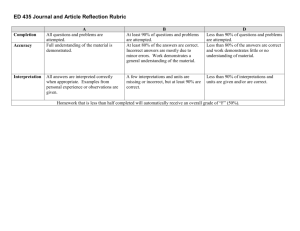
Memo To: Faculty, Department Chairs and Deans From: Assessment and Curriculum Committees Subject: Conversion to Newly Defined Core Learning Outcomes Date: May 1, 2012 Background Over the last three years, the Assessment Committee has worked on new definitions for three of our five Core Learning Outcomes (CLOs). The three CLOs, in both their old and new forms as well as the rationale for the change are documented in the table below. Old Version Computer Literacy -- To be computer literate, graduates of the College will know basic information technology concepts and will be able to use a computer to manage files, perform word processing, and use the Internet and e-mail. New Version Information Literacy is a student’s ability to locate, evaluate, and use electronic and print materials to meet a particular information need in an ethical and legal manner. The information literate student: Determines the nature and extent of the information needed. Defines and articulates the need for information. Accesses needed information effectively and efficiently. Constructs and implements effectively-designed search strategies. Refines the search strategy if necessary. Evaluates information and its sources critically and incorporates selected information into his or her knowledge base and value system. Summarizes the main ideas to be extracted from the information gathered. Articulates and applies initial criteria for evaluating both the information and its sources. Compares new knowledge with prior knowledge to determine the value added, contradictions, or other unique characteristics of the information. Uses information effectively to accomplish a specific purpose. Applies new and prior information to the planning and creation of a particular product or performance. Rationale With the explosion of both quantity and accessibility of information (and misinformation) of recent years, the college faculty recognized that students need to be not just computer literate, but information literate. The new version of the outcome addresses this need and is based on information provided by the Association of College and Research Libraries. NOTE: The Assessment Committee has provided an Information Literacy rubric as a resource for faculty, available at http://www.ncstatecollege.edu/committees/ass essment/default.htm Understands many of the economic, legal, and social issues surrounding the use of information and accesses and uses information ethically and legally. Understands many of the ethical, legal, and socioeconomic issues surrounding information and information technology. Follows laws, regulations, institutional policies, and etiquette related to the access and use of information resources. Acknowledges the use of information sources in communicating the product or performance. Computation Proficiency is the ability to perform mathematical computations found in life situations. Students will be able to recognize and analyze math situations and solve problems using basic mathematical and algebraic computations. Computation Proficiency is the ability to perform the college-level mathematical computations found within the student’s chosen academic discipline or degree. Upon graduation, North Central State College students will be able to recognize, analyze, and solve math problems. The original outcome was based on the college’s previous minimum math requirement of MTH 103 -- Introduction to Algebra, a developmental math course. The college raised the minimum requirement to a college-level math course to be incorporated in the new semester curricula. The new CLO definition recognizes that change while allowing the various disciplines/degrees to determine where and how the outcome will be attained and assessed. Culture & Community – The goal of the College, especially of general education, is to enable students to become articulate, literate, and culturally aware citizens. Students graduating will demonstrate an awareness of culture and community issues, values, resources and diversity. Intercultural Knowledge and Competence is "a set of cognitive, affective, and behavioral skills and characteristics that support effective and appropriate interaction in a variety of cultural contexts.” (Bennett, J. M. 2008. Transformative training: Designing programs for culture learning. In Contemporary leadership and intercultural competence: Understanding and utilizing cultural diversity to build successful organizations, ed. M. A. Moodian, 95-110. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.) Students graduating from the College with an associate degree will demonstrate: The Assessment Committee struggled for years to gain traction with the original version of this outcome. Problems included measurability and the emphasis on general education. As a result, the Committee “started over.” The new version relies heavily on the expertise provided through the Association of American Colleges and Universities VALUE project. Intercultural Knowledge -- through cultural selfawareness, knowledge of cultural worldview frameworks Intercultural Skills -- through empathy, verbal and nonverbal communication Attitudes -- through curiosity and openness NOTE: The Assessment Committee has provided an Intercultural Knowledge and Competence rubric as a resource for faculty, available at http://www.ncstatecollege.edu/committees/ass essment/default.htm Changeover Plan 1. All Master Syllabi will be updated with the new CLO definitions in Fall 2012 by the Curriculum Committee. 2. Course Coordinators will need to consider whether the new CLO definitions necessitate either a change in assessment methods or the removal of the CLO from their course. a. If the current assessment method is still appropriate under the new CLO definition, then the Course Coordinator will not need to pursue this further except to update Student Syllabi. b. If an assessment method is changed or a CLO is removed from a course as a result of a new CLO definition, then the Course Coordinator will need to submit the revised Master Syllabus to the Curriculum Committee for approval via an abbreviated review process. The expedited process will be posted on the Curriculum Committee’s web site and be included in the new Curriculum Handbook. Assessment Resources The college’s Core Learning Outcomes. including definitions and assessment results, as well as program/department level learning outcomes and Program Assessment Reports are provided on our Student Success Plan . On the Assessment Committee’s web site are the Core Learning Outcomes Assessment Schedule and Learning Outcomes Assessment Tools (CLO rubrics, templates for the Program Assessment Report and the Course Assessment Report). The following table, an excerpt from the Course Assessment Report template, suggests possible assessment methods: *Legend for Column II: Evaluation Methods -- A List of Possibilities Direct Measures Indirect Measures (Do not rely solely on indirect measures) Score gains between entry and exit on published or local tests or writing samples Research projects, presentations, oral defenses, exhibitions, performances – scored using a rubric Written documents/essays – scored using a rubric Juried reviews of presentations or performances Performance on licensure, certification, or professional exams Portfolio assessments Scores on quizzes and tests that link to learning outcomes Observations of student behaviors with systematic recording of notes Systematic analyses of electronic discussion threads, “think alouds,” or knowledge maps Skills-based assessments using checklists, etc. Ratings of student skills by field experience supervisors Performance on standardized exams Performance on practical exams Employer rating of graduate skills via survey, interviews or focus groups Scores from classroom response systems (clickers) Feedback from computer simulations Graduate follow-up rating of skills via survey, interviews or focus groups Student ratings of the knowledge or skills gained Systematic analysis of student reflections on the knowledge or skills gained Students’ reflections on their values, attitudes, beliefs Other Resources: For writing learning outcomes o University of Central Florida’s guidelines for writing student learning outcomes that are SMART and MATURE o Bloom’s Taxonomy Matrix with verbs, materials/situations, and potential activities/products o More on Bloom’s Taxonomy including why and how to use it o ThinkWell- LearnWell ™ diagram with learning goals, outcomes and thinking skills For assessing learning outcomes o o The State University of New York rubrics: SUNY Critical Thinking Rubric SUNY Writing Rubric SUNY Math Rubric The Association of American Colleges and Universities Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education (VALUE) project Examples of Core Learning Outcomes Assessment Plans for Master (and Student) Syllabi This following table includes the newly defined CLOs as they will be updated in all Master Syllabi. Examples of assessment plans are provided strictly AS EXAMPLES. Core Learning Objectives Assessment - - How it is met & When it is met All Listed Assignments are graded. EXAMPLES Communication – Written Communication – Speech The student will explore strategies to evaluate computer products and define product standards for an organization via research and written report in conjunction with Ch. 7; assessed using Writing Across the Curriculum rubric. The student will write a research paper on successful web based companies; due end of term; assessed using Writing Across the Curriculum rubric. The student will write analytic essays in weeks 5 and 10; response essays in weeks 3 and 7; evaluated by rubric. The student will find and present a summary of a professional journal article that identifies physical, mental and cognitive impairments and addresses the etiology and impact; assessed using the Speech Intercultural Knowledge & Competence Critical Thinking Information Literacy Checklist; weeks 8 and 9. The student will function as an engineering team member in an academic environment to work on a project and present it; assessed via Speech Rubric; mid-term. The student will do an oral presentation on informational interviewing, due at the end of the semester, as well as mock interviews throughout the semester; assessed using the Speech rubric. The student will discuss and explore their own personal attitude toward disability and mental illness and how that impacts their interactions with clients; assessed in Personal Attitude Reflection assignment (rubric); week 14. The student will identify the influence of cultural practices on an individual's adaptation of stressors and level of wellness; assessed in critical thinking exam questions (exam key) and identified in care plans of clients related to health practices followed (care plan rubric); weeks 2-16. The student will produce a technical marketing brochure that addresses multicultural audience issues; evaluated by brochure rubric; week 9. The student will increase his/her intercultural knowledge/skills/attitudes through small group projects/presentations; evaluated by pre and post self-assessment using the intercultural knowledge/competence rubric; mid-term with self-assessment repeated at end-of-term after clinical experiences. The student will plan, assemble, order, and produce a Portfolio Project that will require the student to prioritize artwork, sequence and group the artwork, and trouble shoot problems that come up along the way; throughout the semester; assessed using Portfolio Project rubric. The student will evaluate a patient scenario (to include patient assessment), select an appropriate therapy, and explain the rationale for the selection; cases in exams 1, 2, and 3; assessed via exam key. Student will study and analyze historical engineering disasters and while working in teams, develop practical Engineering Preventative Management Solutions to these scenarios throughout the semester; evaluated using Solutions rubric. The student will evaluate the effect of ethical considerations and social responsibility given local and global business scenarios; exams/quizzes throughout the semester but primarily assessed on exam during 1st 4 weeks. The student will respond appropriately to a complex “What would you do?” scenario that requires analysis, evaluation, inference, and explanation; scenario provided week 1 and finals week for a pre and post assessment using the critical thinking rubric. The student will find and present a summary of a professional journal article that identifies physical, mental and cognitive impairments and addresses the etiology and impact; assessed using the Information Literacy rubric; weeks 8 and 9. Computation The student will explore strategies to evaluate computer products and define product standards for an organization via research and written report in conjunction with Ch. 7; assessed using Information Literacy rubric. The student will complete a research paper assessed via the research writing rubric; 8th week of the semester. The student will solve homework problems in solar conversions, fuel efficiencies, and power loss (EIEO) using Excel, and temperature conversions using BASIC throughout the semester; assessed with problem answer key. The student will convert numbers among the decimal, binary, and hexadecimal number systems in problems in the midterm and final exams; assessed via answer key. The student will perform clinical medication calculations; Weekly and Final Exams (answer key).