Unit 3 Notes
advertisement

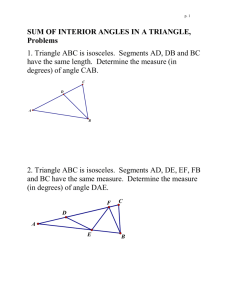
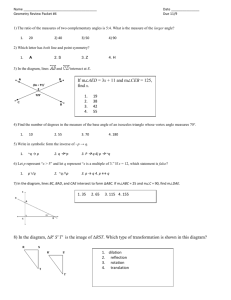
Unit 3: Geometry Word Definition World Tour o this section contains information that students will use as they take an imaginary world tour. Geometry Template o o plastic device with many uses ruler, half circle protractor, full circle protractor, percent circle, pattern block shapes Point o o o a location in space you make a dot with your pencil to show where a point is upper case letters are used to name points. Line Segment o o is made up of 2 points and the straight path between them you can use any tool with a straight edge to draw the path between the two points. the two points are called endpoints of the line segment the points are labeled with upper case letters o o Straightedge o a strip of wood, plastic, or metal that may be used to draw a straight line. Ray o o a straight path that has a starting point and goes on forever in one direction the end point is always the first letter in the name of the ray Line o a straight path that goes on forever in both directions Angle o o o o formed by 2 rays or two line segments that share the same endpoint. the vertex is where the two segments meet the rays or segments are called the sides of the angle when naming an angle the vertex is always in the middle Right angle o o o an angle that measures 90 degrees forms the corner of a square a small square is drawn in the vertex of the angle indicating it is a right angle Acute angle o an angle that measures between 0 degrees and 90 degrees Obtuse angle o an angle that measures between 90 degrees and 180 degrees Straight angle o measures 180 degrees Reflex angle o an angle that measures greater than 180 degrees and less than 360 degrees Adjacent angles o angles that are next to each other and share a side and common vertex Opposite or Vertical angles o when two lines intersect each other 4 angles are formed. The angles "opposite" each other are called vertical angles or opposite angles Polygon o o o a closed figure that is made up of line segments joined end to end the line segments do not cross can have any number of sides as long as it has three Regular polygon o a polygon whose sides are all the same length and whose angles are all equal Convex o all vertices are pushed out Concave o at least one vertex is pushed in Triangle o o a polygon with three sides and three angles the measure of all the angles equals 180 degrees Right Triangle o o a triangle with one right angle the angle looks like the corner of a square Equilateral triangle o o a triangle with 3 equal side and 3 equal angles it is a regular polygon Isosceles triangle o o o at least two sides are the same length an equilateral triangle is also an isosceles triangle can be a right triangle Scalene triangle o o no sides are the same length can be a right triangle Congruent o o a figure that is an exact copy has the same size and shape Quadrangle o o o a polygon with 4 sides the measure of the 4 angles equals 360 degrees also called a quadrilateral Square o o a quadrangle with 4 equal sides and 4 right angles also considered a parallelogram, a rectangle, and a rhombus Rhombus o o a parallelogram that has 4 equal sides the angles are not right angles Rectangle o o a parallelogram with 4 right angles opposite sides are equal in length Parallelogram o o a quadrilateral with 2 pairs of parallel sides opposite sides are parallel Trapezoid o o o a quadrangle that has only one pair of parallel lines it is not a parallelogram the 4 sides can all be of a different length Kite o o o a quadrangle with 2 pair of equal sides the equal sides are next to each other not a parallelogram Parallel lines o o lines or segments on a flat surface that never meet like railroad tracks Intersect o lines or segments that cross each other Perpendicular o lines or line segments that cross and form a right angle Circle o o curved line that forms a closed path on a flat circle not a polygon Center of a circle o all of the points on a circle will be the same distance from the center Compass o tool used to draw circles Radius o any line segment that connects the center of the circle with a point on the circle Diameter o any line segment that passes through the center of the circle and has both of its endpoints on the circle Concentric o circles with the same center that do not cross Inscribed Square o a square whose vertices all lie on a circle Tessellations o a n arrangement of repeated, closed shapes that cover a surface so that no shapes overlap, and there are no gaps between shapes shapes that tessellate-square, equilateral triangle, hexagon. o Notes and Helpful Hints Topic Properties of Polygons Notes Polygons can have more than one property, in fact they may have many. For example: a square has 4 right angles, 4 equal sides, is a parallelogram, is a regular polygon, is a quadrilateral. Parallelograms: square, rectangle, rhombus Not parallelograms: trapezoid, kite Perimeter: add up the length of all the sides *Remember in a regular polygon all the sides are the same length (even if they are not marked on all the sides) *In a rectangle the opposite sides are equal (don't forget to add all of them up) Area: Square and rectangle: length of the base X the height Formula A=b X h Triangle: length of the base X the height divided by 2 Formula A= b X h divided by 2. Circle: *always mark the center of your circle when drawing it with a compass. This way if the compass slips you know where to replace it. Circle measures 360 degrees Circumference: (really the perimeter of the circle) Formula: C= 3.14 (pie) X diameter Angles Always label with upper case letters with the vertex in the middle. Look at the angle and ask yourself "What makes sense?" Is the angle smaller or larger than a right angle? Protractor Always estimate before you measure, it will help you make sure you are reading the correct measurement for the angle. Ask yourself what type of angle do I have? (acute, obtuse, right, straight, reflex) Half-circle: line up one of the sides of the angle with zero making sure the vertex is in the correct spot Full-circle: line up one of the sides with the zero and read clockwise. * If the side of the angle is too short to reach edge of the protractor extend it with a straightedge Pattern Block Angles Triangle: angles must add up to 180 degrees, in an equilateral triangle all the angles measure 60 degrees Quadrilateral: angles must add up to 360 degrees Hexagon: angles measure 120 degrees