Study_Guide_WEATHERCLIM_Weather_Climate_Quiz_web
advertisement

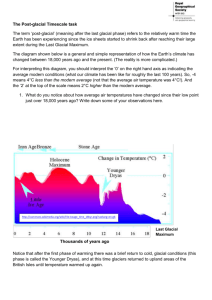
Weather and Climate Quiz Study Guide TOPIC: Air and Layers of the Atmosphere 1. What are the four main layers of the atmosphere, from Earth’s surface upward? Answer: Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere 2. Which layer gets colder as you go up, and is where clouds are located and where weather happens? Answer: Troposphere 3. Which layer gets warmer as you go up, is where planes fly, and is where the ozone layer is located? Answer: Stratosphere 4. Which layer is the coldest place on Earth and is where meteors burn up? Answer: Mesosphere 5. Which layer is very thick and is where auroras occur, where satellites orbit and is divided into the exosphere and ionosphere? Answer: Thermosphere 6. Which gas is most abundant in Earth’s atmosphere? Answer: Nitrogen (78%) 7. What would a barometer show about atmospheric pressure as you go up in altitude? Answer: atmospheric pressure gets less and less as you rise in altitude. 8. What is ozone and what does it protect us from and what is causing the hole in the Ozone layer? Answer: Ozone is a special form of oxygen, made from three atoms of oxygen. It protects us from harmful incoming solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation. CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) chemicals are breaking apart ozone, and they are found in aerosol sprays, foam products and coolant products like air conditioning. TOPIC: Local and Global Winds and Ocean Currents 1. What causes winds? Answer: air moving from regions of high pressure to low pressure. 2. What is the Coriolis Effect? Answer: winds are curved due to Earth’s rotation 3. What is the difference between a land breeze and sea breeze? Answer: A sea breeze occurs in the day time as wind blows from the sea inland due to warm air rising over the land. A land breeze occurs at night as the air above the land cools, sinks, and blows out to sea. 4. What is a monsoon wind? Answer: It is a seasonal wind that blows from the sea, bringing moisture and lots of rain/flooding inland. 5. What is the windward and leeward slope of a mountain? Answer: Windward is the side near the sea where moist air allows for precipitation. Leeward is the opposite slope that is dry and desert-like. 6. What are the three Global Wind Belts? Answer: Polar Easterlies, Prevailing Westerlies, Trade Winds 7. What is El Nino and La Nina? Answer: El Nino is when warm ocean currents happen in the Pacific and La Nina is when cold ocean currents happen in the Pacific. 8. Which warm ocean current flows up the east coast of the U.S. Answer: The Gulf Stream TOPIC: Climate, Climate Change, Global Warming and The Greenhouse Effect 1. What climate zone do we live in? Answer: Temperate 2. What are three of the Greenhouse gases that trap in heat? Answer: carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor 3. What are three effects of the Greenhouse Effect? Answer: global warming, melting glacial ice, rising sea level 4. What human factor is causing an unnaturally high level of carbon dioxide to be put into the air today? Answer: Burning of petroleum fossil fuels, including gasoline, oil, gas and coal 5. Which former vice president won a Nobel Prize because of his efforts to educate the public about Global Warming? Answer: Al Gore 6. What are a few ways that an individual can reduce their “carbon (dioxide) footprint?” Answer: use the car less, turn off electricity when not in use, recycle, use less heat and air conditioning, use efficient light bulbs and appliances in the home 7. What are the five climate zones? Answer: Tropical, Dry, Temperate, Cold and Polar 8. What are some factors that cause climate change on Earth? Answer: Volcanic activity, human pollution, Earth’s precession (wobble), and varying solar activity TOPIC: Glaciers and Ice Ages 1. What are the two remaining continental glaciers? Answer: Greenland and Antarctica 2. What is another name for a mountain glacier? Answer: Alpine Glacier 3. How many major ice ages has Earth experienced? Answer: Five (including the extreme “snowball earth” ice age.) 4. When did the current “Great Ice Age” begin, peak, and decline? Answer: It began 2.6 million years ago, peaked 20,000 years ago, and started to melt/recede/decline about 12,000 years ago. 5. Are we currently in a glacial or interglacial stage of an ice age? Answer: Interglacial 6. The Concord area has many glacial features, including eskers, drumlin hills, and glacial erratic boulders. What kind of glacial feature is Walden Pond and Whites Pond? Answer: Kettle Hole Lakes 7. What shape valleys do mountain glaciers carve? Answer: U-shaped valleys, like the White Mountains of New Hampshire 8. The Pleistocene Epoch of the current ice age was a time when large mammals roamed what is now the United States. Name a few mammals from this time. Answer: saber tooth cat, wooly mammoth, giant ground sloth, Irish Elk TOPIC: Heat Transfer, Weather and Storm Systems 1. Which kind of heat transfer happens by circulating current, by direct contact and through space respectively? Answer: Convection, Conduction and Radiation respectively (in order) 2. Which kind of weather front is shown by blue triangles on a map, and is when cold air pushes the warm air out of the way? Answer: Cold Front 3. Which kind of front is shown by both blue triangles and red semi circles and is when two fronts meet but move past one another horizontally and don’t move much (prolonged rain is associated with this front)? Answer: Stationary Front 4. What causes thunder? Answer: Lightning heats up the air, causing it to rapidly expand. 5. If a storm “vortex” touches down on water it is called a water spout. If it touches down on land, what is it called? Answer: Tornado (measured on the Fujita Scale) 6. If a tropical storm at sea picks up speed, it could become one of three different kinds of storms depending on where it formed. What are those three storms called? Answer: Hurricane, Typhoon or Cyclone (measured on the Saffir-Simpson Scale) 7. What kind of weather is associated with a High and Low pressure system respectively? Answer: High (sunny weather), Low (cloudy weather) 8. What are the four basic types of precipitation? Answer: Rain, Sleet, Hail and Snow