Vertebrate Evolution: Fish to Mammals Reading Material
advertisement

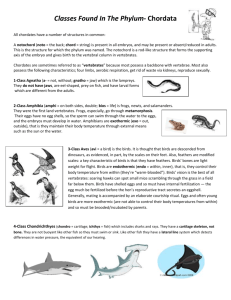
VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would have been found in the oceans. Fish are ectothermic, aquatic vertebrates. Their skin is generally covered with scales. Their limbs are modified into paired fins for swimming. They breathe with gills. They lay eggs (Oviparous)that must be in water They have a two-chambered heart No external ears No eye lids A salmon is a fish because it is ectothermic (cold-blooded), lives in the water, breathes with gills, lays eggs in water, and has fins and scales. Jawless fish (Class Agnatha) o These are among the most primitive of the fish; they are considered primitive because they lack a movable jaw and have a cartilaginous skeleton (Cartilage is a softer more flexible tissue than bone.) Instead, they have a well-toothed circular mouth, which among many species, is used to parasitize other fish. Cartilaginous Fish (Class Chondrichthyes) o This group includes the sharks and rays, and the name reflects that they have a skeleton composed of cartilage, which replaced the bone of ancestral fish. They were the first to evolve jaws (derived from first pair of gills) that greatly enhanced their ability to feed on potential food sources. They also evolved paired fins–pectoral up front, pelvic behind – that allowed greater swimming ability. They have internal fertilization. Ovoviviparous ( developing egg kept inside the female for protection and does not live off of the parent). They are marine organisms only. Bony fish (Class Osteichthyes) o This group includes the vast majority of fresh water and marine fish. These fish retain a bony skeleton, and an internal organ called a swim bladder used to maintain buoyancy. Amphibians Some fish evolved adaptations minimally adequate for life on dry land while retaining a need to reproduce in water. These became amphibians: “Amphi” means “pertaining to opposite ends”, in this case water and land. Many amphibians reproduce in water, emerging from jelly-coated eggs as aquatic larvae, and later maturing into terrestrial, aquatic, or semi-aquatic adults Amphibians are ectothermic vertebrates. Their skin lacks scales, hair, and feathers, and is either smooth (like a frog) or rough (like a toad). They are dependent upon moisture and subject to desiccation; their skin must remain moist to aid in breathing. They respire through poorly developed lungs and moist skin. Their brain is well developed and is attached to a dorsal nerve cord. Most amphibians contain three eye lids. Two are normal and one is transparent. They lay eggs in water, which hatch into an intermediate life form (tadpole or larva) that usually breathes with gills, and change into the adult form that breathes air and can live outside water. They contain a three chambered heart. Two atria and one ventricle. There is a possibility of the oxygenated and unoxygenated blood mixing in the ventricle. They lack claws on their toes. There are three orders of amphibians: frogs, salamanders, and caecilians. Caecilians are a rather obscure group entirely lacking limbs and outwardly resembling worms or snakes Frogs, toads, salamanders, and newts are all amphibians because they are cold-blooded, have no scales, hair, or feathers, their skin is moist, they lay eggs in water, and their life cycle has two stages, the "pollywog" or larval stage and the adult stage. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Reptiles Reptiles were the first animals to fully escape a dependence upon the availability of an open body of water . Reptiles are ectothermic vertebrates. Being ectothermic enables an organism to survive on much less food than an endothermic organism. Their skin has scales, but no hair or feathers. Reptiles molt as they grow. They have three-chambered hearts (except for alligators and crocodiles, which have four-chambered hearts). They have claws on their toes (except those which do not have legs, such as legless lizards). Reptiles are considered the first true land animals. It was this egg that allowed the reptiles to conquer the land and begin a reign that lasted hundreds of millions of years. They are the first animals, in evolution, to develop the amniotic egg. This allows reptiles to lay eggs on land. This is one of the most important evolutionary innovations. In reptilian eggs, the embryo develops within an internal watery compartment, the amnion chamber, provided with a large nutritional supply (in the yolk sac), and surrounded by a tough outer shell. Reproduction is sexual with internal fertilization. Respiration occurs through well developed lungs. Snakes, turtles, and lizards are all reptiles because they are cold-blooded, they lay eggs on dry land, and are covered with scales, never feathers or fur. _____________________________________________________________________________ Aves (birds) Birds are flight orientated organisms. Each part of its anatomy is modified in some way to allow it to keep its body light and energetic for flight. Birds are endothermic vertebrates. Very active metabolism. They can eat, digest, and eliminate the waste in a short amount of time. Their body temperature is rather high 102-103 degrees F. Their skin is covered with feathers. They have four-chambered hearts. Their bones are lightweight and usually hollow. Their forelimbs are modified as wings. They have an extensive air sac system attached to the lungs. This reduces the weight of the bird and supplies the needed air for a fast metabolism. They have no teeth and their beak is made of a light protein keratin. They lay amniotic eggs. Unlike most reptiles, birds care for their young after hatching and until they are able to fend for themselves Many birds migrate over long distances to find suitable breeding grounds and protection from major climatic changes. Jays, robins, and ducks are all birds because they are warm-blooded, have feathers, wings, and lay eggs. Mammals Although mammals appear to have evolved early during the Mesozoic (even before birds), they did not rise to predominance until the ecological niches become vacant with the demise of the dinosaurs. Mammals are endothermic vertebrates They have hair, which varies greatly among species. Most have sudoriferus (sweat) glands. Teeth are imbedded in the jaw bone and come in a variety of forms. They have mammary (milk-secreting) glands. They have sebaceous (fat-secreting) glands. They have a four-chambered heart The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. Internal fetal development. Among placental mammals (the most common type) the circulatory system of the fetus and mother become intimately intertwined within a placenta, where exchange of nutrients and waste products can occur. This allows longterm internal development of the fetus. Placental mammals are most familiar and predominate in most parts of the world. In these animals the fetus develops internally in a uterus. Marsupials (e.g., kangaroos) are less common and predominate in Australia, although some (e.g., the opossum) occur in other regions. The fetus of marsupials develops in an external pouch of the mother. Monotremes (e.g., the platypus) have retained the ancestral characteristic of laying eggs. Among the mammals certain other traits reached new heights, including prolonged care for the offspring and intelligence Deer, mice, opossums, raccoons, and humans are mammals because they are warm-blooded, have hair, and nourish their young on milk.