Vertebrates
advertisement

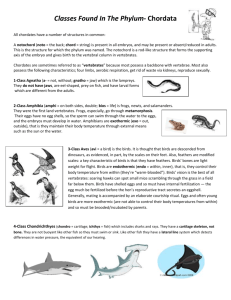
Vertebrates May, 2012 Vertebrates • Vertebrates – Animals with a backbone Vertebrates • Phylum: Chordata Characteristics 1. Backbone 2. Backbone (vertebrate) surrounds and protects a nerve cord 3. Skull and vertebrate are made of either bone or cartilage Vertebrate Characteristics (cont) • 4. Endotherms (warm-blooded animals) that maintained a constant body temperature • 5. Ectotherms (cold-blooded animals) that body temperature changes with their environment Fish Class • Examples- minnows, blue gills, clown fish • Characteristics – 1. Fins- help the fish move steer, stop, and balance – 2. scales- protect the body – 3. Well developed sense of vision, hearing, taste, and smell – 4. lateral line system- row of sense organs Fish Class • Characteristics – 5. Breathe with gills – 6. External and internal fertilization 3 types of fish – 1. Jawless fish- eel like fish, smooth, slimy, no jaw – 2.Cartilaginous fisheshave cartilage, no bones, strong jaws SHARKS! – 3.Bony fishes- bony skeleton, can float in place without swimming because they have a swim bladder • Swim bladder- balloon like organ filled with oxygen and other gases that gives the fish buoyancy Bell Work • Define the following terms • 1. endotherm • 2. ectotherm • 3. swim bladder 4. Name 2 characteristics of fish Amphibian Class • 1. Amphibians evolved from fish and to adapt to life on land they needed lungs for breathing • 2. Lung- saclike organ that takes oxygen from the air and delivers it to the blood Amphibian Characteristics • 1. Amphibian means “double life” because they live in water and on land • 2. Eggs do not have a shell or membrane to prevent water loss so they are laid in water • 3. Ectotherms • 4. Skin is smooth and slimy • 5. They don’t drink water, they absorb it through their skin Amphibian Characteristics (cont.) • 6. breath by taking air into their lungs and they absorb it through their skin • 7. Their skin is so thin and moist they must live in water or in damp habitats • 8. Their skin is brightly colored to warn predators away. This is called warning coloration. • 9. 3 chambered heart • 10. Turn to page 70. in your book and draw the life cycle of a frog. Metamorphosis Frog Metamorphosis Kinds of Amphibians • 1. Caecilians- shaped like worms or snakes, they have no legs. They live in tropical areas • 2. Salamanders- live under stones or logs in damp woods Kinds of Amphibians • 3. Frogs and toads have powerful legs for jumping, well developed ears for hearing, sticky tongues, and vocal cords for calling • Vocal sac-thin sac of skin that inflates with air and vibrates Reptiles • 1. Some amphibians evolved special traits that prepared them for life in a drier environment • 2. They developed thick, dry skin that protected them from water loss • 3. Their legs were stronger so they could walk and they evolved a special egg that could survive on dry land Reptile Characteristics • 1. Some reptiles live in water but they use lungs to breathe air • 2. Thick dry skin, that is water tight and prevents losing water by evaporation • 3. Ectothermic • 4. Amniotic egg-surrounded by a shell that protects an developing embryo (most important adaptation) • 5. Internal fertilization • 6. 3 chamber heart Types of Reptiles • 1. Turtles and Tortoises • 2. Crocodiles and Alligators • 3. Lizards • 4. Snakes Bell Work • 1. Name the 4 types of reptiles. • 2. What animal group did reptiles evolve from? • 3. Are reptiles ectothermic or endothermic? • 4. Name 3 characteristics of reptiles? Tuatara • Oldest living reptile Birds • 1. Class: Aves • 2. Birds are thought to be descendants of dinosaurs • 3. Share some characteristics with reptiles – A. Bird legs and feet are covered with thick dry scales like reptiles – B. Both have amniotic eggs with a shell Bird Characteristics • 1. Beaks instead of teeth or jaws • 2. Feathers • 3. Wings • 4. Need a lot of energy to be able to fly • 5. Eat large amounts of food Bird Characteristics • 6. Air Sacs- special sacs attached to the lungs that increases the amount of oxygen that birds can take in • 7. Lighter skeletonshollow bones • 8. 4 chamber heart • 9. Endothermic Kinds of Birds • 1. Flightless Birds – A. penguins – B. ostrich • 2. Water Birds – A. ducks – B. loons • 3. Birds of Prey – A. owls – B. hawks Kinds of Birds • 4. Perching birds – A. cardinal – B. chickadees • 5. Non Perching birds – A. red-bellied wood pecker Bell Work • 1. Name 4 characteristics of – Fish – Amphibians – Reptiles – Birds Mammals Origin of Mammals • Fossil evidence shows 280 million years ago there were mammal-like reptiles called therapsids Characteristics of Mammals • 1. Mammary glandssecrete nutritious milk • 2. Endothermic • 3. Hair somewhere on their bodies • 4. Specialized teeth • 5. 4 chamber heart • 6. Large brains Characteristics of Mammals • 7. Require oxygen to burn or break down the food they eat • 8. Diaphragm- muscle at the bottom of the rib cage that moves and helps with inhaling and exhaling • 9. Produce sexually Kinds of Mammals • 1. Monotremesmammals that lay eggs • A. have mammary glands • B. echidnas • C. duckbilled platypus Kinds of Mammals • 2. Marsupialsmammals with pouches – A. have mammary glands – B. opossums – C. kangaroos – D. koalas – E. Tasmanian devils Kinds of Mammals • 3. Placental-embryos stay in an organ called an uterus in the mother. The placenta in the uterus supplies food and oxygen to the embryo. • Examples – – – – – Pigs Horses Dolphins Whales Humans • 4.Gestation period- time that the embryo develops in the mother