Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management Resource
advertisement

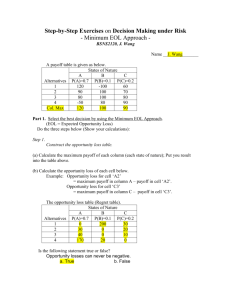
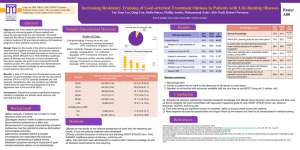
Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management Resource-availability scenario analysis for formal and informal recycling of end-of-life electrical and electronic equipment in China Habuer a, *, Jun Nakatani b, *, and Yuichi Moriguchi b Address correspondence to the following: a, * Department of Global Ecology, Graduate School of Global Environmental Studies, Kyoto University C-1-3-462 Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto 615-8540, Japan TEL: +81-75-383-3339 / FAX: +81-75-383-3338 E-mail: ha.buer.6w@kyoto-u.ac.jp b,* Department of Urban Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, Japan TEL: +81-3-5841-6255 / FAX: +81-3-5841-6255 E-mail: nakatani@env.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp b Department of Urban Engineering, the University of Tokyo Supporting Information Fig. S1 Market-share ratio of desktop and laptop PCs a a: obtained through fitting with historical data; the desktop PC market-share ratio is underestimated believing it may retain its 10% share over the entire PC market, at least until 2030 Fig. S2 Obsolete amount of CRT, LCD monitors, and main units of desktop PCs in China Fig.S3 Annually generated common metal contents from EoL PCs Fig.S4 Annually generated contents of less common metals from EoL PCs Fig.S5 Inflow and outflow per unit weight of EoL CRT TV sets in option I With environmental contaminants land space residue (0.6) metallic parts (14.4) Cables (4.2) waste CRT TV (100) Process md Process M_shr process M_ecs Iron (12.4) Aluminum (0.2) Copper (1.2) plastic (2.5) copper (1.8) Parts (9.4) Process M_gs CRT (42.5) Process process M_es Process Rc & Ru General glass (27.6) Leaded glass (14.8) phosphor (0.02) Electronic component (1.0) IC chips and substrate (7.9) process B PCBoard (8.9) M_c Size-reduced plastic (20.6) Process Lf residue (4.3) plastic (2.4) Aluminum (0.5) copper (0.5) Ferrous (0.3) silver (0.001) gold (3.E-5) platinum (2.E-4) Fig.S6 Inflow and outflow per unit weight of EoL CRT TV sets in option II-b With electricity consumption land space plastic (20.6) Recycled or reused : (iron 12.7; Aluminum 0.6; Copper 3.5; Plastic 25.5; General glass 27.6; Land filled: Leaded glass 14.8;; Electronic component 1.0; (residue 4.9) Silver 0.001; Gold 3E-5; Palladium 2.E-4) Parts 9.4 Process Rc Fig.S7 Inflow and outflow per unit weight of EoL LCD TV sets in option I With environmental contaminants land space residue (0.2) metallic parts (49.6) Process M_shr Recycled or reused : Iron (45.3) Aluminum (4.0) (iron 45.8; Aluminum 4.6; Copper 0.5; Plastic 27.8; LCD panel 10.2; Electronic component 0.9; Organic gas 3.1; Silver 0.0003; Land filled: Gold 0.001; (residue 5.7) Platinum 0.001; Tin 0.3; zinc 0.2; etc. process Lf Cables (0.8) waste LCD TV (100) Process md plastic (0.5) copper (0.4) process M_ecs Process Rc & Ru &Er LCD panel (10.2) plastic (27.3) residue (0.01) Electronic component (0.9) IC chips and substrate (10.2) Organic gas(3.1) Process Pyro Copper alloy (7.2) Lead (0.01) Bismuth (0.001) Antimony (0.0001) zinc (0.2) Nickel (0.001) Fig.S8 Inflow and outflow per unit weight of EoL LCD TV sets in option II-a With electricity consumption Process process M_es Plastic (0.01) Glass (0.9) Aluminum (0.01) Mercury (0.0003) land space process M_mr residue (5.5) Aluminum (0.6) copper (0.1) Ferrous (0.5) silver (0.003) gold (0.001) palladium (0.001) Tin (0.3) Rc PCBoard (11.2) Size-reduced plastic (27.3) process Hydro CCFL (0.9) Process M_gs land space residue (0.2) metallic parts (49.6) Cables (0.84) waste LCD TV (100) Process md Process M_shr Iron (45.3) Aluminum (4.0) plastic (0.49) copper (0.35) process M_ecs LCD panel (10.2) plastic (27.3) process M_mr process M_es process Lf Process Rc & Ru Plastic (0.01) Glass (0.9) Aluminum (0.01) Mercury (0.0003) residue (0.01) Electronic component (0.9) IC chips and substrate (10.2) process B PCBoard (11.2) Size-reduced plastic (27.3) (iron 45.8; Aluminum 4.6; Copper 0.5; Plastic 30.9; LCD panel 10.2; Electronic component 0.9; Land filled: (residue 6.2) Silver 0.0003; Gold 0.002; Platinum 0.001) residue (6.0) plastic (3.1) Aluminum (0.6) copper (0.1) Ferrous (0.5) silver (0.0003) gold (0.002) platinum (0.001) Fig.S9 Inflow and outflow per unit weight of EoL LCD TV sets in option II-b With electricity consumption land space CCFL (0.9) Process M_gs Recycled or reused : Process Rc The abbreviations of processes are listed below: md: Manual dismantling and separation pM: Primitive (outdated) physical mechanical process pM_hs: Hammer smashing pM_hb: Heating board M: Physical mechanical process (including shredding, packaging, axed cutting, eddy current separation, magnetic and gravity separation) M_shr: Shredding and packaging M_gs: Shredding and gravity separation M_es: Electronic component separation M_c: Cutting and shredding M_ecs: Shredding and eddy current separation M_mr: Mechanical separation and mercury recovery pC: Primitive chemical process pPyro: Open burning pHydro: Primitive hydrometallurgical process (such as acid leaching) C: Chemical process Pyro: Pyro metallurgical process Hydro: Hydro metallurgical process Od: Open dumping Lf: Landfill disposal Rd: Resale to downstream manufacture Rc: Recycled Ru: Reused Er: Energy recovery B: Physical process Table.S1. Module composition and average PCs weight Other non-ferrous metal Total Panel glass Funnel glass Outer panel Inner panel Drives (CPU, FDD,HDD) Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFLs) Copper cable (wire) Electronic component c Weight (kg) Copper metal Printed circuit board (PCBoard) Total (%) Aluminum metal Plastic material Battery Ferrous metal Weight (%) of module b 63.0 _ 0.2 _ 63.2 2.8 19.0 _ _ _ _ 13.7 _ _ 0.9 0.4 100 10.1 LCD monitor n.a n.a n.a n.a 54.8 21.6 7.4 _ _ 16.1 n.a 0.0 _ 0.1 _ _ 100 14.0 CRT monitor 4.0 _ _ 0.0 4.0 18.0 12.0 40.3 21.7 _ _ _ _ _ 4.0 _ 100 24.3 16.0 2.4 _ _ 18.4 27.7 14.7 _ _ 13.3 _ 10.0 13.9 0.05 1.0 0.9 100 2.9 Metallic material (metallic housing etc.) Type of PCs e Desktop PC Main unit Laptop PC CRT glass d LCD panel b: The median values of collected data from published literature and technical reports [17, 19, 25–29]; c: capacitors, solder, resistance and diode etc. contained in PC Boards; d: by assuming the percentages of panel and funnel glass 65% and 35% respectively according to [17, 18]; e: The numbers of individual data sets collected are 1 for Main unit, 7 for LCD monitor, 10 for CRT monitor and 15 for Laptop PC. n.a: nonavailable; CRT: cathode ray tube, LCD: liquid crystal display. Table S2. Substances’ contents in a desktop PC f Major fraction PC Board (mg/kg) Substance concentration in a desktop PC Common metals Less common metals Al: aluminum Cu: copper Fe: iron Sn: tin Zn: zinc Ni: nickel Pb: lead Ba: barium 18000 200000 13000 23000 2600 2563 19000 1900 178342 34630 281492 2344 20725 21396 1561 n.a 50 48 n.a n.a 15861 n.a 380 570 5 n.a n.a 134 Au: gold 220 18 Pd: palladium 145 29 Bi: bismuth Co: cobalt Sb: antinomy Hg: mercury Sr: strontium Ag: silver Precious metals f:data from [17–19]. Drives (mg/kg) n.a: nonavailable Table S3. Substances’ contents in laptop PC g Substance concentration in a laptop PC Common metal Less common metal Precious metal Major modules LCD panel Battery (mg/Kg) (mg/Kg) PC Board (mg/Kg) CCFL (mg/Kg) Al: aluminum 17700 n.a 53000 n.a Cu: copper Fe: iron Sn: tin 50825 37000 16500 175 n.a n.a 87500 207500 n.a n.a n.a n.a Zn: zinc 15500 3 n.a n.a 991 1848 773 115 2 13 60 n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a Co: cobalt Sb: antinomy Hg: mercury Sr: strontium 80 210 380 n.d n.d n.a n.a 167000 n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a 300 n.a Ag: silver Au: gold Pd: palladium 99 625 204 12 n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a n.a Ni: nickel Pb: lead Ba: barium Bi: bismuth g: data from [18, 25, 30–33] n.a: nonavailable, n.d: nondetected. Table S4.Characteristics of each group by cumulative metal contents and damage factors Group (G) 1 2 3 4 5 Cumulative metal content (C) large middle large small large middle middle small small Damage factor (D) high high middle high low middle low middle low Potential negative maximum impact (C×D) high Middle-high Middle-high middle middle middle middle-low middle-low low Table S5. Summary of categorization of metals in EoL TV sets and PCs discarded in 2010-2030 Group G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 Metals included in Co in EoL TV sets Ba in EoL TV sets Zn, Sb, Co in EoL TV sets; Zn, Sb in EoL PCs Cu in EoL PCs Sb, Pb in EoL TV sets; Ba, Sb, Pb in EoL PCs Fe, Zn, Ni, Ag, Sn, Pd, Au in in EoL TV sets; Fe, Co, Zn, Ni, Ag, Sn in EoL PCs Fe, Cu, Pb, Al, Sn, Ni, Ag, Bi, Pd, Au in EoL TV sets; Fe, Cu, Pb, Al, Sn, Co, Ni, Ag, Bi in EoL PCs Pb, Ba, Ni, Zn, Ag in EoL TV sets; Pb, Co, Ni, Zn, Ag in EoL PCs Cu, Ni, Zn, Hg in EoL TV sets; Cu, Ni, Zn, Ag, Co in EoL PCs Pb, Cu in EoL TV sets; Pb, Cu, Pd, Au in EoL PCs Pd, Au in EoL PCs Sn, Sb, Hg, Co in EoL TV sets; Ba, Sn, Sb in EoL PCs Sn in EoL TV sets; Sn in EoL PCs Co in EoL TV sets Description low positive incentive for resource availability (RA) low positive incentive for resource recovery (MV) high negative potential environmental impact (ED) high negative potential environmental impact (HH) middle-low positive incentive for resource availability (RA) middle-low positive incentive for resource recovery (MV) middle- high negative potential environmental impact (ED) middle- high negative potential environmental impact (HH) middle positive incentive for resource availability (RA) middle positive incentive for resource recovery (MV) middle negative potential environmental impact (ED) middle negative potential environmental impact (HH) middle-high positive incentive for resource availability (RA) middle-high positive incentive for resource recovery (MV) middle-low negative potential environmental impact (ED) middle-low negative potential environmental impact (HH) high positive incentive for resource availability (RA) high positive incentive for resource recovery (MV) low negative potential environmental impacts (ED) low negative potential environmental impact (HH)