Stellar Coordinates Just as we use a map of the Earth to find
advertisement

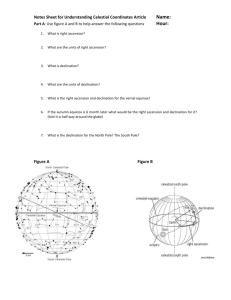
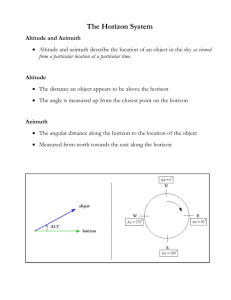
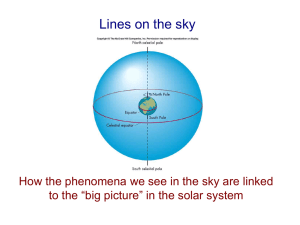
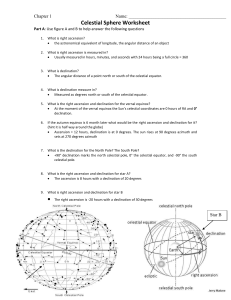
Stellar Coordinates Just as we use a map of the Earth to find different locations, we can use a map of the sky to find stars and other objects. Every place on Earth has a pair of coordinates to identify it and every point on the celestial sphere has a pair of coordinates too. There are two systems for this: Azimuth and Altitude and Right Ascension and Declination. Azimuth and Altitude Azimuth and altitude are probably how you would point out a star to someone. Azimuth is the angle around the horizon from due north and corresponds to the points on a compass. An azimuth of 0 degrees is due North, 90 degrees is due East, 180 degrees is due South, and 270 is due West. Altitude is the height of the star, in degrees above the horizon. Altitude can range from 0 degrees (on the horizon) to 90 degrees (directly overhead). The drawback to this system is that as a star rises and sets, it's position in the sky relative to the due north and its height change. This means that the azimuth and altitude change throughout the night and that observers at two different locations could see the same star at different azimuth altitude coordinates. Right Ascension and Declination Right ascension and declination are similar to longitude and latitude. The lines similar to the longitude lines on a globe are called Right Ascension. Right ascension is measured around the celestial equator towards the east. This angle is measured in hours, minutes, and seconds. A full rotation of 360 degrees is 24 hours, so each hour of right ascension is about 15 degrees along the celestial equator. An object with a right ascension of 0 hours lies on the Vernal Equinox. Declination is similar to latitude and measures how far above or below the celestial equator an object is. On object below the celestial equator has a negative declination; an object on the celestial equator has a declination of zero. Since the Right Ascension and Declination are relative to fixed stars, these coordinates do not change over time or with the position of the observer. Questions (please answer on a separate paper) 1. Why would astronomers prefer Right Ascension and Declination to Azimuth and Altitude? 2. At what altitude is a star that is rising? 3. At what altitude is a star directly overhead at the zenith? 4. At what altitude is a star that is setting? 5. At what two azimuth values does the celestial equator meet the horizon? 6. What is the azimuth of any object crossing the meridian in the southern sky?