Biome Book
advertisement

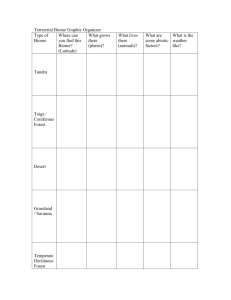
Biome Book Instructions: Use the data given to create a climate diagram for each biome. Precipitation data should be graphed with bars and temperature with a line. Identify each biome using the completed climate diagrams. Biome numbers are in random order. There are three extra graphs if you mess up. Create a biome book with the following items on each page: o Biome name/title (determine from climate diagram) o Completed climate diagram o Climate data (below) o Abiotic factors (matching) o Dominant plants (matching) o Two animals (with a description of an adaptation for each) (look up) o Example/Photo of a location within the biome (matching) o Productivity rank (use chapter 3, page 64) o Growing season (months) o General latitude range (use map) o Important human interferences (descriptions for two for each biome) (look up) Put your book together in the same order as the textbook (chapter 4) for easier studying Biome 1 Biome 2 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 0.7 Ave. Temp. (°C) 14 Feb. 0.7 Mar. Biome 3 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 18 Ave. Temp. (°C) 21 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 1.2 Ave. Temp. (°C) -28.5 15.5 Feb. 14.5 21 Feb. .9 -25.3 0.7 20.5 Mar. 9.5 20 Mar. .7 -16.9 Apr. 0.7 26 Apr. 4 19 Apr. .5 -5.7 May 0.7 31 May 1 16 May .8 6.7 Jun. 0.7 34 Jun. .2 14 Jun. 1.9 15.2 Jul. 0.7 35 Jul. .2 13 Jul. 2 16.7 Aug. 0.7 34.5 Aug. .2 16 Aug. 2.6 13 Sep. 0.7 31.5 Sep. .9 19 Sep. 2 5.2 Oct. 0.7 28 Oct. 3.7 21 Oct. 1.5 -6.8 Nov. 0.7 22 Nov. 10 21 Nov. 1 -21.3 Dec. 0.7 18 Dec. 17 21 Dec. 1.3 -27 Month Month Month Biome 4 Biome 5 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 6 Ave. Temp. (°C) -5 Feb. 5 Mar. Biome 6 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 11 Ave. Temp. (°C) 27.5 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 6.2 Ave. Temp. (°C) -8.5 -5 Feb. 11 27.5 Feb. 5.2 -7 5 2 Mar. 12 27.5 Mar. 6 -1 Apr. 3 7 Apr. 13 27.5 Apr. 6.8 6 May 6 12 May 8 27.5 May 8.6 12 Jun. 9 17 Jun. 3.5 27.5 Jun. 10 17 Jul. 8 19 Jul. 4 28 Jul. 10.5 20 Aug. 8 17 Aug. 3 29 Aug. 10 18.5 Sep. 6 15 Sep. 3 29 Sep. 8 14 Oct. 7.5 6 Oct. 4 29 Oct. 9 7.5 Nov. 5 -2 Nov. 10 29 Nov. 8 2 Dec. 5 -6.5 Dec. 11 28.5 Dec. 7 -5 Month Month Biome 7 Month Biome 8 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 2.6 Ave. Temp. (°C) 2 Feb. 2.6 Mar. Biome 9 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 4.5 Ave. Temp. (°C) 16.5 Jan. Ave. Precip. (cm) 2.5 Ave. Temp. (°C) -2 4.5 Feb. 3.8 16.5 Feb. 3.5 .6 2 7.5 Mar. 4.8 15 Mar. 7 6.2 Apr. 1.2 10.5 Apr. 6.2 12.5 Apr. 10 12 May 1 15.3 May 7.8 11 May 13.5 18 Jun. 1.3 20 Jun. 8.3 9 Jun. 15 23 Jul. 0.5 24 Jul. 10 8.5 Jul. 10.5 26 Aug. 0.6 23 Aug. 9.1 9 Aug. 10.3 20 Sep. 1 18.5 Sep. 7.6 10 Sep. 10.7 20 Oct. 1.3 12.3 Oct. 6.7 11.5 Oct. 8.5 13.5 Nov. 2.1 6 Nov. 5.7 12.5 Nov. 5.5 6.3 Dec. 2.6 2 Dec. 5.2 14.5 Dec. 4 -0.5 Month Month Month 36 32 28 16 8 6 4 2 0 J F M A M J J Month A S O N 16 0 10 8 6 4 2 0 A M J J Month A S O N D M A M J J Month A S O N D 36 32 28 16 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 J F M A M J J Month A S O N D Temperature (°C) 12 F 18 Temperature (°C) Precipitation (cm) 2 J 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 M 8 4 36 32 28 F 10 D 18 J 12 6 Precipitation (cm) Precipitation (cm) 10 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 Temperature (°C) 12 36 32 28 16 Temperature (°C) 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 18 Precipitation (cm) 18 36 32 28 16 8 6 4 2 0 J F M A M J J Month A S O N 16 0 10 8 6 4 2 0 A M J J Month A S O N D M A M J J Month A S O N D 36 32 28 16 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 J F M A M J J Month A S O N D Temperature (°C) 12 F 18 Temperature (°C) Precipitation (cm) 2 J 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 M 8 4 36 32 28 F 10 D 18 J 12 6 Precipitation (cm) Precipitation (cm) 10 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 Temperature (°C) 12 36 32 28 16 Temperature (°C) 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 18 Precipitation (cm) 18 36 32 28 16 8 6 4 2 0 J F M A M J J Month A S O N 16 0 10 8 6 4 2 0 A M J J Month A S O N D M A M J J Month A S O N D 36 32 28 16 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 J F M A M J J Month A S O N D Temperature (°C) 12 F 18 Temperature (°C) Precipitation (cm) 2 J 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 M 8 4 36 32 28 F 10 D 18 J 12 6 Precipitation (cm) Precipitation (cm) 10 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 Temperature (°C) 12 36 32 28 16 Temperature (°C) 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 14 18 Precipitation (cm) 18 ABIOTIC FACTORS ABIOTIC FACTORS ABIOTIC FACTORS low precipitation, variable temperatures; soils rich in minerals but poor in organic material cold to moderate winters; warm summers; year-round precipitation; fertile soils ABIOTIC FACTORS ABIOTIC FACTORS hot and wet year-round; thin, nutrient-poor soils warm to hot summers; cold winters; moderate, seasonal precipitation; fertile soils; occasional fires mild temperatures; abundant precipitation during fall, winter, and spring; relatively cool, dry summer; rocky, acidic soils ABIOTIC FACTORS ABIOTIC FACTORS warm temperatures; seasonal rainfall; compact soil; frequent fires set by lightning hot, dry summers; cool, moist winters; thin, nutrient-poor soils; periodic fires strong winds; low precipitation; short and soggy summers; long, cold, and dark winters; poorly developed soils; permafrost DOMINANT PLANTS DOMINANT PLANTS DOMINANT PLANTS broad-leaved evergreen trees; ferns; large woody vines and climbing plants; orchids and bromeliads woody evergreen shrubs with small, leathery leaves; fragrant, oily herbs that grow during winter and die in summer Douglas fir, Sitka spruce, western hemlock, redwood; ground layer of mosses and ferns DOMINANT PLANTS DOMINANT PLANTS cacti and other succulents; creosote bush and other plants with short growth cycles needle-leaf coniferous trees such as spruce and fir; some broadleaf deciduous trees; small, berry-bearing shrubs broadleaf deciduous trees; some conifers; flowering shrubs; herbs DOMINANT PLANTS DOMINANT PLANTS DOMINANT PLANTS lush, perennial grasses and herbs; most are resistant to drought, fire, and cold tall, perennial grasses; sometimes drought-tolerant and fire resistant trees or shrubs ground-hugging plants such as mosses, lichens, sedges, and short grasses long, cold winters; short, mild summers; moderate precipitation; high humidity; acidic, nutrient-poor soils ABIOTIC FACTORS DOMINANT PLANTS ABIOTIC FACTORS Fort Yukon, Alaska Manaus, Brazil Reno, Nevada Harare, Zimbabwe Moscow, Russia Tarkine Wilderness, Tasmania Montpelier, Vermont Lawrence, Kansas Arabian Desert, Saudi Arabia ANIMAL 1 ANIMAL 1 ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: Adaptation: ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: Adaptation: ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: ANIMAL 1 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: ANIMAL 2 Adaptation: Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Growing Season: __________ Growing Season: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Growing Season: __________ Growing Season: __________ Growing Season: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Growing Season: __________ Growing Season: __________ Growing Season: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Latitude Range: __________ Productivity Rank: _____ of 9 Growing Season: __________ Latitude Range: __________ HUMAN INTERFERENCE HUMAN INTERFERENCE G G G g G HUMAN INTERFERENCE HUMAN INTERFERENCE G G g g HUMAN INTERFERENCE HUMAN INTERFERENCE G G g g HUMAN INTERFERENCE HUMAN INTERFERENCE G G g g HUMAN INTERFERENCE HUMAN INTERFERENCE G G g g