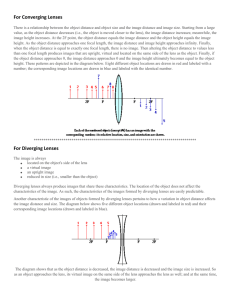
Thin lenses. Object O stands on the central axis of a thin, symmetric
advertisement

Week 37 Assignment 2013-2014 (5742517) 1. - Question Details HRW8 34.P.050. [788301] Thin lenses. Object O stands on the central axis of a thin, symmetric lens. The table gives the object distance p, the type of lens and the focal distance f. Find the image distance i and the lateral magnification m of the object, including signs. p (cm) Lens f (cm) +10 diverging *7.0 i (cm) m -4.12 0.412 * sign not given Describe the image. (Select all that apply.) real virtual opposite side of the lens upright inverted on the same side of the lens as O on the 2. - Question Details HRW8 34.P.052. [788284] Thin lenses. Object O stands on the central axis of a thin, symmetric lens. The table gives the object distance p, the type of lens and the focal distance f. Find the image distance i and the lateral magnification m of the object, including signs. p (cm) Lens f (cm) +14 converging *4.7 i (cm) m 7.08 -0.505 * sign not given Describe the image. (Select all that apply.) real virtual opposite side of the lens upright inverted on the same side of the lens as O on the 3. - Question Details HRW8 34.P.069. [788255] Thin lenses. Object O stands on the central axis of a thin, symmetric lens. The table refers to the object distance p, the focal distance f, the image distance i and the magnification m. Fill in the missing information, including signs. p (cm) f (cm) i (cm) +13 m +0.24 -4.11 -3.12 Describe the lens and image. (Select all that apply.) converging lens diverging lens image on same side of lens as O real image virtual image upright image inverted image image on opposite side of lens 4. - Question Details HRW8 34.P.070. [2085880] Thin lenses. Object O stands on the central axis of a thin, symmetric lens. The table refers to the object distance p, the focal distance f, the image distance i and the magnification m. Fill in the missing information, including signs. p (cm) +19 f (cm) i (cm) m -0.26 3.92 4.94 Describe the lens and image. (Select all that apply.) converging lens diverging lens image on same side of lens as O real image virtual image upright image inverted image image on opposite side of lens 5. - Question Details HRW8 34.P.089.ssm. [788238] The figure below shows a thin-lens representation of a compound microscope (not to scale). The objective produces a real image I of object O just inside the focal point F1 of the eyepiece. Image I then acts as an object for the eyepiece, which produces a virtual final image I that is seen by the observer. Assume that in such a microscope the objective has focal length fob = 3.96 cm and the eyepiece has focal length fey = 7.98 cm. The distance between the lenses is 24.5 cm. (Assume a near point of 25cm.) (a) What is the tube length s? 12.6cm (b) If image I is to be just inside focal point F'1, how far from the objective should the object be? 5.21cm (c) What then is the lateral magnification m of the objective? -3.17 (d) What then is the angular magnification mθ of the eyepiece? 3.13 (e) What then is the overall magnification M of the microscope? -9.94 6. - Question Details HRW8 34.P.093.ssm. [788198] Figure (a) shows the basic structure of a human eye. Light refracts into the eye through the cornea and is then further redirected by a lens whose shape (and thus ability to focus the light) is controlled by muscles. We can treat the cornea and eye lens as a single effective thin lens as shown in Figure (b). A "normal" eye can focus parallel light rays from a distant object O to a point on the retina at the back of the eye, where processing of the visual information begins. As an object is brought close to the eye, however, the muscles must change the shape of the lens so that rays form an inverted real image on the retina as in Figure (c). (a) Suppose that for the parallel rays of Figure (a) and Figure (b), the focal length f of the effective thin lens of the eye is 2.50 cm. For an object at distance p = 34.0 cm, what focal length f' of the effective lens is required for the object to be seen clearly? 2.33 cm (b) Must the eye muscles increase or decrease the radii of curvature of the eye lens to give focal length f'? changing the radii doesn't affect the focal length insufficient information 7. - Question Details Optics microscope 1 [1762389] Consider the compound microscope shown below. The objective lens has a focal length of 0.292 cm, and the eyepiece lens has a focal length of 11.7 cm; the distance L between the lenses is 13.6 cm. The object height is 1.25 μm, and it is placed 0.342 cm from the objective lens. (Note the metric prefix μ = 10-6). A. What is the image distance for image 1? 2.00 cm B. What is the object distance for the eyepiece lens? 11.6 cm C. What is the image distance for image 2? -1.40e+03 cm D. What is the overall magnification of the microscope? -702 decrease increase