File - Continuing Staff Education
advertisement

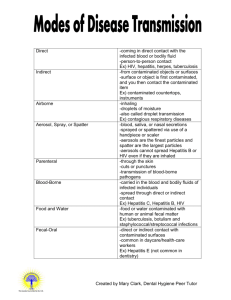
Procare Hospice Bloodborne Pathogen OSHA regulations mandate that employees who come into contact with blood or body fluids complete bloodborne pathogen refresher course on an annual basis and upon hire. Upon completion, staff will display knowledge on modes of transmission of HIV, HBC, and HCV Proper disposal of potentially infectious materials The use and limitations of universal standard precautions, proper use of personal protective equipment Actions to take when an exposure occurs HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Health care workers are exposed to blood and other body fluids from patients with active infections or are carriers of infections. Staff who are at highest risk are: 1. Nurses 2. Physicians 3. Staff who handle body fluids (HA, phlebotomist) Many people infected with HIV with no symptoms, presenting a high risk of transmission. Exposure occurs through accidental needle sticks, cuts, exposure to body fluid on broken skin or mucus membranes. Tears, saliva, urine and sweat are a mode of transmission only if they contain visible blood. HIV is spread through body fluids, primarily blood, semen, vaginal secretions, the primary mode of transmission is sexual contact and sharing of needles. It is not transmitted through casual contact, touching, shaking hands. Symptoms of AIDS Enlarged lymph nodes raised purple areas on the skin, mouth, nose, rectum thrush (candida) Patients with AIDS are often diagnosed with the following diseases: Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Kaposi’s Sarcoma Severe herpes simplex, Testing for AIDS Elisa test : if the patient receives two positive results the test is confirmed by the Western Blot Test. It they are all positive it indicates the person has been infected with the HIV virus. These results can take up to six weeks Ora Quick Test : tests saliva or plasma with a 99.3% sensitivity Vaccine: none available Hepatitis Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by infectious agents, medications or other toxins. There are several types of hepatitis ( A, B, C and D) hepatitis B and C pose the greatest risk to health care workers Hepatitis B: (HBV) Occurs through sexual contact or needle sharing, or accidental needle sticks, exposure to blood through broken skin and mucus membrane. Hepatitis B can live on hard surfaces for several days causing transmission by equipment that has not been cleaned properly. Symptoms: After contact it takes around six weeks before symptoms will show up. Flu like symptoms Fever Nausea/vomiting Fatigue Jaundice Vaccine: There is a hepatitis B vaccine available with a 95-97% effective rate. It is given in a series of three injections over a six -month period Exposure: Staff who are exposed, can receive an injection of HBIG (hepatitis B immune globulin) that helps fights the disease but is not as effective as the vaccination and will not give lasting protection. Hepatitis C (HCV) transmitted by large or repeat exposures to blood for example, blood transfusions received from an infected donor or sharing infected needles. Hepatitis C infected patients may not feel sick, others may develop cirrhosis and liver failure that may take several years to develop. Symptoms: Jaundice Fatigue Abdominal pain appetite loss nausea/vomiting Vaccine: none available Preventing needle sticks: Using needles with safety features: The use of syringes with a protective sheath that covers the needle after use Needles that retract into the syringe after use All needle sticks are investigated for cause. List of Potentially infectious material Human tissue semen Vaginal secretions cerebrospinal fluid synovial fluid pleural fluid peritoneal fluid amniotic fluid any body fluid visibly contaminated with blood Health care facilities are mandated to do everything possible to prevent exposure by offering the following: 1. Exposure control plan provides hepatitis B vaccine available to eligible staff 2. Minimizing or eliminating potential for exposure by using equipment with safety features. 3. Training staff on hazards of exposure and methods on protecting themselves. 4. Providing medical care following exposure 5.Protect Yourself 6 Get vaccinated for HBV (free to eligible employees) 7 If you refuse the vaccination you must sign a form declining the vaccination. Standard Precautions: Treat all blood and body fluids if they are contaminated Protective clothing and equipment If gloves have blood on them, remove carefully, and immediately wash hands Remove gloves before you touch non contaminated items Wear gowns, eye protection, and mask for procedures that can involve splashing of body fluids If protective equipment does not fit properly, ask supervisor for the correct size. Standard Work Practice Do not eat, drink, smoke, apply cosmetics in an area that has a chance for exposure Wash hands after removing gloves, and immediately after contact with blood or body fluids Never bend needles or recap a needle Waste Disposal Handle sharp containers with care discard all sharps into puncture resistant sharp containers immediately after use Discard potentially infectious waste into red bags Blood and blood products Materials saturated with blood Place any waste that may leak, into closed, leak proof, containers before discarding them. Spills Disinfect blood spills with 1:10 dilution of household bleach Exposure 1. Needle stick, squeeze area under running water until it bleeds 2. Skin exposure, wash area with soap and water for several minutes 3. Eye contact , flush eyes with copious amounts of running water 4. Do not use bleach on skin 5. Report incident to supervisor as immediately as possible 6. Fill out injury report Hand washing According to the CDC hand washing is the single most important method for preventing spread of infection. Proper Hand Washing 1. Remove rings 2. Wet hands under warm running water 3. Apply soap, work into lather vigorously scrub for 15 -20 seconds 4. Rinse under running water pointing fingertips down Blood Bourne Pathogen Post Test 1. What is the best way to protect you from blood, body fluids? A.Always wash your hands after caring for patient. B. Take vitamin C every day to boost immune system C. Wear personal protective equipment. 2. What are the symptoms of AIDS? A. Unexplained weight loss B. enlarged lymph nodes C. Lack of appetite 3. How long should you wash your hands? A. 10 minutes B. Sing happy birthday once C. 15-20 seconds. 4. What should you do after a needle stick? A. Cry B. Ask the patient if they have a blood borne disease. C. Put hand under running water, squeeze needle stick area making it bleed. D. Notifiy your supervisor E. C and D 5. You are taking care of your best friend’s grandmother you have known for years. While caring for her you are emptying urine from foley bag and are splashed in the eyes. You do not worry about it as you have known her for so long. A few weeks later you notice that you feeling tired, stomach hurts you pass it off as a stomach bug. What did you do wrong? A. Did not follow proper protocol from coming into contact with body fluids. B. Assumed your friends grandmother was not infectious C. Did not flush eyes out immediately after contact E. All of the above. 6. List types of personal protection equipment below 7. Is it mandatory that your employers supply you personal protective equipment? (Circle Yes No). 8. As a social worker or chaplain, you know you can be contaminated by: A. Patients touching you B. Coming into contact with dried blood on hard surface. C. Holding patient’s hand 9. Why should you receive vaccine for Hepatitis B? A. Minimizing or eliminating potential for acquiring hepatitis B B. My boss told you to do it. C. It is the right thing to do. 10. BONUS: what does OSHA stand for? ___________________________________ Name (print) ________________________ Date___________________________ Educator name: Rose Marie Van Dee RN, MSN Educator signature: _________________________ final score ____________ 1. Which of the following is FALSE about the tests to screen for HIV infection? a) The ELISA test is used to screen for HIV infection. b) The Western Blot is used to confirm the results of ELISA testing. c) If the results of either your ELISA test or your Western Blot are positive, you are infected with HIV. d) You can be infected with HIV and still have a negative ELISA test. 2. Which of the following is LEAST LIKELY to cause infection with hepatitis B? a) having blood splash into your eyes b) getting stuck with a needle used to draw blood c) getting cut with a broken blood vial d) having urine spill from a bedpan onto broken skin 3. Which of the following IS NOT a common symptom of hepatitis B infection? a) nausea b) jaundice c) anemia d) fever 4. Which of the following is FALSE? a) Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. b) There are several types of infectious hepatitis. c) The Hepatitis B virus dies very rapidly after it comes into contact with air d) One of the symptoms of hepatitis is jaundice. 5. Which of the following is TRUE about the Hepatitis B vaccine? a) The vaccine has serious side effects. b) The vaccine is available to eligible employees though your employer c) Eligible employees pay only a nominal charge for the vaccine. d) After 1 injection, the vaccine is 100% effective in protecting people from Hepatitis B. 6. Which of the following is TRUE about the hepatitis C virus? a) If patient is infected with HCV, they carry the virus for the rest of their lives. b) The hepatitis C vaccine 100% effective in protecting people from HCV. c) Hepatitis C is usually treated with immune globulin. d) patients who are treated for hepatitis C gets rid of the virus. 7 According to OSHA, which of the following IS NOT infectious for HIV, HBV or HCV. a) blood b) semen c) tears d) saliva with visible blood 8 You should use Standard Precautions when handling blood from: a) elderly patients b) IV-drug abusers c) children d) all of the above 9. Which of the following is TRUE: a) Physicians don’t need to wear gloves when drawing blood from a patient. b) You should not wear contaminated lab coats when eating C) You don’t need to wash your hands after removing gloves, unless your gloves has a hole in it. 10. If you spill blood it should be cleaned up: a) immediately, or as soon as possible b) using an appropriate disinfectant, such as 10% bleach c) wearing gloves d) all of the above