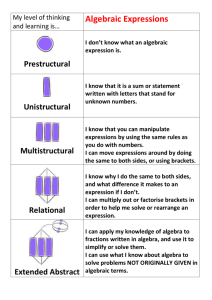
Algebra Variables and Expressions
advertisement

Talent Management Division Supporting All Employees 333 South Beaudry Avenue, 14th Floor Los Angeles, CA 90017 Telephone: (213) 241-6608 Fax: (213) 241-8442 Revised Lesson Design Template FBB: Basic: 1 15 Class Profile Subject/Grade Level: Lesson Date/Time: Math/6 Grade October 2013 Algebra: Variables and Expressions Class Composition (Record in numbers) Adv: SWD: Language Proficiency Levels: 9 0 LEP, IFEP, RFEP, EO Prof: GATE: 36 2 Teacher Name: W. Martin Male: 36 Female: BB: 18 34 ELs: 1 SELs: 1 Other: ADHD Instructional Goals and Objectives Standards (1a El.1): What standard(s) or portion of a standard does your lesson address? CCSS.Math.Content.6.NS.A.1 Learning Outcomes (1a El. 1; 1c El. 2): What are the conceptual understandings, content, and/or procedural knowledge that you want students to learn? What do you want students to understand, know or be able to do in relation to the standard(s)? CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.1 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.2 Write, read, and evaluate expressions in which letters stand for numbers. CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.2.a Write expressions that record operations with numbers and with letters standing for numbers. For example, express the calculation "Subtract y from 5" as 5 - y. CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.2.b Identify parts of an expression using mathematical terms (sum, term, product, factor, quotient, coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expression 2 (8 + 7) as a product of two factors; view (8 + 7) as both a single entity and a sum of two terms. CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.A.2.c Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. Include expressions that arise from formulas used in real-world problems. Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving wholenumber exponents, in the conventional order when there are no parentheses to specify a particular order (Order of Operations). For example, use the formulas V = s³ and A = 6 s² to find the volume and surface area of a cube with sides of length s = 1/2. Assessment (1e El. 1): What formal or informal assessment at the close of the lesson will serve as evidence that students have met the lesson objectives (e.g.: student work, exit slip, etc.) Formal assessment will be a written test of at least 10 problems from the student's homework assignment. The homework consist of 36 problems on page 46 and 22 problems on page 131. Students must be able to perform the following steps: Students, at the close of this lesson, will be able to apply and extend previous understanding of arithmetic to algebraic expressions and apply these expressions and equations to real life situations using complete sentences. Informal assessment will involve students constructing the Foldables and keeping their notes about the variables and expressions on the tabs. They will also take a review quiz on Brain Pop. There will be an exit question which involves a problem from their homework and they will also work with variables and expressions in ST Math which is part of the Blended Learning component with technology. Language Objective (1b El. 1; 1c El. 2): What language forms and functions will make content comprehensible for English Learners and Standard English Learners? We will be implementing the English Learner Master Plan fully in each lesson plan. Our sources will be SDAIE/Access to CoreInstructional/Observation Tools, using the LAUSD Teaching & Learning Framework Rubrics, Blended Learning, AVID strategies, and incorporating the eight mathematical practices establish by Common Core Standards. For English Language learners we will be decoding the vocabulary throughout the lesson. Each student will work in Cooperative Learning teams and be required to make a word web. Students write the words on a large sheet of paper and they must provide the main concepts, supporting elements, and bridges showing relationships between ideas in a concept. The Math Department has developed a "Story Problem" template. It works perfectly for English Language learners. The template has 6 main areas as follows: 1. Rewrite the problem (1 point) - students are required to rewrite the formal standard in their own words. 2. Restate the Final Question (4 points) - Students must put the final question in this area and put it in their own words. They are asked "What are you solving for?" 3. Model/Picture/Graph (4 points) - This area is for Kinesthetic Learners where they can visualize the problem. 4. Show Your Work (4 points) - In this area of the template the students puts down all their math work and calculations. 5. Solution (4 points) - What is the final solution? Write in 1 sentence. 6. Reflection & Analysis (3 points) - In this area we check for understanding from our English Learners. What was the TOPIC of this problem? What did you learn from this problem? What was easy or hard? Why was it easy or hard? Explain. Academic Language taught or reviewed (1a El.1; 1c El. 1; 1c El. 2): What academic language will be taught or reviewed? In data-driven differentiated instruction we have noticed students who need work on their everyday English patterns. We will form collaborative learning groups so that these English Learners can see peer-editing from other students with similar grammar needs. The teacher will read the lessons aloud and have students use the vocabulary words in a sentence and paste them on a word web. The vocabulary words in this lesson are listed below: Variable Algebra Algebraic expression coefficient Home Language Academic English I am using a variety to solve the equation. I am using a variable to solve the equation. (academic vocabulary) We use the letters instead of the numbers. We use variables to represent the value of a unknown number. (target vocabulary) I will be place number for the variable. I will be placing a number for the variable. (Gerunds) Some other methods we will be using to decode the English language for our English learners are listed below: Students will highlight words and phrases they do not know before the lessons. We will emphasize root words, break them apart and show what the prefix and suffix of words mean. Students will be required to read out loud in class at least 5 minutes per period and 30 minutes at home. Teachers will provide immediate feedback if words are mispronounced or spelled incorrectly. Model pronunciation of math vocabulary, formulas, and graphic displays. Give verbal praise to all students each and every day. Students will use target vocabulary using the correct gerund, possessive nouns, and past tense. Students will use the story problem template to reinforce critical thinking and language objectives. Student Progress Prerequisite Skills (1a El. 1): What prerequisite skills are essential for students to be successful in accomplishing the objectives? In order to master the variables and expressions component in the CCSS Number System standard in Grade 6, students must have the following prerequisite skill sets mastered by Grade 5: Write and interpret numerical expressions. 1. Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. 2. Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product. 2.1 Express a whole number in the range 2–50 as a product of its prime factors. For example, find the prime factors of 24 and express 24 as 2 × 2 × 2 × 3. CA Analyze patterns and relationships. 3. Generate two numerical patterns using two given rules. Identify apparent relationships between corresponding terms. Form ordered pairs consisting of corresponding terms from the two patterns, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 0, and given the rule “Add 6” and the starting number 0, generate terms in the resulting sequences, and observe that the terms in one sequence are twice the corresponding terms in the other sequence. Explain informally why this is so. Number and Operations in Base Ten 5.NBT Prior Knowledge (1b El. 1; 1c El. 2; 1e El. 4): What do students know and understand in relation to the objectives? What data (formal or informal) provides evidence for their prior knowledge? Students should remember to use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. (5AF1.2) What student misunderstandings/misconceptions do you anticipate, and how will you address those (1d, El. 4)? Students may have some difficulty understanding how to add and subtract fractions. I will address these by: 1. In algebraic expression, a variable represents an unknown number or numbers. 2. Make sure students understand there is nothing special about which letters are used for variables. 3. It is common to use letters signifying the object being replaced, such as "a" for age. 4. Students must practice using expressions with different variables to become accustomed to using a variety of letters. 5. Students must understand that to evaluate an algebraic expression, replace the variables with their given values and follow the order of operations. Procedures Materials (1d El. 2): What materials, resources, and/or technology will be used in the lesson? How will they support the instructional outcomes for this lesson? Students will need: Paper and pencil ruler hand calculator Teacher will need: algebra tiles 5-Minute Check Transparency Interactive Classroom CD-ROM Computer and LCD projector Technology Tools for Students ca.gr6math.com Extra Examples, Chapter 1, lesson 6. Self-Check Quiz, Chapter 1, lesson 6. Structures/procedures (1d El. 4): What structures and classroom routines/procedures will increase academic engaged time in this lesson? 1. Capture the Kids' Heart Social Contract - this contract is an agreed upon norms on how students will behave and interact with other students as they learn the lessons in the classroom. 2. Class Rules - defines the classroom routine and daily procedures which are common in most classrooms with respects to using the restroom, medical emergencies, acquiring classroom material, etc. 3. Kagan's Cooperative Learning strategies - this program contains a self-contained body of structures used to engage and motivate students. Each structure is designed to engage students in team and class building activities. The specific structures we will use in this lesson plan to engage students to process information is as follows: Inside - Outside Circle Quiz-Quiz-Trade Rally Coach Round Robin Think-Write-Round Robin Timed Pair Share Grouping (1d El. 3): How will you group students (whole class, small groups, pairs)? How will you use data to assist you in forming these groups? Students will sit in small groups of four students per team. Kagan Cooperative Learning program recommends the first group be randomly selected. They should remain in this small group for about 6 weeks. The structures activities are perform in pairs and the culminating activities are whole class involvement. Each four student team has been assigned a job. At each table, there is a Coach, Recorder, Material Monitor, and a Quiet Captain. I will continue to use the data acquired from the "My Data" website and Common Assessments from the Partnership to assist me in forming groups when the students are able to work effectively as a team and a class. I will also monitor their progress on homework assignments, Common Assessment tests, ST Math, data compiled by our school data specialist, and Math Department data and analysis. Instructional Sequence Consider the following questions when designing your plan: What opportunities will you provide for students to make sense of what they are learning and construct new knowledge? (1d El.1) How will you make content relevant to students’ interests and cultural heritage? (1b El.4) What strategies, linked to lesson objectives, will you use to maximize participation of all students for the entire instructional block? (e.g. discussion, student talk, inquiry, questioning, reflection) (1d El.1; 1a El. 2) What opportunities are you providing for students to engage in higher level thinking (e.g. analysis, synthesis, application) (1d. El1) What questions do you plan to ask students so that they can demonstrate their reasoning? (1d. El 1) (These questions do not need to be answered directly but are important guiding questions to support your lesson design. You may be asked to respond to these questions during your pre-observation conference.) Grade Level: 6th grade Subject: Algebra: Variables and Expressions Standard: CCSS.Math.Content.6.EE.1.2.a.b.c. Length of Time: 5 Hours Description: Students will evaluate an algebraic expression for a given situation. Solve problems manually by using the correct order of operations from Standards 6AF1.2 and 6AF1.4. Motivation: (1 hour) Ask students the following questions: 1. What does the word variable mean in an everyday context? Answer: subject to change. 2. What do you think variable means in math? Answer: a letter or symbol with no fixed quantitative value. 3. Why are variables important in math? Answer: they can be used whenever you do not know a number or when the number could change based on the situation. For Kinesthetic Learners have them practice writing expressions with different variables to become accustomed to using a variety of letters. For ELL students have them write the following words in their primary language and choose variables to represent the quantities: age, time, number. Procedure: (2 hour) Have students go to the math lab in room 105 and interact with the following math lessons: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Balancing Equations - Spy Guys Interactive Lesson 11 Interactive Algebra Tiles - Use this to model an equation or to solve an equation Late Delivery - Find the value of expression written on each door to deliver the mail Math Quiz Game: Jeopardy style - Jeopardy style PowerPoint review game Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions - Practice from Regents Prep Practice problems in solving an equation with variables on both sides - Ten practice problems, answers are checked Represent Functions - Seven slide PowerPoint show illustrating various representations; using models, tables, graphs, and equations effective use of animation Solving an Equation - Practice at manipulating expressions and finding the value of variables Teacher Dodgeball - Re-arrange the numbers and operational signs to form a correct equation in the time given. If you are correct, you will hit the teacher with the dodgeball and move on to a more challenging round. Defeat all five teachers and earn your dodgeball champion certificate. Using Graphs, Equations, and Tables to Investigate the Elimination of Medicine from the Body: Modeling the Situation - Lesson plan from NCTM 11. Weigh the Wangdoodles - Your job is to find the weight of each Wangdoodle using the information provided by the scales. To be successful, you will have to make sure that the weight you assign to each Wangdoodle works on each scale. This activity is a fun but challenging introduction to multiple algebraic equations. 12. Writing Equations - Sentences to translate into equations ST Math (1 hours) Students are required to interact with ST Math for at least 1 hour each week. They will work on variables and expressions. Assessment: (1 hour) Students will copy and answer the five problems on Chapter 1-6 Algebra: Variables and Expressions on the Glencoe McGraw Hill math web site. They must achieve 70% proficiency to be considered in mastering this standard. Grading Each problem is worth 1 point. A - 0 to 1 wrong B - 2 wrong C - 3 wrong D - 4 wrong F - 5 wrong 100 to 90 = A 89 to 80 = B 79 to 70 = C 69 to 60 = D Below 60 = F Additional Support for Specific Groups of Learners English Learners/Standard English Learners (1d El. 1): What strategies will be used to help English Learners and Standard English Learners access the content? In this lesson to help English Learners and Standard English Learners access the content will be using essential techniques as defined Doug Lemov's book called "Teach Like a Champion: The essential Techniques. In the Structuring and Delivering Your Lessons section, our group has decided to use the following techniques: Technique 12: The Hook Technique 13: Name the Steps Technique 16: Break it Down Technique 18: Check for Understanding Technique 20: Exit Ticket As our English Learners perform their math work, we will look at the following processes: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Show students and model the work - we will tell students what they have to do each day by having a White Board Configuration Model that shows what is expected of them each day and in every class. We will also provide them with an agenda and class syllabus so they can take it home so that their parents can monitor their progress. Start each day by having students read their work and share with other students. An Alpha Smart word processer is available for each student so they can type their work in the unit and use the spell checking application to check for misspelled words. A Spanish/English Dictionary is available for each students as well as the Math curriculum is bilingual in text. Define Pattern - I will help the students find their way through their text book. They will have a Brainstorming and Scavenger Hunt exercise that is designed for them to explore all the areas of their math book so they know how to use the Table of Contents, Glossary, Appendix, workbooks and on-line material that is provided with their text books. English Learners will not be required to read a large amount of text at one time. Students will be encouraged to mark up the text, use highlighters, post-its and Cornell notes to highlight important points. Teachers will use their personal experiences if appropriate to enhance the learning experience. English learners will be able to illustrate what they have learned by creating stories or using the Story Problem templates. There will be a daily review of the math vocabulary words, formulas, symbols, story problems, common assessments, and technical training using Math programs. Students will be provide a feedback "Parking Lot" area where they can post matters of concern on the board to get help before and after class. Students with Disabilities (1b El. 3): What modifications and/or accommodations are needed for students with disabilities in this lesson? Ms. Howell and Mrs. King and Mrs. Doyle are the designated RSP teachers and City Year associate assisting me with students who need modifications and/or accommodations. As a rule of thumb, we allow these students to have more time to master the material. Some strategies we are using that seems to increase productivity in these students are: We do not take off for spelling and minor mathematical errors. Allow them to read with a study buddy Encourage peer-tutoring with students that have similar abilities. Do not require oral reading or physical presentations. Give constant praise each day. Allow students to access and leave the classroom at an earlier time. Place these students closer to the front of the classroom. Allow students to make up the test or take an oral assessment. Limit classroom distracters. Stand by the student when giving the lecture or classroom directions. Look for limiting or aggressive body language. Enrichment (1b El. 3): How will you enrich and deepen learning opportunities for students who have already achieved mastery? Students that have already achieved mastery are encouraged to participate in Blended Learning. They have a great opportunity to enrich and deepen their learning opportunities by accessing the ST Math program with available on-line. Students can work on a wide variety of math concepts in the various computer labs located on campus or they can use their computers at their homes if one is available. Students were given a challenge by the Principal to develop a Power Point Presentation that illustrates their ability to learn while using technology. Students will be encouraged to use Microsoft Excel spread sheet programs to develop strategies to solve fraction problems, graphs, and manipulate data by interjecting formulas and equations. Any successful work produced by these students will be assessed as extra credit to increase their Grade Point Average. If the entire class achieves mastery, they usually rewarded with a Class Pizza Party. Students can also be quite beneficial by show casing their talents by assisting their peers in mastering the math concepts. The homework assignments and Story Problems will be placed on the bulletin board to model extraordinary work for other students. Assessment How will you communicate to students what proficiency or mastery looks like? What distinguishes mastery/proficiency from non-mastery/below proficiency) (1e El. 2) 1. The Math Department routinely engages math teachers to collaborate and develop Math Rubrics that are used to distinguish mastery/proficiency from non-mastery/below proficiency. As a general rule, the Department has used 70% mastery of the material as a proficient level. 2. Graded work is posted in the classroom so that the student can clearly see what an "A" paper ranks and how an "F" paper ranks by the teacher's assessment. Graded work in combination with the Grading Rubrics is the best tool for students to gauge their work. 3. Math teachers should model out the problem before allowing students to work them out. 4. Through Differentiated Instruction, teachers should be able distinguish mastery and proficiency on a given standard. Usually students are successful with Core and Advanced level questions on their homework and assessment challenges. 5. In this lessons, students will be required to construct line plots in the Exercises. They will have to verbally justify why selecting a line plot is appropriate to display the data. 6. The data for class performance is routinely placed on performance spreadsheets and analyzed by the Math Department. Each math teacher is able to print out these performance spreadsheets and post them in their classroom. There are spread sheets available for: Common Assessments by the Partnership My Data ST Math Syllabus and Standards Mastery results Math Text book Tests CST data from 5th grade data for Math and ELA SMARTER Balance What evidence will let you know that all (EL, Sp Ed, etc.) students understand how to demonstrate proficiency/mastery?(1e El.2) Special Needs and English Language learners will show evidence that they have demonstrated proficiency/mastery if they can perform the following tasks: 1. Write down the target vocabulary and use the words correctly in a complete sentence. 2. Compute at least five simple equations using positive numbers. 3. Identify an equation and variable by pointing it out on a sheet of paper. 4. Be able to participate in the Kagan team building exercises for this lesson. 5. Give a reasonable explanation on what they believe variable means to them. 6. Answer at least 3 out of the 5 questions located on page 46 in the section called "Check for Understand". 7. Work on a team, make a foldable, and use the vocabulary words in a word web. What opportunities will students have to self- or peer assess? (1e El. 3) At the end of each week, students are given an opportunity to provide feedback on their learning experiences for that week. Students are given an Alpha Smart word processer where they can type their concerns or critique their peers performance. Each Alpha Smart is downloaded to the teacher's main computer for quality control purposes and editing. The classroom composition can be published in a weekly progress report or projected on the screen and read by an electronic word recognition reading program. Students are also allow to grade their peers quizzes, homework, and test. They are provided with a 10 week course syllabus that requires them to chart their daily homework, test grades, and work habit grades. Parents are required to initial the syllabus each week showing evidence they are aware of their child's academic progress. In the Blended component of the math curriculum, students engage in ST Math. Each time they log out the program keeps track of their academic progress. Students are able to access their abilities on how their peers are progressing through the course work. Progress reports are generated by the School counselors which are given to students so that they may chart their daily progress, period by period. This process is generally used for struggling students or students that exhibit behavioral problems that inhibit them to learn effectively in the classroom. During the lesson, what are some of the different strategies you will use to check for understanding? (1e El. 3, El. 4) Thumbs Check - if students are understanding the lesson I will tell them to give me a "thumbs up". If they do not understand, then they will give me the "thumbs down". If they are a little confused, then they give me the "sideways thumb" and swing it back and forth. 2. Body Language Check - if students are easily distracted, yawning, sleeping, appear easily frustrated, not completing the work, consistently failing the tests, exhibiting excessive motor activity, grimacing, frequently tardy or absent from class, and shy, this gives me clues that they are not understanding the lesson. In these situations, students are asked to repeat the directions verbally or write them down on a piece of paper so that I can check for understanding. 3. Pointing - students are told to point to a required text or problem so that I know they are focused on the material. 4. Showcasing - students are allow to pick a math problem they can explain and use that for their "exit ticket" when it is time to leave the classroom. 5. Stand-by-the-door - I stand by the door and ask the students a warm up question before they enter the classroom. If they fail to answer the question, they must fall in the back of the line. 6. Wiggle the Pencil - this technique is much like the thumb check except for the student is required to wiggle their pencils in their fingers if they understand the material. Next Steps What will be your next steps after this lesson? (1c El. 1) I will prepare the class for the next lesson which is "Order of Operations". Before I present Lesson 1-4, I will have students review the following vocabulary terms and write their definitions on index cards: numerical expression order of operations How will you record and utilize evidence of student learning to inform your next steps? (1e El. 4, 1e El. 3) All grades are recorded on a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet which tells the following? Computes the student G.P.A. Computes the classroom passing rate. Charts a visible Pie Graph illustrating students who are passing or failing the curriculum. Records the progress scores for each student for the entire school year. Student Portfolios - students are require to file their work in their student portfolios to provide evidence of their work in case it is need for academic intervention with the School Counselors, Parents, Dean, RSP teachers, or for an IEP and re-designation. Grades Verification - all grades are recorded on ISIS. Teachers can print out student grades and analyze the measure of central tendency for grade marks per classroom. With a normal distribution of grade marks, if the data is distributed in the D and F range, I will have to revisit the this standard for at least two more days in the following week.