Honors Bio
advertisement

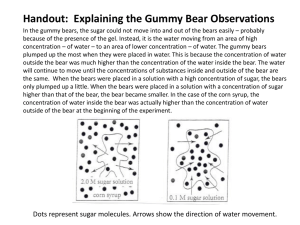
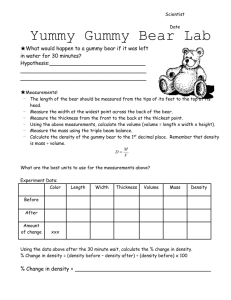
Biology 1-2 Name _______________________ Per___ Laboratory: Observing Osmosis in Gummy Bears Purpose: To investigate the movement of water into or out of a Gummy Bear. Problem: Is the concentration of H2O molecules higher in tap water, salt water or gummi bears? Background Information: Gummy Bears are made of gelatin, starch, and sugar. Molecules are in constant motion, and tend to move from areas of higher concentrations to lesser concentrations. Diffusion is defined as the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The diffusion of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane is known as OSMOSIS. Semipermeable means that some molecules can move through a membrane while others cannot. Movement through membranes is called transport. Diffusion and osmosis are forms of PASSIVE TRANSPORT; this means that they do not need energy to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. ACTIVE TRANSPORT requires energy to transport molecules from low concentration to high concentration. OSMOSIS is the movement (transport) of water through a semipermeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Gummy Bears do some interesting things when put into different liquids. In this experiment, we will find out what will happen when we put the Gummy Bears into water, salt water, vinegar, and baking soda water. Part A: As a group of 4 1) Choose 4 gummy bears from the container. 2) Each person measures (directions below) one of the gummy bears and records the data in the chart for Day 1 a. The length of your gummy bear should be measured from the top of its head to the bottom of its feet to the nearest millimeter. b. Measure the width at the widest point across the back of the bear to the nearest millimeter. c. Measure the height from the front to the back at the thickest point to the nearest millimeter. d. Calculate the volume by multiplying the length, width, and height – round to the nearest hundredth. (V = L x W x H) e. Measure the mass using an electronic scale to the nearest tenth of a gram. f. Calculate the density by dividing the mass by the volume – Round answer to the nearest hundredth. (D = M/V) Part B: As a group of 4 each member does one of the following (1a-1d): 1) In each of the four cups: a. Pour 50 ml of Water into one b. Pour 50 ml of Vinegar into one cup. c. Mix 50 ml of Water with 15 ml (1 tbsp.) of Baking Soda in one cup. d. Mix 50 ml of Water with 15 ml (1 tbsp.) of Salt in one cup. 2) Drop your Gummy Bear into your prepared cup and place the cup onto the labelled sheet of paper under the correct heading. Let sit for one day. Biology 1-2 Name _______________________ Per___ 3) On Day 2, remove your Gummy Bear from the mixture and use a paper towel to dry it off to prevent it from dripping all over the place. 4) Repeat the measurements from Part A for each Gummy Bear and record your data in the correct portion of the chart. Also, determine the amount of change for each measurement, for each Gummy Bear and record in the chart. Experimental Data Chart Water Day 1 2 Change Salt Water Day 1 2 Change Vinegar Day 1 2 Change Length Width Height LxWxH Volume Mass M/V Density Length Width Height LxWxH Volume Mass M/V Density Length Width Height LxWxH Volume Mass M/V Density Height LxWxH Volume Mass M/V Density Baking Soda Water Day Length 1 2 Change Width Analysis/Conclusion: Write a paragraph to explain the results of this experiment using the concept of osmosis. Include your specific data to explain your results and support conclusions. (What happened to the bears when placed in tap water? Why?; What happened to the bears when placed in salt water? Why?; What happened to the bears when placed in vinegar? Why?; What happened to the bears when placed in baking soda water? Why?)