6.SP.4-5 Task 1 - commoncoremathtasks
advertisement

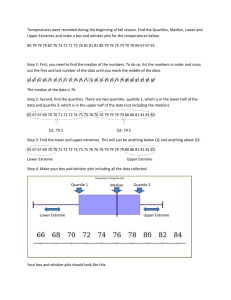
Mathematical Tasks Displaying Jumping Distances- 6.SP.4 and 6.SP.5 Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Geometry Summarize and describe distributions. 6.SP.4 Display numerical data in plots on a number line, including dot plots, histograms, and box plots. 6.SP.5 Summarize numerical data sets in relation to their context, such as by: 6.SP.5a Reporting the number of observations. 6.SP.5b Describing the nature of the attribute under investigation, including how it was measured and its units of measurement. 6.SP.5c Giving quantitative measures of center (median and/or mean) and variability (interquartile range and/or mean absolute deviation), as well as describing any overall pattern and any striking deviations from the overall pattern with reference to the context in which the data were gathered. 6.SP.5d Relating the choice of measures of center and variability to the shape of the data distribution and the context in which the data were gathered. Activity sheet Displaying Jumping Distances Below is a list of distances from the Long Jump in Physical Education class. All distances are in inches. 36, 36, 37, 39, 39, 40, 41, 39, 39, 38, 39, 39, 40, 41, 41, 41, 42, 39, 39, 39 Part 1: How many students jumped? What was the unit of measurement? Part 2: Plot the data on a number line (line plot). Write a sentence describing you data based on what you notice. Part 3: Identify the median and mean of the data set. Part 4: Find the interquartile ranges and make a box plot of the data. Part 5: How is box plot different from the number line representation? How does each representation help when looking at the data? Mathematical Tasks Sixth Grade Mathematical Tasks Rubric Level I Developing Proficiency Student uses inappropriate solution strategy and does not get the correct answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Level II Not Yet Proficient There are one or two errors. Level III Proficient in Performance Accurately solves problem. Part 1: 20 students jumped. The unit of measurement was inches. Part 2: The number line (line plot) is done correctly. The sentence describes the spread, frequent data points, etc. Part 3: Median: 39. Mean: 39.2. Part 4: 1st quartile: 36-39; 2nd quartile: 39-39; 3rd quartile: 3940; 4th quartile: 41-42. Part 5: The description clearly and accurately describes the differences. The number line allows you to easily see frequently occurring data points as well as the spread, and possible outliers. The box plot allows you to look more closely at the spread because it displays the data into four quartiles. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. Mathematical Tasks Sixth Grade Mathematical Tasks Displaying Jumping Distances Below is a list of distances from the Long Jump in Physical Education class. All distances are in inches. 36, 36, 37, 39, 39, 40, 41, 39, 39, 38, 39, 39, 40, 41, 41, 41, 42, 39, 39, 39 Part 1: How many students jumped? What was the unit of measurement? Part 2: Plot the data on a number line (line plot). Write a sentence describing you data based on what you notice. Part 3: Identify the median and mean of the data set. Part 4: Find the interquartile ranges and make a box plot of the data. Part 5: How is box plot different from the number line representation? How does each representation help when looking at the data? Mathematical Tasks Sixth Grade