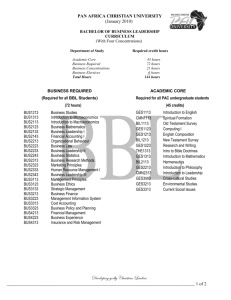
Quarter 3 Midterm topics

Topics for the Quarter 3 Midterm
Chapter 10 – Gases
Convert Pressure units (will get standard pressures)
Pressure = Force/Area (know units)
Gas Laws
Boyle’s
Charles’
Ideal
Molecular mass
Density
Partial pressure
Chapter 11 – Liquids & Intermolecular Forces
Dispersion forces and boiling point
Dipole vs. H-bonding vs. Ionic
Phase diagram – critical and triple points
Chapter 13 – Properties of Solutions
Henry’s Law (constant provided)
Molarity, molality, mass % and mole fractions
Colligative Properties – freezing & boiling points – chart given
Solubility curve
Chapter 14 – Chemical Kinetics
Average rate of a reaction
Rate laws (determining the orders, rate constant)
Calculating the rate of a reaction given k and concentrations
Determining half-lives (first and second order reactions)
Finding concentrations given another concentration, k & t
Activation Energy – calculating and graphing
Chapter 15 – Chemical Equilibrium
Writing an equilibrium expression & calculating the eq. constant
Calculating eq. concentrations given K and other eq. concentrations
K c
and K p
– convert between the two values
Create and use an ICE table
Calculate Q and compare to K (which side is favored?)
LeChatelier’s Principle – calculate ∆H, identify the shift with changing pressure, concentration and temperature
Topics for the Quarter 3 Midterm
Chapter 10 – Gases
Convert Pressure units (will get standard pressures)
Pressure = Force/Area (know units)
Gas Laws
Boyle’s
Charles’
Ideal
Molecular mass
Density
Partial pressure
Chapter 11 – Liquids & Intermolecular Forces
Dispersion forces and boiling point
Dipole vs. H-bonding vs. Ionic
Phase diagram – critical and triple points
Chapter 13 – Properties of Solutions
Henry’s Law (constant provided)
Molarity, molality, mass % and mole fractions
Colligative Properties – freezing & boiling points – chart given
Solubility curve
Chapter 14 – Chemical Kinetics
Average rate of a reaction
Rate laws (determining the orders, rate constant)
Calculating the rate of a reaction given k and concentrations
Determining half-lives (first and second order reactions)
Finding concentrations given another concentration, k & t
Activation Energy – calculating and graphing
Chapter 15 – Chemical Equilibrium
Writing an equilibrium expression & calculating the eq. constant
Calculating eq. concentrations given K and other eq. concentrations
K c
and K p
– convert between the two values
Create and use an ICE table
Calculate Q and compare to K (which side is favored?)
LeChatelier’s Principle – calculate ∆H, identify the shift with changing pressure, concentration and temperature