File
advertisement
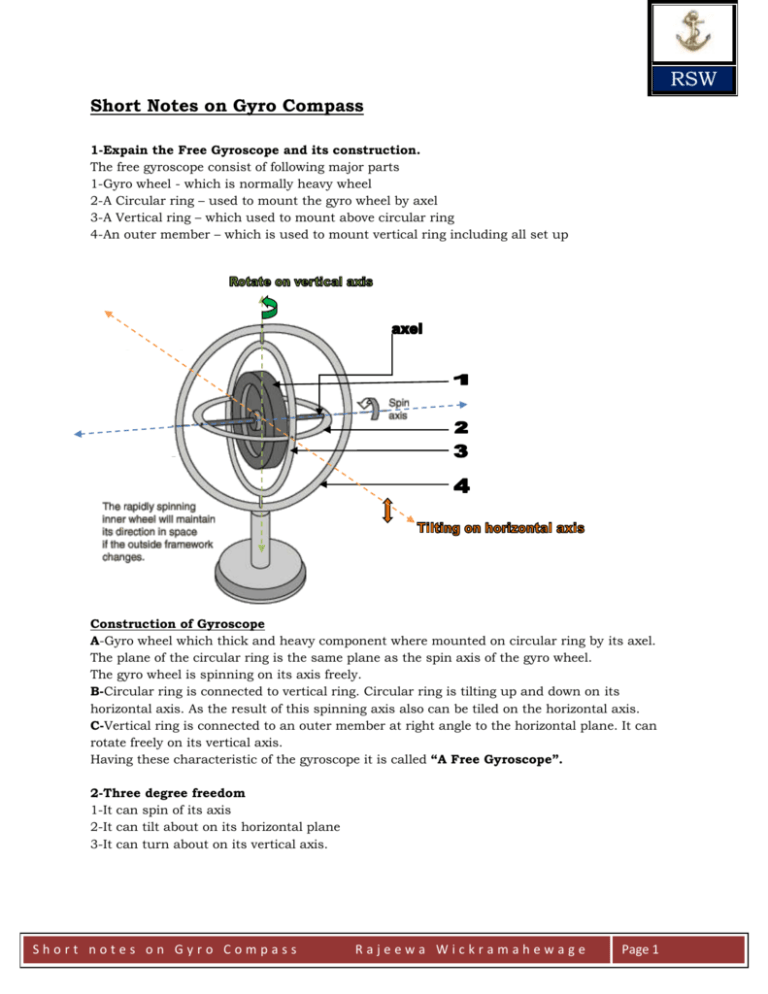
RSW Short Notes on Gyro Compass 1-Expain the Free Gyroscope and its construction. The free gyroscope consist of following major parts 1-Gyro wheel - which is normally heavy wheel 2-A Circular ring – used to mount the gyro wheel by axel 3-A Vertical ring – which used to mount above circular ring 4-An outer member – which is used to mount vertical ring including all set up Construction of Gyroscope A-Gyro wheel which thick and heavy component where mounted on circular ring by its axel. The plane of the circular ring is the same plane as the spin axis of the gyro wheel. The gyro wheel is spinning on its axis freely. B-Circular ring is connected to vertical ring. Circular ring is tilting up and down on its horizontal axis. As the result of this spinning axis also can be tiled on the horizontal axis. C-Vertical ring is connected to an outer member at right angle to the horizontal plane. It can rotate freely on its vertical axis. Having these characteristic of the gyroscope it is called “A Free Gyroscope”. 2-Three degree freedom 1-It can spin of its axis 2-It can tilt about on its horizontal plane 3-It can turn about on its vertical axis. Short notes on Gyro Compass Rajeewa Wickramahewage Page 1 RSW 3-Explain what you understand by “Rigidity of the Space” When the free gyroscope made to spin on its axis, it’s continuously pointing to a fixed direction as same direction as it was started. It will not change the direction although the supporting base is moved or tiled. This unique property of spinning free gyroscope is called “Rigidity of the Space”. 4-What is the gyro star? When the free gyroscope made to spin on its axis, it’s continuously pointing to a fixed direction as same direction as it was started. Assuming, it is directing to a distance imaginary point in the space. As refer to gyro compass it is called by “Gyro Star” 5-Describe the Gyroscopic Inertia. When the gyro wheel start spinning rapidly on its axis. It’s continuously pointing to a fixed direction means it showing a directional stability. A resistance to move. It’s called the Gyroscopic Inertia. When the gyro wheel is spinning, the outward force creating on the gyro wheel is called “Certrifugunal force” and inward force which counteract to above force as acting towards the centre of the wheel is called “Centripetal Force”. Due to equilibrium of these two forces gyroscope has a tendency to remain in the same direction. This is called the Gyroscopic Inertia. Factors that governing gyroscope inertia, Angular moment of the gyro wheel ∝ gyroscope inertia Then, Angular moment= moment of inertia x Angular velocity Moment of Inertia=Mass of the rotor x Radius of gyration Then, Angular moment=Mass of the rotor x radius of gyration x angular velocity 1-Mass of the rotor – this is the entire mass of gyro wheel and axel 2-the radius of gyration – it is the distance from the center of the rotor to the point through Which the mass of the rotor is considered to act. 3-Angular velocity-the speed of rotor spin Note: by increasing any one or more of above three factors will result in an increase of gyroscope inertia and rigidity in space. 6-Explain the Precession of free Gyroscope. Precession is the moment of the spin axis of the gyro wheel when a force is applied to the end of gyro axle. On a free gyroscope when a force is applied to the spin axis of gyro wheel, it will turn at right angle to the direction of applied force. The direction of the turn will depend on the direction of spinning wheel is turning. There for when a force is applied to the spin axis on the horizontal plane or horizontal axis the spin axis will turn on to vertical axis. Short notes on Gyro Compass Rajeewa Wickramahewage Page 2 RSW 7-What are the factors affecting the rate of precession. The rate of precession is directly proportional to the applied torque and inversely proportional to the gyroscopic inertia of the spinning rotor. Rate of Precession ∝ Applied torque Rate of Precession 1/∝ Gyroscopic Inertia Assume: P=rate of procession T=Torque I=Moment of Inertia of gyro wheel S=Angular Velocity P=T/IxS 8-explain the procedure to predict the direction of Precession The following should be known, 1-The direction in which the gyro rotor is spinning 2-the direction of the applied torque Assumed, that torque is applied at one end of the gyro axle. The resultant precession can be predicted as follows. A- Place a tip of pencil at the end of the axel where the torque is applied. B- Rotate the pencil by 90degree along the direction of the spin using the tip of pencil as pivoting point. C- Present position and the direction of the pencil indicate the precession. Short notes on Gyro Compass Rajeewa Wickramahewage Page 3 RSW 9-Define, Tilt, Tilting, Drift, Drifting Tilt: this is the angle by which the spin axis of gyro has apparently moved up and down from the horizontal plane. Tilting: This is the apparent motion of gyro axel on the vertical plane, it may be upward and downward defending of factors which it causing. Drift: this is the angle by which gyro axel has drifted and moved away from the original direction in the horizontal plan Drifting: This is the apparent motion of gyro axel on the horizontal plane. 10-Explain the Natural Gyroscope of Earth Earth can be considered as a natural gyroscope as it showing same characteristic as gyroscope. The axis of the earth also pointing to a spot in the space. The earth rotates from WEST to EAST When looking above the north pole from the space, it appears to be that the horizontal plane of the North pole is having a turn table movement above the vertical axis in a anti clock wise direction. In the same way from the south pole it appears that rotation in clockwise direction If the observer stand on the equinoxes and observe the Equator he can see horizontal plane is tilting up above north and south axis. so he will see that East end will go down and West end will coming up. Then west end passes through zenith and going down towards to east end. In summery. It can be finalized that as relative to space at the poles both north and south are having turn table movement and at the equator the moment of the horizontal plane is Easterly a tilting movement. In between any intermediate latitude the movement is a combination of turn table movement and tilting movement. 11- How do you compare Earths natural gyroscopic movement with Gyro axel? Since the gyro axel is fixed relative to space just as the earth. So gyro axel will exhibit the same movement relative to the horizontal plane on the earth just as horizontal plane on the earth exhibited to the space. Note- But the only exception is that the movement is opposite to the earth movement. 12- Gyro placed on the North Pole. Gyro placed on the North Pole with axel horizontal. Means along the prime meridian. (000°-180°) Then axel can be seen that rotating clockwise in relation to horizon. The axel will complete 360° in one day called sidereal day. There are only Drifting movement can be seen and not any tilting movement. 13-Gyro placed on the South Pole Gyro placed on the South Pole with axel horizontal. Means along the prime meridian. (000°-180°) Then axel can be seen that rotating anti clockwise relation to the horizon. Short notes on Gyro Compass Rajeewa Wickramahewage Page 4 RSW There are only Drifting movement can be seen and not any tilting movement. 14-Gyro placed on the equator Place the gyro with axel horizontal heading north and south direction. Along a longitude. That means the axis of gyro is pointing to North and South Pole and also parallel to the axis of the earth. There for gyro star is the pole star. As the pole star remain in the same with relation to the earth. Gyro axis also remains pointing to the same plane. There for tilting and drifting is minimum and near zero. 15-Gyro place on the Equator axel horizontal and East and West direction Gyro is placed on the equator with the axel horizontal and pointing East West direction Then the East end of the axel can be seen rising up (Tilting up) relative to the earth. Then it approach to zenith and passes through. After that start to dip down towards to west and complete 360°. In this there will be only tilting and not any movement of drifting at all 16-Gyro place on the any intermediate North latitude If the gyro axel is set on any meridian at horizontal The north end will turned to east due to turn table movement. The moment it is off the meridian it will start to rise due to the tilting movement. So the movement is tilting and drifting. 17- Gyro place on the any intermediate South latitude If the gyro axel is set on any meridian at horizontal The north end will turned to west due to turn table movement. As soon as it turns to the west of the meridian it start to dip down due to tilting movement So the movement is tilting and drifting. Note: from the above description can be seen that apparent motion of the free gyro scope defend on following, 1-Latitude of the position of the gyro 2-Azimuth of the spin axis The rate of tilting is maximum when axel is on the equator and pointing east west direction. Rate of tilting per hour = 15° Cos latitude x Sin Azimuth Short notes on Gyro Compass Rajeewa Wickramahewage Page 5 RSW 18-explain the rate of drifting with latitude On the Equator Axel horizontal and pointing E/W direction Experience only Tilting and No drifting at all. On the Equator Axel pointing North and South direction No drifting at all North pole Spin axel horizontal (on the line of Prime meridian) South pole Spin axel horizontal (on the line of Prime meridian) Intermediate latitude North and South hemisphere Axel pointing North and South direction It will drift in a direction opposite to the spin of earth (Clockwise) It will drift in a direction opposite to the spin of earth (Anticlockwise) Will experience tilting and drifting in both hemispheres Note: The drifting is minimum at the Equator and maximum at the poles There for the drifting various with Sin lat: Rate of drifting per hour = 15° x Sin Lat: 19-calculating the tilting and drifting Free gyroscope located in 30deg north latitude in started with its spinning axis horizontal and pointing in the direction of 60deg to the east of North. Calculate the rate of tilting and drifting for this situation. Rate of tilting per hour = 15 x cos lat x sin azimuth = 15 x cos 30 x sin 60 = 11.15 (11.25) Rate of drifting per hour = 15 x sin Lat = 15 x sin 30 = 7.30 (7.5) 20-What are the requirements of gyroscope? Short notes on Gyro Compass Rajeewa Wickramahewage Page 6