Seismology fill in the blanks asst 2015
advertisement

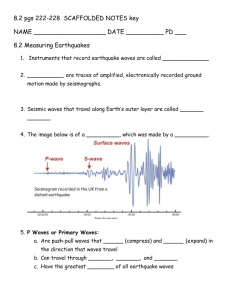
Seismology Name: __________________________ is the study of __________________________ and __________________________ that move through and around the earth. A __________________________ is a scientist who studies earthquakes and seismic waves. 1._________________ Theory =an explanation for how _________________________ __________________________ during earthquakes. a) As plates on opposite sides of a fault are subjected to force and shift, they accumulate energy and slowly __________________________ until their internal strength is __________________________. b) At that time, a sudden movement occurs along the fault, __________________________ the accumulated energy, and the rocks __________________________ to their original __________________________ shape. __________________________ = point __________________________ the Earth where an earthquake begins __________________________ = point on Earth’s __________________________ above focus How are Earthquakes Measured? Mercalli Intensity Scale The strength of an earthquake is usually measured on one of two scales, the Modified __________________________ Scale and the __________________________ Scale. The Mercalli Scale is a rather arbitrary set of definitions based upon what people in the area __________________________, and their __________________________ of damage to __________________________ around them. These scales are important to business and __________________________ in earthquake affected areas. Richter Scale It used a formula based on __________________________ of the __________________________ recorded on a specific type of seismometer and the __________________________ between the earthquake and the seismometer. The Intensity Scale differs from the Richter Magnitude Scale in that the effects of any one earthquake ___________________ greatly from __________________________, so there may be many __________________________ values (e.g.: IV, VII) measured for the same earthquake. Each earthquake, on the other hand, should have only one __________________________, although the various methods of calculating it may give slightly different values (e.g.: 4.5, 4.6). The Richter Scale is designed to allow easier comparison of earthquake __________________________, regardless of the __________________________. 2. Seismic Waves = the waves of __________________________ caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the earth or an explosion. They are the __________________________ that travels through the earth and is recorded on __________________________. Types of waves The two main types of waves are __________________________ waves and __________________________ waves. a) Body waves can travel through the ____________________________ (including _____________________) b) __________________ waves can only move along the surface of the planet like ________________________. Body Waves P wave or __________________________ wave. a) This is the __________________________ kind of seismic wave b) the __________________________ to 'arrive' at a seismic station. c) can move through _______________________ and ______________________, like water or the liquid layers of the earth. d) It __________________________ the rock it moves through just like sound waves push and pull the air. e) also called __________________________ waves S Waves a) Stands for __________________________ wave. b) the __________________________ wave you feel in an earthquake. c) An S wave is __________________________ than a P wave d) can only move through __________________________, not through any liquid medium. e) move rock particles __________________________, or __________________________ -perpendicular to the direction that the wave is traveling in (the direction of wave propagation). Surface Waves a) Travel only through the __________________________ (__________________________) b) are of a __________________________ than body waves c) __________________________ seen on a seismogram as a result. (________________________ waves) d) arrive __________________________ body waves e) surface waves are almost entirely responsible for the ___________________________________ _________________ associated with earthquakes. f) This damage and the strength of the surface waves are reduced in __________________________ earthquakes. L waves a) named after A.E.H. Love, a British mathematician who worked out the mathematical model for this kind of wave in 1911. b) the __________________________ __________________________ wave c) moves the ground from __________________________. d) Found only on the __________________________ of the crust, Love waves produce entirely __________________________ motion. Seismographs a) measure the amount of __________________________. b) Many seismographs are used together as an __________________________. c) The data from this array is taken and __________________________ is used to find the __________________________ and other information about the earthquake. Major Hazards of Earthquakes Safest & Most Dangerous Buildings • __________________________ • __________________________ House - Safest • __________________________ • __________________________ • __________________________ • Reinforced Concrete • __________________________ (Not Tidal Waves!) • __________________________ Masonry • __________________________ - Most Dangerous