Experiment
advertisement

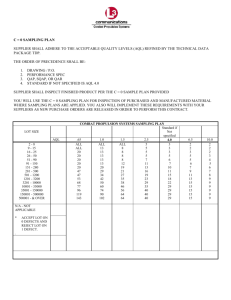
Soran University Module Specification Template 1. Module Title: Introduction to geochemistry 2. Module Code: PGE201 3. Module Level: --4. Module Leader: Mohammad Gh. Askandar 5. Teaching Semester: First semester 6. Credit Rating for the module: 3 7. Prerequisites and co-requisites Prerequisites: Chemistry, General geology Co-requisites: Mineralogy 8. Module Summary The main goal of this course is to help you develop an understanding of basic principles of geochemistry as it applies to fundamental geological and environmental processes, including distribution of elements, chemical reactions, and geochemical cycles, develop the requisite skills to apply chemistry skills to solve environmental problems, and learn how to do geochemical sampling, analyses samples, using data and interpretation of data to determine the anomalies in a region. In addition to these goals you will also learn about isotopes and how you can use them in geology processes. 9. Module Aims The aim of this course is to introduce the fundamental of geochemistry, including an introduction to The structure and composition of the earth and its relation with universe, isotopes and dating by isotopes, geochmical sampling techniques in diferent environment, preparing of samples for analyses and interpretation of data. students learn to how determine geochemical anomalis and interpret them. 10. Learning Outcomes after completing this course, students will be able to: • • Knows about distribution of element in different layers of earth Interpret magmatism and sedimentation as a geochemical processes. • • • • • • • Interpretation of geological processes and dating. Sampling in different environment. Preparing of samples. Digestion of samples and preparing of them for analysis. Data analysis Find geochemical anomalies and interpret them. Produce geochemical maps for anomalies. 11. Syllabus Chapter 1 (introduction) • Atoms, elements, periodic table, bonding, acids & bases , salts & ions and classification of elements. Chapter 2 (The structure and composition of the earth and solar system) • The earth in relation to the universe • The structure, composition and distribution of elements in different parts of the earth • • Chapter 3 (sampling) • Sampling Technique in different environments including : Type Of Survey Straem sediment sampling and water sampling Rock Sampling, soil and heavy mineral sampling • Geobotani and biogeochemical sampling Chapter 4 (Isotopes) • Stable Isotope • Radiogenic Isotope • Application of isotopes in Geology Chapter 5 (Instrumental analysis) • Instrumental Analysis: ICP-ES, And ICP-MS • Instrumental Analysis: AA, INAA, SEM, XRF, And XRD Chapter 6 (Data analysis) • Data analysis: Data Quality Controlling • Data analysis: Interpretation Of Data. Chapter 7 (sedimentation and magmatism as geochemical processes) • Magmatism and igneous rocks • Sedimentation and sedimentary rocks • Dating of geological samples Chapter 8 (thermodynamic and crystal chemistry) • Thermodynamic and crystal chemistry Chapter 9 (Geochemical cycle) • Geochemical cycle 12. Assessment Strategy Method of Assessment: 1 x 2 h lectures and 1 x 3 h laboratory sessions per week. Examination and grading Theory (70% of total course marks) • The average of 4 written examinations will stand for 20% of the total course marks. • A Final examination will stand for the remaining 45% of total course marks. Practical (30% of total course marks) • The average of 4 written examinations will stand for 10% of the total course marks. • Practical reports and homework will be 5% • A final examination will stand for 15% of the total course marks. The average grade of several practical reports will account for 5% of the total course marks. Each group of 2 students has to submit a report about the laboratory work. The reports have to be approved by the lecturers in order for the group to be granted admission for the final examination. 13. Summary description of assessment items Assessment Type Class attendance Homework Description of Item All students are required to be presence during class sessions Homework is due one week from the time of assignment at the beginning of the lecture unless otherwise specified. No late homework % Weighting 5% Grading Tariff 100 - 5% 100 Week due Practical works Midterms exams Will be accepted. Prepare report and activity in lab works At least 2 midterms exam Final exam (theory) Final exam (practical) 10% 100 20% 100 40% 100 4 exams, 2 hours per exam 3 hours 15% 100 1 hour 14. Learning Session Structure University Academic Week 1 Week beginning 2013/09/30 2 2013/10/07 3 2013/10/14 4 2013/10/21 5 2013/10/28 Lecture Title & Content Introduction: atoms, elements, periodic table, bonding, acids & bases , salts & ions and classification of elements. The earth in relation to the universe, structure, composition and distribution of elements in different parts of the earth Sampling Technique in different environments: Type Of Survey, Straem sediment sampling and water sampling Assessment I Eid Al Adha Holiday Sampling Technique in different Assessments 6 2013/11/04 7 2013/11/11 8 2013/11/18 9 2013/11/25 10 11 2013/12/02 2013/12/09 environments: Rock Sampling, soil and heavy mineral sampling, geobotani and biogeochemical sampling Isotope geochemistry: stable Isotope Isotope geochemistry: Radiogenic Isotope Application of isotopes in Geology Instrumental Analysis: ICP-ES, And ICP-MS Instrumental Analysis: AA, INAA, SEM, XRF, And XRD Assessment II Data analysis: Data Quality Controlling Data analysis: Interpretation of Data. Determination of geological anomalies and interpretation of them. Magmatism and igneous rocks An introduction to magma and igneous rocks Distribution of element in igneous rock Partition (Distribution) coefficient and Bulk distribution coefficient for elements Compatible and incompatible elements Residual solution and pegmatites 12 2013/12/16 Sedimentation and Sedimentary rocks An introduction to Sedimentation and Sedimentary rocks Oxidation and Reduction Complexes and metal mobility Red-Ox (Reduction- Oxidation) Reactions Red-Ox (Reduction- Oxidation) Reactions 13 2013/12/23 14 2013/12/25 To 2013/01/01 15 2013/01/06 Assessment III Winter Holiday thermodynamic and crystal chemistry An introduction to thermodynamic Type of energy States of matter Electronegativity and coordination number Isomorphism and polymorphism Atomic substitution Solid solution and type of solid solution Geochemical cycle 16 2013/01/13 Introduction Geochemical cycling of elements Geochemical cycle of oxygen Geochemical cycle of CO2 Effect of humans 17 2013/01/20 18 2013/01/27 19 2013/02/03 20 2013/02/10 21 2013/02/17 University Academic Week 1 2 3 4 5-6-7 Assessment IV Revision Week Revision Week Revision Week Final Examination Experiment Introduction to Laboratory activity Sampling: Drainage Sampling, and water sampling Sampling: Rock Sampling, soil and heavy mineral sampling Isotopes: some problems about Stable and Radiogenic Isotopes Analytical Methods: Wet Digestion: Acid digestion Analytical Methods: Wet Digestion: Alkali Fusion Analytical Methods: Dry methods: XRD XRF 8-9 Data analysis and interpretation: Data Quality Controlling Data analysis and interpretation: interpretation of data, 10 Data analysis and interpretation: Using Data, determination of anomalies and interpretation of anomalies. 15. Learning and Teaching Methods Teaching involves conventional lectures combined with coursework, tutorials, case studies, projects, practical and discussion classes. Methods of teaching and assessment in the early stages of the programs aim to ensure the acquisition of techniques and relevant knowledge, including practice in finding information and deciding whether it is relevant. Also, it is comprise review, evaluate, and recommend student textbooks and learning materials. Therefore, in order to competence and more interest in the course class and also high quality of education, Lectures maybe delivered through the use of • white board • Powerpoint presentations Student Responsibilities • • • • • • • Attendance is important for you to sit in a exam. 75% at least. To be Punctual to class (You may be marked absent or not allowed to enter). To be attentive and engaged in class. Do ask questions. To spend adequate time understanding and learning in your own time. Seek help when appropriate Preparing report after each lab. The report should contain the following elements: 1: Introduction: Provides background on the problem, including any relevant previous work or references, and outlines the objectives of the lab. 2: Methods: Includes detailed description of what was done in the lab. Pictures or diagrams are often helpful in this section. 3: Results: Data collected during the lab. 4: Discussion: An interpretation of what the data mean, including how they relate to the objectives of the lab. If I provide thought questions for a particular lab, it is appropriate to incorporate the answers into the discussion. Note, this should fit with the prose of the paper and not be a list of questions with answers. 5: Conclusion: Brief wrap-up of the report. This section is often a summary of the most significant findings of the lab. 16. Bibliography • Principle of geochemistry, B. Mason, C.B. Moore, 1982. • • • Using geochemical data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation, Hugh R. Rollinson. Introduction to exploration geochemistry, A.A. Levinson. Krauskopf, K.B., and Bird, D.K. Introduction to geochemistry, 3/e (1995), McGraw-Hill, 647 pp. ISBN: 0070358206 / softback ISBN: 007113929X. 17. Authored by Mohammad Piroui 18. Validated and Verified by Prof. Dr. Kamal Yusef Odisho