course-outlinemfg123
advertisement
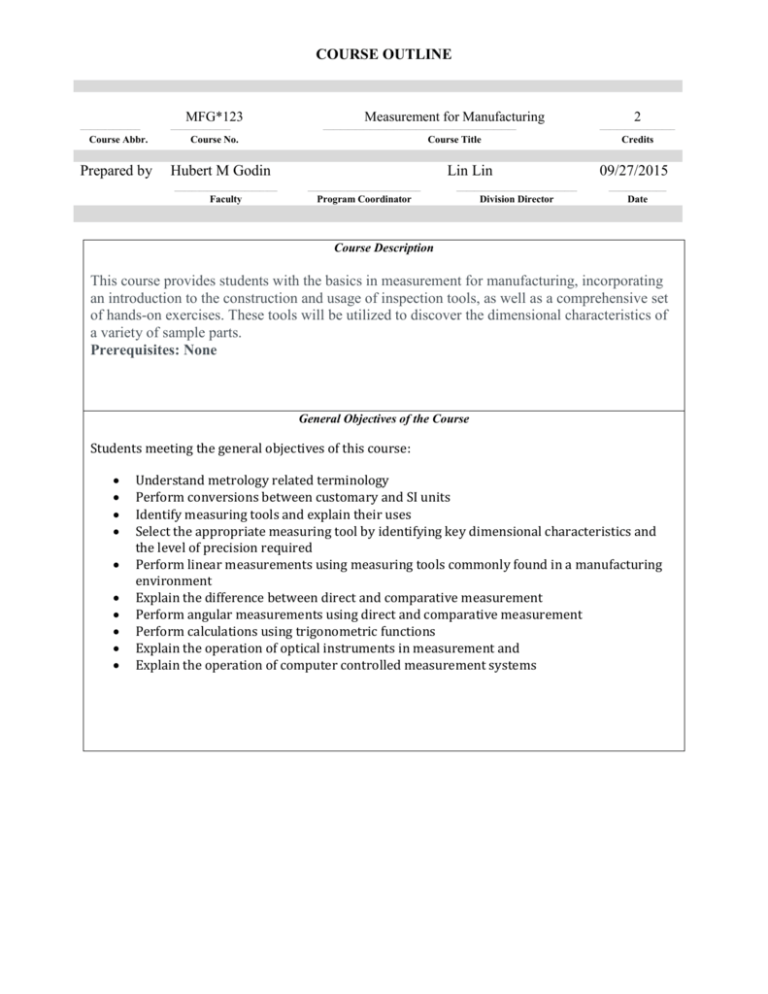
COURSE OUTLINE MFG*123 ________________________ Course Abbr. Prepared by ________________________ Measurement for Manufacturing _____________________________________________________________________________ Course No. Course Title Hubert M Godin Lin Lin 2 ______________________________ Credits 09/27/2015 _________________________________________ _____________________________________________ ________________________________________________ _______________________ Faculty Program Coordinator Division Director Date Course Description This course provides students with the basics in measurement for manufacturing, incorporating an introduction to the construction and usage of inspection tools, as well as a comprehensive set of hands-on exercises. These tools will be utilized to discover the dimensional characteristics of a variety of sample parts. Prerequisites: None General Objectives of the Course Students meeting the general objectives of this course: Understand metrology related terminology Perform conversions between customary and SI units Identify measuring tools and explain their uses Select the appropriate measuring tool by identifying key dimensional characteristics and the level of precision required Perform linear measurements using measuring tools commonly found in a manufacturing environment Explain the difference between direct and comparative measurement Perform angular measurements using direct and comparative measurement Perform calculations using trigonometric functions Explain the operation of optical instruments in measurement and Explain the operation of computer controlled measurement systems Unit # Instructional Unit Specific Objectives of Unit 1 Common Fractions, Decimal Fractions and Mixed Numbers 2 Measurement and Metrology 3 Language and Systems Measurement 4 The Rule 5 Vernier Instruments 6 Micrometer Instruments 7 Gage Blocks 8 Measurement by Comparison 9 Reference Planes 10 Angular Measurement Fractions and decimal conversion Performing arithmetic operations of fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers Rounding decimal numbers Metrology defined Explain why measurements are relative Explain the role of measurement in commerce Define linear measurement Define the terms accuracy, precision, and reliability Degree of precision, greatest possible error, absolute error and relative error Describe the metric and English systems of measurement Conversions between the metric and English systems Level of precision Recognize the sources of error when using a rule Proper use of the rule to minimize error when performing measurements Describe basic measuring tools that use a rule Describe basic transfer instruments Describe the Vernier Instruments Read Vernier Instruments Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using Vernier scaled instruments Compare of Vernier instruments to dial and electronic instruments Explain how amplification results in better readability Explain the basic operation of the micrometer Describe micrometer construction Identify different types of micrometers Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using a micrometer Describe fundamental characteristics of gage block materials Identify classifications of gage blocks and their uses Identify characteristics of gage blocks that may be unreliable Explain the rules for proper care of gage blocks Use combination of gage blocks to get a desired dimension Identify uses of gage blocks Explain the difference between comparative and direct measurement Explain the operation of the dial indicator Identify different types of indicators and explain their uses State the importance of flatness and perpendicularity in industry Identify materials used to manufacture reference planes State basic rules for using surface plates Identify uses for the grades of surface plates Identify the tools and level of precision for angular measurement The role of squares, levels, angle blocks, and protractors in angular measurements Explain use of sine bars and sine plates in angular measurements Apply the circle, trigonometric functions, sine bars, and sine plates in angular measurements 11 Optical Metrology 12 The CMM (Coordinate Measurement Machine) The role of the microscope in inspection Parts of the microscope Operation of the Optical Comparator Comparison of the Optical Comparator with the microscope Measurements made with the Optical Comparator Limitations of the Optical Comparator Machine Vision Systems The role of the CMM Types of CMMs Operational Modes