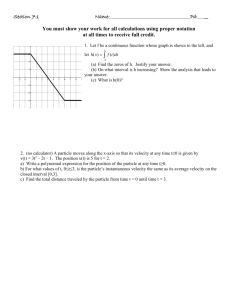
objects appear
advertisement

Final review 1 MKS units a) Meters m g) Joule b) kilograms kg h) Wall c) seconds sec or s i) kg·m/sec d) m/sec j) N-m e) m/sec2 k) N f) Joule J 2) ~13.6 Billion years Mercury = M Jupiter = J l) N ~5.6 billion years Venus = V Earth = E Saturn = S Uranus = U 3) Ma, J, S, U, N Mars = Ma Neptune = N M, V 4) M, V, E, Ma J, S ,U,N 5) M, V, E, Ma J, S U, N 6) Sun at center of Universe 7) a) Red W or J/sec Earth at center of Universe Everything else revolves only around Earth b) Blue 8) cloud of dust, gas in space. Can be drawn together by gravity to form star. 9) stars with specific ratio of Luminosity to mass while fusing hydrogen into helium in core. 90% of stars are on main sequence. When hydrogen used up, star leaves main sequence. 10) very large, cooler star. Sun will become Red Giant when it leaves main sequence 11) very small, very hot star. Sun will become white dwarf after red giant stage. 12) supergiant star after many stages, expands massively when fuel has fused to iron. Shrinks and explodes, fusing many other elements at core. 13) remnant of supernova of supergiant star. As star collapses final time, fuses protons and electrons into neutrons 1 14) remnant of supernova of largest stars. Collapses into point so dense that light cannot escape. 15) radius of black hole: Rs = 2 GM c2 16) theory of origin of Universe. that all of universe originally a small point, exploded apart and accelerating apart still. 17) stars/galaxies moving away appear to have longer wavelength, are redder.. stars/galaxies approaching appear to have shorter wavelength, are bluer. 18) measure of apparent brightness of a star, especially compared to the Sun. 19) AU is distance from Earth to Sun Ly is distance light travels in one year [not most scientific term] ps is used to measure distance in space. = 3.3 light year. ½ apparent 20) apparent motion of object when viewed from 2 different places. Closer objects appear to move further. Used to determine the distance stars are from Earth. 21) unstable nucleus splitting into smaller nuclei, nucleus emitting particles; responsible for most of the internal heat inside of Earth. Opposite of fission, smaller nuclei fused together to from larger nucleus. Fission occurs inside of stars. 22) apparent motion of object when viewed from 2 different places. Closer objects appear to move further. Used to determine the distance stars are from Earth. 23) unstable [radioactive] isotope of an atom that fissions. Isotopes are atoms with same atomic number [number of protons] but different number of neutrons [so mass is different] . 24) p = positively charged subatomic particle 2 n = Uncharged subatomic particle in nucleus e= Negatively charged subatomic particle carbon-14 is 146 C 6 is atomic number [number of p= #p] and 14 is the mass number[number of protons +neutrons = #p +#n] carbon-14 has 6 p and 8 n 25) protons and neutrons bound together in center of atom. 26) : radiation when alpha particle emitted from nucleus. Alpha particle is postitively charged particle comprised of 2 protons and 2 neutrons bound together particle = Helium nucleus : 42 He2+ Alpha radiation is least penetrating radiation, can be blocked by paper, can be deflected by magnetic field. 27) alpha decay: subtract 4 from mass number 234 92U , subtract 2 from atomic number → 42He + 23090Th 28) beta radiation: negatively charged particle emitted from unstable nucleus . one neutron splits into one proton + one electron and the electron is ejected from the nucleus Neutron → proton + electon. Can represent particle as 0-1e- Beta radiation is more penetrating than alpha, can be blocked by aluminum foil or skin, can be deflected by magnetic field 29) beta decay: mass remains the same. ADD 1 to atomic number 234 92U → 0-1e- + 23493Np 30) gamma radiation: electromagnetic radiation = stream of high energy photons Most dangerous and most penetrating radiation. Can be blocked by several feet of concrete or lead. 3 31) 1st - when surface solidified, Hydrogen and helium outgassed [gases escaped] from interior. First Atmosphere escaped Earth’s gravity into space. 32) 2nd - volcanic explosions, released steam [water] , ammonia [NH3] and carbon dioxide [CO2 ] Water condensed into oceans. Ammonia broke down in sunlight into hydrogen gas and nitrogen gas Hydrogen, H2, escaped Nitrogen , N2 remained 2NH3 → N2 + 3H2 Finally, blue-green algae in oceans converted carbon dioxide into oxygen O2 by photosynthesis. 33) Primarily N2 78% and O2 22% plus traces of other gases. 34) sum of the forces = 0. F = 0. Object is at rest or is moving at constant velocity. 35) sum of torques = 0 = 0. Sum of clockwise torques = sum of counter clockwise torques. 36) an unbalanced force causes an object to accelerate in direction of unbalanced force. F = ma 37) F = ma F= 2000N m=500 kg a=? 2000 = 500 a a= 4 m/sec2 38) every action has an equal and opposite reaction. Forces occur in action-reaction force pairs. 39) force of man on table = force of table on man Force of man on table = mg = 600 N. 4 40) forces occur in pairs. Action force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to reaction force. 41) balanced : forces equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Object in equilibirum Unbalanced: causes acceleration [ change in velocity] 42) the symbol // means parallel work = force X distance// done. if force and distance are perpendicular, then ZERO work is Work is done lifting 20 kg mass up 2 meters vertically [weight // to direction of travel] Zero work if carrying 20kg mass 2 meters horizontally [weight not to direction of motion] Unit of work is the JOULE = J Power is the rate of doing work = work/time Unit of power = joule/sec = WATT = W 43) Energy is the ability to do work. Unit of energy = JOULE. 44) energy of motion KE = ½ mv2 45) stored energy. Can be gravitational, spring, chemical stored energy. Gravitational PE = mgh 46) GPE = mgh GPE=? M= 500 kg g=10 m/sec2 h=40 PE = mgh PE = [500][10][40] = 200,000 J 5 47) Spring energy= EPE or elastic potential energy EPE is energy stored when spring stretched or compressed distance x. EPE = ½ kx2 k = spring constant spring force : force to stretch or compress a spring distance x. Fspring = kx k = spring constant 48) energy neither created nor destroyed. At any point, the sum of the PE + KE is the same. PE1 + KE1 = PE2 + KE2 = PE3 + KE3 = constant. Kinetic energy is conserved if there is no friction. Kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions. 49) momentum = mass X velocity. Symbol for momentum is p. p = mv units of momentum = kg•m/sec Momentum is always conserved. Elastic collision: no permanent deformation, objects bounce apart, no loss of KE, momentum conserved Partially inelastic collision: objects deformed [“fender bender” ]object bounce apart, loss of KE; momentum conserved Perfectly inelastic : objects deformed, objects stick together, momentum conserved Conservation during collision: m1 = mass of object 1 m2= mass of object 2 V1 = initial velocity of object 1 v2= initial velocity object 2 V 3 = final velocity of object 1 v4= final velocity of object 2 m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v3 + m2 v4 6 50) m = 500 kg v= 15 m/sec w = mg w= [500 kg][10m/sec2] w =5000 kg•m/sec2 w = 5000 N 51) p=mv p= [500 kg] [15 m/sec] p=7500 kg•m/sec g = 10 m/sec2 52) KE = ½ mv2 KE = 1/2 [500kg][15 m/sec][15 m/sec] KE = 225,000 kg m2/sec2 = 225,000 N▪m = 225,000 J 53) radioisotopes decay at known rate. calculate precise age of object by measuring the amount of radioisotopes that remain. 54) time for one half of atoms of an isotope to decay. Every radioisotope has a unique half life 55) a) number of half lives n = Total time elapsed Time for 1 half life n = 120 years = 3 40 years b) n = 200/40 = 5 half lives half life n 0 1 2 3 4 5 amount of isotope remaining 120 g 60 g 30 g 15 g 7.5 g 3.75 g 56) “magnetic north” has reversed direction several times since the Earth’s surface cooled. A record of the magnetic reversals is found in the rocks in the Mid Atlantic Ridge. As plates diverge, magma pours up. Iron in magma aligns with the magnetic pole and solidifies. Later deposits of rock show opposite direction. 57) can only tell if one rock is older than another, not the exact age. Used to determine relative age of layers of sedimentary rocks. 7 58) oldest layers on the bottom. Like stacking newspapers 59) sediments settle into horizontal layers, like sand art 60) if layers cut vertically and separated, cake. same order of layers . like cutting a layer 61) intrusions of igneous rocks are newer than the rocks they cut through 62) erosion of layers before next layer forms = jagged top surface of layer. 63) Sun is at center , planets orbit the Sun. 64) sun spots, moons orbiting Jupiter, craters on moon 65) recorded motion of visible stars and planets for 20 years [no telescope] 66) 1st: planets in elliptical orbits, Sun at one focus point 2nd equal areas swept out in equal times 3rd: orbital period squared[in years] = orbital distance cubed[ in AU] T2 = d3 67) Earth in center of universe, all planets and stars circle the Earth. Sun and moon and all other celestial objects are perfect [no blemishes] 68) Continental Drift: continents have drifted over the surface of the Earth; South America and Africa once were next to each other. Observed: similar coastlines Similar fossils Similar mountain and rock formations 69) Plate Tectonics and Sea Floor Spreading: discovered sea floor is pushing apart at undersea mountains. Proposed this is how continents drift. Plate tectonics: surface broken into many large pieces that move continuously and reshape position of continents. Earth and atmosphere beyond A: exosphere A: thermosphere B: mesosphere 8 C: stratosphere D: ozone layer E: troposphere F: crust G: mantle H: outer core J: inner core Rock strata Oldest to Youngest events: layer A, intrusion B, fault C unconformity [ erosion ]D layer E, layer F, layer G , unconformity H, layer I, igneous Intrusion J, igneous Intrusion K 70) a) b) T +y Object at rest Equilibrium F = 0 T – mg = 0 T = mg = 50(10) = 500 N a +x +x W = mg c) +y +y +x T T W = mg Object at moving with constant +velocity Equilibrium F = 0 T – mg = 0 T = mg = 500 N W = mg Object at moving up with constant +acceleration not Equilibrium F = +ma T – mg = ma T = mg + ma T = 50(10) + 50(5) T = 750 N 9