A&P I 2014 Exam 2 Answers
advertisement

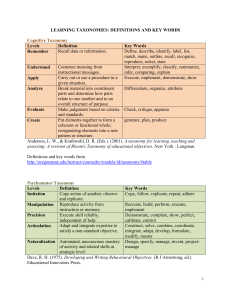
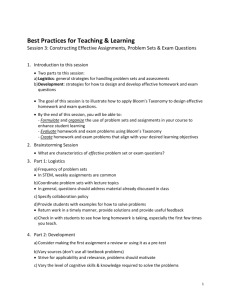
A&P I 2014 Exam 2 Answers Name______________________________________ Multiple Choice 1) mRNA is needed to synthesize ________ in the cytoplasm. A) carbohydrates B) lipids C) proteins D) phospholipids E) salts Answer: C Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 2) As each codon arrives at the active site of a ribosome, it attracts another molecule containing the anticodon. This molecule is called A) DNA. B) mRNA. C) rRNA. D) tRNA. E) RER. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 3) The process of protein formation directed by mRNA is called A) replication. B) transcription. C) translation. D) mitosis. E) auscultation. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 4) The process of forming mRNA is called A) replication. B) transcription. C) translation. D) ribolation. E) auscultation. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 5) Specific proteins are manufactured through the interaction of multiple ________ and ________. A) enzymes; three types of RNA B) enzymes; two types of RNA C) carbohydrates; three types of DNA D) proteins; three types of DNA E) enzymes; three types of DNA Answer: A Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 6) The mRNA sequence that is complementary to the sequence ATC on DNA is A) ATC. B) TAG. C) UAG. D) AUG. E) AUC. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 7) Before the mRNA transcribed from a gene can be used to translate into a protein, it must be A) edited to remove introns. B) edited to remove exons. C) transported into the cytoplasm. D) edited to remove introns and transported into the cytoplasm. E) coated with phospholipids for transport out of the nucleus. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Figure 6.2 Using Figure 6.2, match the following: 8) Compact bone. Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 178; Fig. 6.4 9) Location of the epiphyseal line. Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 178; Fig. 6.4 10) Area where yellow marrow is found. Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 178; Fig. 6.4 11) Epiphysis of the bone. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 178; Fig. 6.4 Match the following: A) Diaphysis B) Appositional growth C) Epiphyseal line D) Chondrocytes E) Epiphyseal plate 12) The cells responsible for the early stages of endochondral ossification. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 174, 184 13) The growth pattern of bone in which matrix is laid down on the surface. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 174 14) The area of long bones where cartilage cells are replaced by bone cells. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 184-185 15) The appearance of this structure signals the end of bone growth. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 185 16) Area where bone longitudinal growth takes place. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 185-186 Answers: 12) D 13) B 14) A 15) C 16) E T/F 17) An osteon contains osteocytes, lamellae, and a central canal, and is found in compact bone only. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 181 18) The trabeculae of spongy bone are oriented toward lines of stress. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 181-182 19) The hormone that is primarily involved in the control of bone remodeling is the parathyroid hormone. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 187 20) Each consecutive bone lamella has collagen fibers that wrap in alternating directions. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 181 21) Cartilage has a flexible matrix that can accommodate mitosis of chondrocytes. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 174 Multiple Choice 22) Which of the following labels best matches osteocyte? A) stem cell B) dissolves matrix C) mature bone cell D) secretes organic matrix E) immature bone cell Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 23) Cells that secrete the organic components of the bone matrix are called A) osteocytes. B) osteoprogenitor cells. C) osteoblasts. D) osteoclasts. E) osteoid cells. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 24) ________ are squamous stem cells that develop into osteoblasts. A) Osteoclasts B) Osteocytes C) Osteomedullary cells D) Osteoprogenitor cells E) Osteoid cells Answer: D Learning Outcome: 6-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 25) Through the action of osteoclasts, A) new bone is formed. B) an organic framework is formed. C) bony matrix is dissolved. D) osteoid is calcified. E) fractured bones regenerate. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 26) The space occupied by an osteocyte is called A) Volkmann's canal. B) a lacuna. C) a trabecula. D) a Haversian canal. E) a canaliculus. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 6-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 27) The central canal of an osteon contains A) bone marrow. B) osteocytes. C) concentric lamellae. D) blood vessels. E) lacunae. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 6-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 28) The interconnecting tiny arches of bone tissue found in spongy bone are called A) osteons. B) trabeculae. C) concentric lamellae. D) interstitial lamellae. E) lacunae. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 6-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 29) The type of bone that is adapted to withstand stresses that arrive from many directions is ________ bone. A) spongy B) osteon C) compact D) lamellar E) irregular Answer: A Learning Outcome: 6-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 30) The structural units of mature compact bone are called A) trabeculae. B) osteocytes. C) osteons. D) canaliculi. E) lamellae. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 31) The deposition of calcium salts in bone tissues is referred to as A) hardening. B) ossification. C) calcification. D) osteogenesis. E) remodeling. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 32) Which of the following is formed by intramembranous ossification? A) roof of the skull B) carpal bones C) femur D) clavicle E) the roof of the skull and the clavicle Answer: E Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 33) Endochondral ossification begins with the formation of a(n) A) fibrous connective-tissue model. B) cartilage model. C) membranous model. D) calcified model. E) osteoid model. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 34) The deposition of calcium salts in bone tissues is referred to as A) hardening. B) ossification. C) calcification. D) osteogenesis. E) remodeling. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 35) Which of the following is formed by intramembranous ossification? A) roof of the skull B) carpal bones C) femur D) clavicle E) the roof of the skull and the clavicle Answer: E Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 36) Endochondral ossification begins with the formation of a(n) A) fibrous connective-tissue model. B) cartilage model. C) membranous model. D) calcified model. E) osteoid model. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge Figure 6-2 Endochondral Ossification Use Figure 6-2 to answer the following question(s): 37) Where does growth in length occur? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Answer: C Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 38) What type of tissue occurs at #1? A) elastic tissue B) fibrocartilage C) bone D) hyaline cartilage E) marrow tissue Answer: D Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 39) What process is shown at #6? A) primary ossification B) secondary ossification C) length growth D) width growth E) fracture repair Answer: B Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 40) Identify the structure at #4. A) intramembranous bone B) spongy bone C) hyaline cartilage D) periosteum E) mesenchyme Answer: D Learning Outcome: 6-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 41) Elevated levels of calcium ion in the blood stimulate the secretion of the hormone A) calcitonin. B) thyroid hormone. C) parathyroid hormone. D) growth hormone. E) testosterone. Answer: A Learning Outcome: 6-8 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 42) The hormone calcitonin functions to A) stimulate osteoclast activity. B) decrease the rate of calcium excretion. C) decrease the rate of calcium absorption. D) decrease the level of calcium ion in the blood. E) stimulate osteoblasts and inhibit osteoclasts. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 6-8 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 43) A fascicle is a A) group of muscle fibers that are encased in the perimysium. B) layer of connective tissue that separates muscle from skin. C) group of muscle fibers that are all part of the same motor unit. D) group of muscle fibers and motor neurons. E) collection of myofibrils in a muscle fiber. Answer: A Learning Outcome: 10-2 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 44) The delicate connective tissue that surrounds the skeletal muscle fibers and ties adjacent muscle fibers together is the A) endomysium. B) perimysium. C) epimysium. D) superficial fascia. E) periosteum. Answer: A Learning Outcome: 10-2 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 45) In a sarcomere, the central portion of thick filaments are linked laterally by proteins of the A) Z line. B) M line. C) H band. D) A band. E) I band. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 46) The advantage of having many nuclei in a skeletal muscle fiber is the ability to A) contract much more forcefully. B) produce more ATP with little oxygen. C) store extra DNA for metabolism. D) produce large amounts of muscle proteins. E) produce nutrients for muscle contraction. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 47) Which of the following best describes the term sarcomere? A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils C) storage site for calcium ions D) thin filaments are anchored here E) largely made of myosin molecules Answer: B Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 48) Muscle fibers differ from "typical cells" in that muscle fibers A) lack a plasma membrane. B) have many nuclei. C) are very small. D) lack mitochondria. E) have large gaps in the cell membrane. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 49) Which of the following best describes the term sarcoplasmic reticulum? A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils C) storage and release site for calcium ions D) thin filaments are anchored here E) largely made of myosin molecules Answer: C Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 50) The advantage of having many nuclei in a skeletal muscle fiber is the ability to A) contract much more forcefully. B) produce more ATP with little oxygen. C) store extra DNA for metabolism. D) produce large amounts of muscle proteins. E) produce nutrients for muscle contraction. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 51) The plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber is called the A) sarcolemma. B) sarcomere. C) sarcosome. D) sarcoplasmic reticulum. E) sarcoplasm. Answer: A Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 52) The skeletal muscle complex known as the triad consists of A) actin, myosin, and titin filaments. B) a transverse tubule and two terminal cisternae. C) filaments, myofibrils, and sarcomeres. D) A bands, H bands, and I bands. E) actin, myosin, and sarcomeres. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 53) Cross-bridges are portions of A) actin molecules. B) myosin molecules. C) troponin molecules. D) tropomyosin molecules. E) calcium ions. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge Figure 9.1 Using Figure 9.1, match the following: 54) Connective tissue sheath surrounding individual muscle fibers Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 279; Fig. 9.1 55) Bundle of muscle cells surrounded by a perimysium Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 279; Fig. 9.1 56) Connective tissue covering the exterior of a muscle organ. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 279; Fig. 9.1 57) Connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber bundles Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 279; Fig. 9.1 58) Individual muscle fiber. Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 279; Fig. 9.1 Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following questions: 59) Identify the structure labeled "1." A) mitochondria B) glycogen C) ATP D) myofibril E) synaptic vesicle Answer: A Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 60) Which of the following are found in the structure labeled "3"? A) actin B) myosin C) titin D) tropomyosin E) All of the answers are correct. Answer: E Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Xtra Credit (1 point each) 1) A mature red blood cell lacks a nucleus; therefore, it A) can repair itself readily. B) is malformed. C) can only divide once more. D) will be a long-lived cell. E) cannot make new proteins and will be worn out within a few months. Answer: E Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Application 2) The anticodon for the triplet UCA is A) AGU. B) AGC. C) TCA. D) TGT. E) AGT. Answer: A Learning Outcome: 3-4 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 3) Factors that are necessary for proper bone formation include all of the following, except A) vitamin A. B) vitamin E. C) vitamin C. D) the hormone thyroxine. E) vitamin D. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 6-7 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 4) Put the following structures in order from superficial to deep. 1. muscle fiber 2. perimysium 3. myofibril 4. fascicle 5. endomysium 6. epimysium A) 1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6 B) 6, 2, 5, 4, 1, 3 C) 6, 2, 4, 5, 1, 3 D) 1, 3, 5, 6, 4, 2 E) 2, 3, 1, 4, 6, 5 Answer: C Learning Outcome: 10-2 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 5) Each skeletal muscle fiber contains ________ myofibrils. A) 50 to 100 B) 100 to 150 C) 150 to 200 D) 200 to 500 E) hundreds to thousands Answer: E Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge