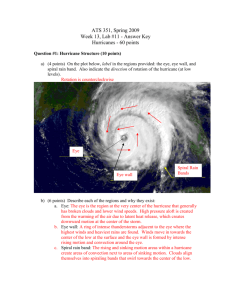
Concept 2: Sample
advertisement
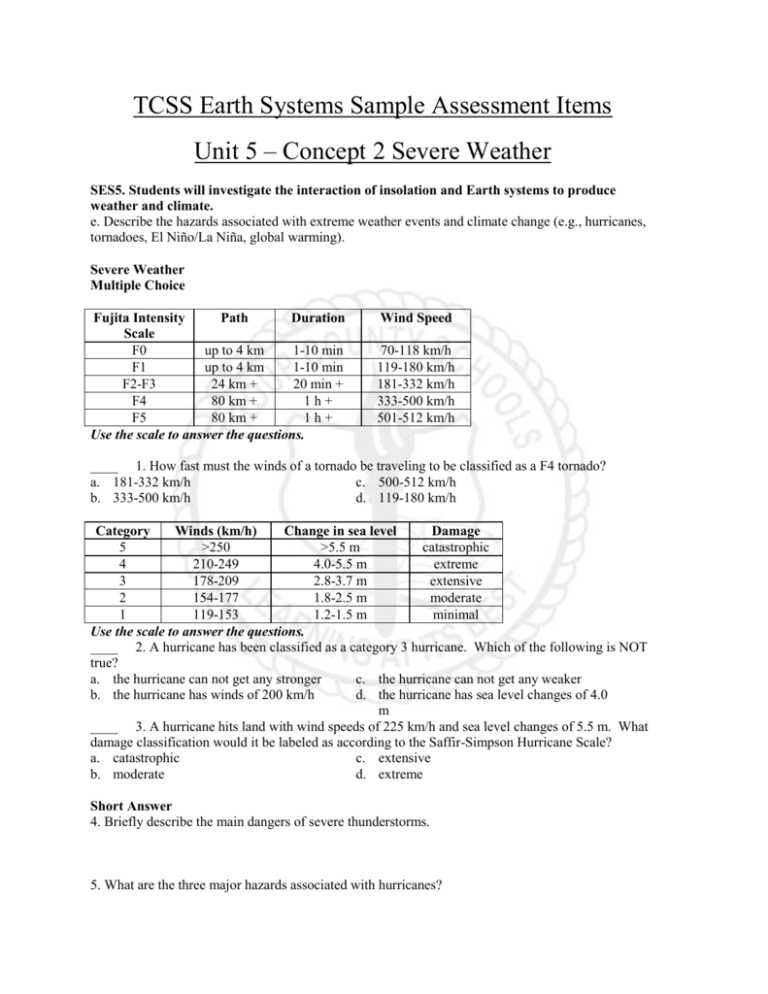
TCSS Earth Systems Sample Assessment Items Unit 5 – Concept 2 Severe Weather SES5. Students will investigate the interaction of insolation and Earth systems to produce weather and climate. e. Describe the hazards associated with extreme weather events and climate change (e.g., hurricanes, tornadoes, El Niño/La Niña, global warming). Severe Weather Multiple Choice Fujita Intensity Path Duration Scale F0 up to 4 km 1-10 min F1 up to 4 km 1-10 min F2-F3 24 km + 20 min + F4 80 km + 1h+ F5 80 km + 1h+ Use the scale to answer the questions. Wind Speed 70-118 km/h 119-180 km/h 181-332 km/h 333-500 km/h 501-512 km/h ____ 1. How fast must the winds of a tornado be traveling to be classified as a F4 tornado? a. 181-332 km/h c. 500-512 km/h b. 333-500 km/h d. 119-180 km/h Category Winds (km/h) Change in sea level Damage 5 >250 >5.5 m catastrophic 4 210-249 4.0-5.5 m extreme 3 178-209 2.8-3.7 m extensive 2 154-177 1.8-2.5 m moderate 1 119-153 1.2-1.5 m minimal Use the scale to answer the questions. ____ 2. A hurricane has been classified as a category 3 hurricane. Which of the following is NOT true? a. the hurricane can not get any stronger c. the hurricane can not get any weaker b. the hurricane has winds of 200 km/h d. the hurricane has sea level changes of 4.0 m ____ 3. A hurricane hits land with wind speeds of 225 km/h and sea level changes of 5.5 m. What damage classification would it be labeled as according to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale? a. catastrophic c. extensive b. moderate d. extreme Short Answer 4. Briefly describe the main dangers of severe thunderstorms. 5. What are the three major hazards associated with hurricanes? 6. Which lettered area of the hurricane shown below would produce the greatest wind damage? Explain.