Supplementary materials
advertisement

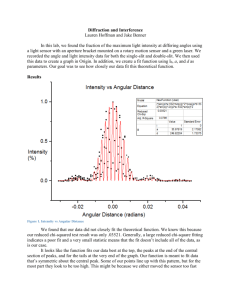
Supplementary materials In the studies of SPCE spectroscopy, it is common to achieve a dramatic increase in the emission intensity compared to the FS emission. However, the event seems more difficult for SPCE imaging. In previous reports, for gold substrate, the enhancement of the fluorescence signal in SPCE imaging due to the high light-collection efficiency is about two fold,1, 2 which is lower than that (about 5 fold) in RK configuration SPCE spectroscopy.3, 4 We believe that the reason for such a disparity between spectroscopy and imaging is that the fluorescence signal collected in imaging comes from a wider angle range than spectroscopy due to the imaging lens. As shown in the Figure S1, a simulated SPCE intensity curve (red line) for the emission wavelength of 580 nm was calculated via the Fresnel equation in a four-phase system (BK7 prism/50 nm silver film/30 nm RhB-PVA film/air). And an ideal FS intensity curve (black line) with isotropic distribution was used for the discussion. The normalized intensity of FS (compared to the SPCE peak intensity) was assumed to be 0.1, so the fluorescence enhancement was 10 fold. The integrated intensities of SPCE and FS with different angular integration intervals were calculated and shown in Table S1. The intensity ratios of SPCE to FS (fluorescence enhancement factor) decrease with the increase of the angular integration intervals. When the angular integration interval is 2°, the fluorescence enhancement factor reduces to about 3. For imaging, the imaging lens has a wider angle collection range than spectroscopy which is typically equipped with a slit.3,4 Therefore, it is more difficult to achieve an exciting fluorescence enhancement in SPCE imaging than SPCE spectroscopy. 1 Normalized Intensity 1.0 47.94o 0.8 SPCE FS 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 40 45 50 55 60 Angle Figure S1. Simulated angular distribution of the SPCE intensity (red line) and the ideal isotropic angular distribution of the FS intensity (black line). Table S1. The intensity ratios of SPCE to FS with different angular integration intervals Angular integration interval integrated intensity of SPCE integrated intensity of FS Ratio of SPCE to FS SPCE angle 47.94° 1.00 0.10 10.0 0.5°(47.69°~48.19°) 0.39 0.05 7.8 1°(47.44°~48.44°) 0.56 0.10 5.6 1.5°(47.19°~48.69°) 0.63 0.15 4.2 2°(46.94°~48.94°) 0.66 0.20 3.3 2.5°(46.69°~49.19°) 0.68 0.25 2.7 3°(46.44°~49.44°) 0.69 0.30 2.3 Supplementary References 1 J. S. Yuk, M. Trnavsky, C. McDonagh and B. D. MacCraith Biosens Bioelectron 25, 1344 (2010). 2 2 W. P. Cai, Q. Liu, S. H. Cao, Y. H. Weng, X. Q. Liu and Y. Q. Li ChemPhysChem 13, 3848 (2012). 3 C. D. Geddes, I. Gryczynski, J. Malicka, Z. Gryczynski and J. R. Lakowicz J. Fluoresc. 14, 119 (2004). 4 I. Gryczynski, J. Malicka, Z. Gryczynski and J. R. Lakowicz J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 12568 (2004). 3