Dynamic Assessment - Special Education Support Service
advertisement

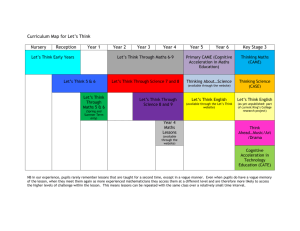
Dynamic Assessment A Framework Pre-test Assess student’s current performance Teach Using a mediated learning experience (MLE) Help the student develop strategies Observe the student's modifiability Post Test Compare performance to pre-test Assess transfer of strategies Teaching Sessions / Mediated Learning Experiences (MLE) A key to mediated learning experiences (MLE) is that the teacher deliberately teaches, watches how the student responds to instruction, and adjusts teaching accordingly. The aim during the teaching MLE) phase is for the students to become self-regulated and active in their learning. Component Intentionality What Relate intention to change student functioning to the student. Tell them the target and the reason for the MLE. ‘Today we are going to…’ Why Teach, create awareness in the student Meaning Focus the student's attention on what is important. Help the student to attend to important features of the task and ignore unimportant features. ‘This is important because…’ Help student to understand why task is important Transcendence Bridging of concepts & events beyond the immediate task; introduction of abstract ideas. Examples included questions like, "What would happen if…?" and "Have you ever…?" Help student think hypothetically. Competence Help the student develop plan. Help them think through how they will use the targeted strategy. Discuss appropriate times to use particular skill. ‘What do you have to do..? ’How will you do that..?’ Teach student to be self-regulated & active participant in own learning. Modifiability Modifiability is the term used to describe the student’s response to a MLE based on our observations during a teaching session. It is important to consider a student's modifiability when applying the MLE. Specifically, we need to consider student responsiveness, transfer skills, and teacher input. Student Responsiveness How well does the student respond to the MLE? Does the student attend to the task, and maintain attention? Does the student demonstrate efficient learning strategies? Does student use skills such as looking, comparing, and verbalising? Transfer How well does student apply the target skills from one item to the next? From one task to the next? Does student apply learned strategies soon after learning them? Teacher Input / Consideration How much support does the student need? What is the nature of the support required? Planning for Dynamic Assessment Identify area of relative weakness Pre-test Conduct a mediated learning experience (MLE). Be sure to include the components Intentionality Meaning Transcendence Competence Observe Modifiability Make recommendations Through a mediated learning experience, teachers can explore emerging skills. This process helps to pinpoint intervention goals, and can help make better predications. Targets should be selected for those skills in which student showed some awareness, but below expectations. Goals are set in developmental order that will help the student within the classroom setting. Dynamic Maths Assessment By providing an in-depth picture of a student's mathematical understanding of specific maths concepts/skills, a dynamic maths assessment helps teachers to determine how to best teach the student. Students with special educational needs often have gaps in mathematical understanding that make it difficult for them to achieve success in maths. Teachers who are able to gain insight into their students' mathematical thinking as well as their conceptual and procedural knowledge related to the particular mathematic concepts/skills, will be better equipped to provide effective maths instruction. By planning instruction that is based on a student's level of proficiency, their level of understanding and their mathematical thinking, teachers can better pinpoint what prerequisite concepts/skills a student needs to develop, what particular non-successful strategies they are using, and whether they have established conceptual and procedural understanding at the concrete, representational/semi-concrete, or abstract levels. Based on this mathematical learning picture, appropriate instructional goals and instructional practices can be developed for a student. Implementing Dynamic Maths Assessment 1. Target the particular maths concepts/skills you are interested in evaluating. 2. Develop an abstract level assessment of target concepts/skills that includes at least 5 to 10 items for each target maths concept/skill. 3. Evaluate whether students are at a mastery level (90-100% accuracy), instructional level (75%-89%), or frustration level (below 75%) using the abstract level assessment. 4. For concepts/skills that the student is not at a mastery level, conduct an error pattern analysis. 5. Based on your findings, conduct a flexible maths interview to get a picture of your student's mathematical thinking and understanding of selected maths concepts/skills (include use of concrete materials and/or drawings). 6. Use the information gained to: Select appropriate concepts/skills for instruction, including any prerequisite concepts/skills (e.g., place value). Determine what level of understanding instruction should first incorporate (e.g., concrete, representational/semi-concrete, abstract). Teach conceptual understanding and procedural understanding.