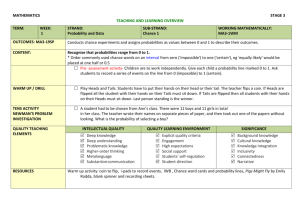
7.SP.5 Estimating Probability on Number Line (Lesson Plan)

Estimating Probability using a Number Line (7.SP.5)
Statistics and Probability Domain:
Big Idea (Cluster):
Investigate chance processes and develop, use, and evaluate probability models
Common Core Standards:
7.SP.5 Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event.
Mathematical Practice(s):
MP 1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
MP 2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively
MP 3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
MP 7: Look for and make sure of structure
Content Objectives:
Students will be able to understand the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1
Students will be able to explain the probability of an event as likely, unlikely, or equally likely based on event occurring
Students will be able to express the likelihood of an event occurring as a number between 0 and 1
Students will be able to describe values closer to 1 as having a greater likelihood of occurring and values closer to 0 as unlikely
Vocabulary:
Chance
Equally Likely
Event
Likelihood
Likely
Outcome
Probability
Unlikely
Language Objectives:
Talk with your group about what each card means
Talk with your group about where each card might go along the number line between 0 and 1
Write a number to describe unlikely, equally likely, and likely
Prior Knowledge: Concepts students need to know
In Grade 7, students write the same value represented as a fraction, decimal or percent.
Beginning the 2014-2015 school year, Grade 7 will be the only K-8 grade level where probability is taught. Deep understanding will need to be the focus of instruction.
1
Edited 3/10/13
Estimating Probability using a Number Line (7.SP.5)
Questions to Develop Mathematical Thinking:
What are the possible outcomes for the event in this situation?
How do the outcomes help you identify probability?
How should a spinner look if all outcomes are equally likely?
What is an example of an equal chance on a number cube?
What does it mean for the probability of
is close to 0, ½, or 1?
Common Misconceptions/Challenges :
Challenge: Students often struggle when converting forms of probability from fractions to percent and vice versa.
Strategy: To help students with the discussion of probability, don’t allow the conversions to detract from the meaning of the probability model. By having students use technology such as a calculator, the focus is on the interpretation of the probability model.
Challenge: Students may also attempt to give a probability as a number greater than one rather than representing the probability as a number between zero and one.
Strategy: Check for student understanding of how percentage can be used to represent the number of times an outcome would likely occur if an event took place 100 times. Also, revisit prior connections of one whole equal to 100% of the outcomes.
ASSESSMENT:
Observe student work and listen to student discussions for:
Explanations of vocabulary or probability scenario card as closer to 0, ½ or 1
Descriptions of the likelihood of the probability scenario or vocabulary card
Students making sense of similar vocabulary words such as “unlikely,” “small chance,” and “hardly ever”
Strategies to decide the placement of the card from 0 to 1
You might use problem F as a formative assessment. Students should identify that likely is a chance of an event occurring that is closer to 1, equally likely is a ½ chance, and unlikely is a chance closer to 0.
MATERIALS:
One set of vocabulary cards per group
Masking tape strip per group
Scissors
Marker
2
Edited 3/10/13
Estimating Probability using a Number Line (7.SP.5)
Launch: (5-10 minutes)
Have the students work on the warm-up question with their group. Students should justify their reasoning with numbers and words. While students are working on the launch, listen for understanding of
“likelihood” and prior knowledge of accurate placement of values on a number line.
When students finish the warm-up, ask students what is meant by “likelihood.” As of 2015-2016, this will likely be the first time students use this vocabulary in a math class. Students should understand that likelihood is the chance an event will occur. In addition, have students identify key words in the statement that might help identify the likelihood of the event occurring. For example, “it will rain today” versus “it will rain today at 3pm.” With a more specific description, the likelihood might actually increase or decrease based on the additional description. When students begin the task today, they will have to pay attention to the words and probability models that relate to benchmark fractions and their numerical conversions.
Possible solution :
A.
Since the chance of rain today is 80%, it is very likely it will rain during the day. There is a really
B.
good chance of rain since the percent is close to 100%.
0 Chance of rain 1
Explore: (20 minutes)
Hand out the task and have students read task in their groups. Have students share out to the class or group student actions the teacher and students should see and hear during the task. For example, we should see all students cutting the probability cards, leaning in to work together, and placing the cards on, above, or below the number line between 0 and 1. We should hear all students discussing each vocabulary or probability card, explaining their reasoning, and asking questions of each other when they disagree on the placement of a card.
When I observe students :
Look at student work for estimation of card placement based on the meaning of the card and its approximate value on the number line (MP 6)
Listen for student disagreement around placement of cards as closer to 0, ½ or 1 (MP 2 and MP 3)
When students disagree, encourage students to ask clarifying questions of each other in order to come to a consensus. Encourage students to use mathematical or real-world evidence to reason through the card being closer to 0, ½, or 1.
Listen for students making sense of similar words or phrases such as “unlikely,” “small chance,” and “hardly ever” (MP 6)
When students struggle to make sense of the vocabulary words, ask students to look up the word, use it in a sentence, or make use of the word in a real-world scenario to determine if they all have the same meaning or if one word is closer to zero than another.
Listen and read student responses for strategies to decide the placement of card from 0 to 1 (MP 1)
Listen for students describing likelihood of events and using probability related vocabulary (MP 1 and MP 6)
3
Edited 3/10/13
Estimating Probability using a Number Line (7.SP.5)
Questions to Develop Mathematical Thinking as you observe:
What are the possible outcomes for the event in this situation?
How do the outcomes help you estimate probability?
How are the numbers zero, half, and one used to classify probability events?
How should a spinner look if all outcomes are equally likely?
What is an example of an equal chance on a number cube?
What does it mean for the probability of is close to 0, ½, or 1?
Summarize: (10 minutes)
Have students complete a gallery walk around the room to look for similarities and differences between each other’s placement of the cards between 0 and 1. Have students take note on where groups placed cards such as, “hardly ever,” “almost always,” “you will watch TV sometime today,” and cards that are less obvious to place between 0 and 1. Did the students place them in similar positions along the number line? Also, use the student disagreements from Problem D to help summarize with the class how to make decisions about probability estimations.
Ask the students:
How did your group determine accuracy of the card placement?
What were the strategies used by your group when placing a card from 0 to 1 along the number line?
Have students share out their numerical descriptions for likely, equally likely, and unlikely. Students should identify that likely is a chance closer to 1, equally likely is a ½ chance, and unlikely is a chance closer to 0. Emphasize that very few events have a probability of 0 or 1. This would also be an opportunity to introduce outcomes for a probability model and how outcomes are used to identify an event’s likelihood.
Solutions:
C.
See sample at end of solutions.
D.
Have groups share out strategies observed during the task. One strategy students might share is placing the numerical values cards based on their understanding of benchmark fractions or conversions. A second strategy for students might be writing out the possible outcomes that could occur for a probability scenario. Another strategy might be using the words that describe probability in a sentence to better understand the chance being closer to 0, ½, or 1.
E.
Have groups share out the cards that were challenging to place and the evidence they used to come to an agreement.
4
Edited 3/10/13
Estimating Probability using a Number Line (7.SP.5)
F.
Students should identify that likely is a chance closer to 1, equally likely is a ½ chance, and unlikely is a chance closer to 0.
Feedback for lesson improvement:
Edited 3/10/13
5