Training Risk Management Methodology no 2
advertisement

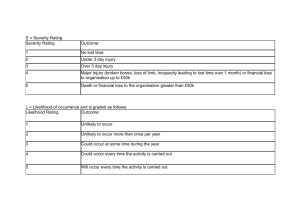
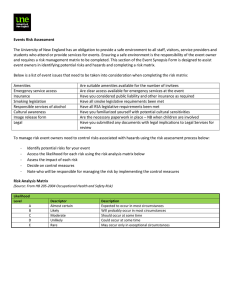
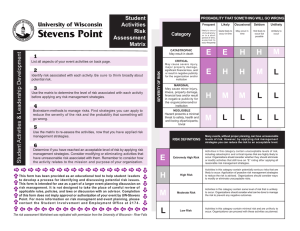
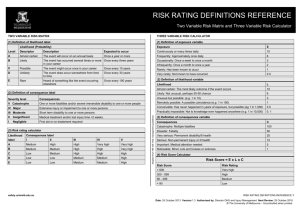
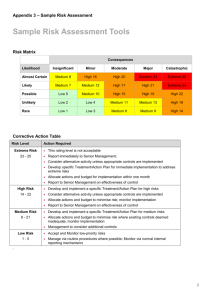
TRAINING RISK MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGY RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS Risk Assessment - Analysis - Categorize - Prioritise Risk Response Risk Identification - Handling/action Plan Communication Continuous monitoring & Reporting RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK Risk identification Risk classification Risk assessment Risk analysis Risk prioritization Risk management Risk handling Risk reporting Risk control Risk monitoring Fraud management STRATEGIC GOALS - Provision of Strategic leadership and creation of social compact for better health Increase life expectancy Decreasing Maternal and Child Mortality Combating HIV & AIDS and decreasing the burden of decease from TB Strengthening Health Systems effectiveness o Re-engineering the Primary Health Care system o Improving Patient Care and Satisfaction o Accreditation of Health Establishments for compliance o Availability of the improved health Infrastructure o Improved Human Resources for health o Strengthening Financial Management through M & E o Improve Health Care Financial through implementation of NHI o Strengthening health Information Systems RISK IDENTIFICATION PROCESS Each area / function is assessed and identified from micro structure of the Department The activities / processes that occur within each area / function The risks are identified The risks are categorized RISK CATEGORIES ORGANIZATIONAL RISK RESOURCE RISK COMPLIANCE RISK Quality Care & Patient Safety Human Resources & Staff Relations Environment Health & Safety Corporate Governance Financial Legal & Regulatory Operations & Organizational Support Information, Systems & Technology Policies Reputation & Public Image Physical Assets Inventories Standards Fraud & Corruption RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX Impact Likelihood Extreme (5) None (1) Low risk (5) Minor (2) Medium risk (10) Moderate (3) High risk (15) Major (4) High risk (20) Likely (4) Low risk (4) Medium risk (8) High risk (16) High risk (20) Possible (3) Low risk (3) Low risk (6) Medium risk (12) Medium risk (9) Medium risk (12) High Risk (15) Unlikely (2) Low risk (2) Low risk (4) Low risk (6) Medium risk (8) Medium risk (10) Rare (1) Low risk (1) Low risk (2) Low risk (3) Low risk (4) Low risk (5) Certainly (5) High risk (25) RISK RATING IMPACT Rating Assessment Definition 1 None 2 Minor 3 Moderate Negative outcome/ opportunity likely to have relatively moderate impact on ability to meet objectives 4 Major Negative outcome/ opportunity likely to have relatively substantial impact on ability to meet objectives 5 Extreme Negative outcome/ opportunity likely to have negligible impact on ability to meet objectives Negative outcome/ opportunity likely to have relatively low impact on ability to meet objectives Negative outcome/ opportunity likely to have critical importance on ability to meet objectives LIKELIHOOD Rating Assessment 1 Rare 2 Unlikely 3 Possible 4 Likely 5 Certainly Definition Risk is conceivable but only likely to occur in extreme circumstances Risk occurs infrequently and is unlikely to occur in the next 3 years Risk has an above average chance of occurring at least once in the next 3 years Risk could easily occur, and is likely to occur at least once in the next 12 months Risk is already occurring, or is likely to occur more than once in the next 12 months CURRENT CONTROLS EFFECTIVENESS CATEGORY CATEGORY DEFINITION FACTOR Very good Risk exposure is effectively controlled and managed 20% Good Majority of risk exposure is effectively controlled and managed 40% Satisfactory There is room for some improvement 65% Weak Some of the risk exposure appears to be controlled, but there are major deficiencies 80% Unsatisfactory Control measures are ineffective 90% RATING OF RISKS Risks were rated according to likelihood and impact : Rate risks according to impact and likelihood in absolute terms (inherent risk) i.e. without taking controls into consideration Rate the effectiveness and adequacy of controls that are currently in place Rate the risks according to impact and likelihood giving consideration to the effectiveness and adequacy of the controls (residual risk) RISK TOLERANCE LEVELS RISK LEVEL ACTION AND LEVEL OF INVOLVEMENT REQUIRED • Accept, but monitor • Manage by routine procedures within the program Low Risk Score 1-7: Areas require no further review or attention Medium Risk Score 8-14: Areas require • Unacceptable level of risk management attention within • Inform CEO/Senior Manager/ the next three months responsible manager • FS Health Senior Management involvement/ attention is essential to manage risks – provide appropriate report High Risk Score 15-25: Areas require immediate management attention • Unacceptable level of risk • Inform CEO/Senior Management/ responsible committees • Immediate action required RISK APPETITE LEVELS Risk appetite levels were set at risk scores 1-7. Areas assessed with risk scores of 1 – 7 require no further review or attention and were therefore acceptable THE RISK OWNER • Risk owners nominated should assume responsibility for developing effective risk response plans • The risk Owner should be senior staff member or manager • He/she should have sufficient technical knowledge about the risk and/or risk area for which a response is required • The risk owner may delegate responsibility (but not accountability) to his/her direct reports for detailed plan development and implementation