Late Permian to Late Jurassic "microproblematica" of Saudi Arabia

Late Permian to Late Jurassic "microproblematica" of Saudi Arabia: Possible
palaeobiological assignments and roles in the palaeoenviromental reconstructions
By: Hughes, GW (Hughes, Geraint Wyn) [ 1 ]
GEOARABIA
Volume: 18
Issue: 1
Pages: 57-92
Published: 2013
View Journal Information
Abstract
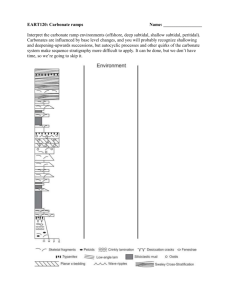
Palaeoenvironmental interpretation of Permian and Jurassic intertidal to very shallowmarine carbonates is difficult where typical shallow-marine microfossils are either absent or sparse. A collection of microfossils originally considered as "microproblematica" because of their uncertain biological affinities are, however, often present. These include species of Aeolisaccus, Gakhumella, Prethocoprolithus, Thaumatoporella, Favreina and
Terebella. Observations of their vertical distribution and relationship with carbonate fabrics reveal their environmental preferences, and these contribute to palaeoenvironmental interpretation within a spectrum of very shallow-marine settings that previously precluded refinement. The recognition of high-frequency depositional cycles and definition of cryptic reservoir layering in such shallow to marginal-marine carbonates is now facilitated by the use of these microfossils from the Khuff, Hanifa,
Jubaila, Arab and Hith formations.
Aeolisaccus dunningtoni is interpreted as either a fossilised cyanobacterial tube or possible foraminifera of Early Permian to Late Jurassic age. It is well represented within mudstones, wackestones and packstones of supratidal flats to very shallow intertidal palaeoenvironments with occasional freshwater influence. The microbialitic Gakhumella cf. huberi is locally present in these Upper Jurassic intertidal to very shallow-marine bioconstructions. Prethocoprolithus centripetalus is a faecal ribbon, considered to be of mollusk origin, within shallow subtidal grainstones and packstones. Thaumatoporella parvovesiculifera is considered a green alga that is typically found encrusting biocomponent fragments. It ranges from the Middle Triassic to Upper Cretaceous and is extensively present in intertidal, possibly hypersaline to shallow-marine, normal salinity lagoon grainstones and mud-lean packstones. Certain types of the distinctively canaliculate, microcoprolitic decapod crustacean faecal pellets, of the genus Favreina, are diagnostic of
Late Jurassic intertidal to shallow subtidal conditions found within packstones. Terebella lapilloides is an agglutinated polychaete tube, typical of Upper Jurassic intertidal to shallow-marine packstones.
Keywords
KeyWords Plus: CRUSTACEAN MICROCOPROLITES ; FECAL PELLETS ; ALGAE ;
CARBONATES ; MIDDLE ; ORGANISMS
Author Information
Addresses:
[ 1 ] King Fahd Univ Petr & Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia
Organization-Enhanced Name(s)
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
E-mail Addresses: wynapgwilym@gmail.com
Document Information
Document Type:Article
Language:English
Accession Number: WOS:000314741400003
ISSN: 1025-6059