Variability in microbial community composition and function between
advertisement

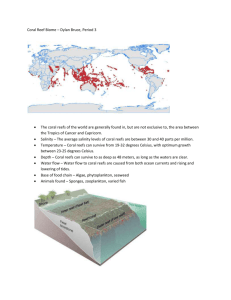
Variability in microbial community composition and function between different niches within a coral reef Jessica Tout1*, Thomas C. Jeffries 1, Nicole S. Webster2, Roman Stocker 3, Peter J. Ralph1, Justin R. Seymour1 1 Plant Functional Biology & Climate Change Cluster, University of Technology, Sydney, NSW, Australia. 2 Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, Qld, Australia. 3 Ralph M. Parsons Laboratory, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge MA USA. * Jessica.tout@student.uts.edu.au +61 4 31 499 465 Online Resource Table 1 PRIMER table showing SIMPER analysis of the top seven Genera between coral (lagoon-coral and reef crest-coral) and non-coral (open water and sandy substrate) metagenomes with an average dissimilarity of 9.73. Oligotrophic genera such as Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus were discriminating genera of the non-coral metagenomes as they had a higher average abundance compared to the coral metagenomes and overall contributed to a cumulative 5.7% of dissimilarity between the metagenomes. Copiotrophic genera such as Alteromonas, Mycobacterium and Vibrio were shown to be discriminating genera in the coral metagenomes as they had a higher average abundance compared to the non-coral metagenome and contributed up to 3.6% of the dissimilarity between metagenomes. Groups Coral (reef crest & lagoon) Non coral (sandy substrate & open water) Average abundance Average abundance Average dissimilarity Dissimilarity/SD Contribution % Cumulative % Synechococcus 1.87 2.76 0.32 1.34 3.33 3.33 Prochlorococcus 1.49 2.12 0.23 1.42 2.32 5.65 Alteromonas 0.88 0.46 0.15 0.95 1.58 7.23 T4-like phages 1.65 1.34 0.11 2.38 1.17 8.40 Ciona (sea squirt) 0.00 0.30 0.11 125.97 1.10 9.50 Mycobacterium 0.75 0.53 0.10 1.41 1.02 10.52 Vibrio 1.51 1.24 0.10 1.27 0.99 11.52 Genera