Exceptions & Deviations
advertisement

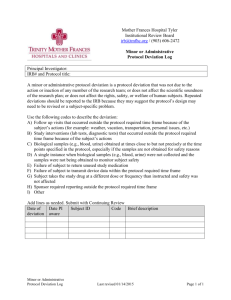
Exceptions & Deviations Purpose The purpose of this policy is to outline the procedure for reporting and reviewing exceptions and deviations. Defined Terms Deviation: Any change/alteration to the CRC IRB-approved protocol without prospective IRB approval. Major Deviation: Any change/alteration that has the potential to: 1) adversely affect the rights, welfare or safety of the subjects, 2) adversely affect the integrity of the research data, or 3) affect the subject’s willingness to participate. Minor Deviation: Any change/alteration that has NOT or does NOT have the potential to: 1) adversely affect the rights, welfare or safety of the subjects, 2) adversely affect the integrity of the research data, or 3) affect the subject’s willingness to participate. Exception: A one time, intentional change/alteration to the IRB-approved protocol that is approved by the IRB prior to implementation. Policy Federal regulations require that the IRB reviews all changes to an approved research study and ensures that these changes are not initiated without prior IRB review and approval except when necessary to eliminate immediate hazards to the subject. When an investigator anticipates a one time change/alteration to the IRB-approved protocol, a protocol exception should be submitted to the IRB for review and approval prior to implementation. Any changes/alterations that are noted after they occur are considered to be deviations. Deviations can be categorized as either major or minor. Major deviations should be reported to the IRB within 5 working days. Minor deviations should be reported to the IRB within 20 working days. The investigator is responsible for determining if the deviation is major or minor. The IRB will make a determination for all major deviations if the event constitutes serious and/or continuing non-compliance. Major Deviation Examples (this list is considered to be guidance and is not all-inclusive): Failure to obtain informed consent Obtaining informed consent after study procedures are initiated Performing study procedures not approved by the IRB Enrolling a prisoner into the study if the study is not approved to enroll prisoners Failure to report serious adverse events and unanticipated problems to the IRB, Sponsor, and other agencies as applicable Failure to follow the safety monitoring plan Enrollment of a subject who did not meet the inclusion/exclusion criteria Assent not obtained when required by the IRB Verbal consent obtained when IRB requires written consent Failure to perform a required study procedure that may affect subject safety or data integrity Minor Deviation Examples* (this list is considered to be guidance and is not all-inclusive): Over-enrollment Use of an expired consent form that includes all the required information and elements of informed consent Study visits/procedures that are either omitted, conducted outside of the visit window or in a different order than specified in the protocol that do NOT affect or have the potential to affect subject safety or data integrity Failure to submit continuing review to the IRB before study expiration Inappropriate documentation of informed consent (e.g. missing signatures, missing dates, copy not given to the subject) *Similar minor violations that occur frequently may be considered to be a major violation Procedures Submission of Deviation or Exception: 1. The Principal Investigator is responsible for submitting the deviation/exception using the Deviation/Exception Form. Major deviations should be reported within 5 working days upon discovery. Minor deviations should be reported within 20 working days upon discovery. 2. The Principal Investigator must submit all deviations/exceptions to the Sponsor and other applicable agencies as required. Screening of Submissions: 1. The Deviation/Exception is received by the IRB Coordinator and screened for completeness. If information is missing, the IRB Coordinator will request the missing information from the Principal Investigator. Determining Review Type (Expedited vs. Full Board): 1. The IRB Coordinator forwards the Deviation/Exception form to the IRB Director for review. The IRB Director confirms the completeness and accuracy of the form and then forwards to the IRB Chair or Vice-Chair for review. 2. The IRB Chair/Vice-Chair and IRB Director makes a determination whether the deviation/exception is major or minor and whether to review the event using full or expedited review procedures. 3. If the deviation/exception is determined to be minor, the IRB Chair and IRB Director conducts the review using expedited procedures. 4. Minor administrative deviations including, but not limited to, over-enrollment, lapsed protocol, etc. may be reviewed by the IRB Director. 5. If the deviation/exception is determined to be major, it will be referred to the full board for review. 6. If the IRB Chair/Vice-Chair and IRB Director are unable to determine if the event is major or minor, it will be referred to the full board for review. 7. If additional expertise is needed, the IRB Director will contact the appropriate IRB member for consultation. Expedited Review Procedure for Minor Deviations/Exceptions: 1. If the Deviation/Exception is determined to be minor, the IRB Chair/Vice-Chair will review the event using expedited procedures. The review will be documented by the use of the appropriate reviewer checklist. 2. The IRB Chair/Vice-Chair will determine the appropriate corrective action plan. 3. The Principal Investigator will be notified of the determination and corrective action plan via letter. 4. Minor administrative deviations will be reviewed by the IRB Director. 5. All deviations/exceptions will be reported to the full board at the next convened meeting. Full Board Review Procedure for Major Deviations/Exceptions: 1. If the Deviation/Exception is determined to be major, the event will be reviewed by the full board. 2. The IRB Chair/Vice-Chair and Director will assign the event to an IRB member(s) for review. The review will be documented by the use of the appropriate reviewer checklist. 3. The assigned reviewer will present the event at the full board. 4. The full board will review the event and determine the appropriate corrective action. Corrective actions may include: o Education o Modifications to the protocol o Notification of current and/or past subjects o More frequent IRB review o Additional monitoring o Prohibit use of study data o Suspension o Termination 5. For all major deviations, the IRB will determine if the event meets the definition of serious and/or continuing non-compliance. 6. If the event meets the definition of serious and/or continuing non-compliance it will be processed as outlined in the “Noncompliance Policy” and “Reporting Policy.” 7. The Principal Investigator will be notified of the determination and correction action plan via letter. Title Author Effective Date Last Review/Update Date Revision # Approved Exceptions and Deviations Cynthia Monahan 10/01/2012 09/19/2012 Cynthia Monahan, IRB Director Ara Tahmassian, PhD, Associate Vice President-Research Compliance