plate boundaries

Monday
: Students will take notes describing the Earth Layers
FF:
R OAD SALT , THE MINERAL HALITE , IS SOMETIMES USED TO MELT SNOW AND ICE .
A SCIENTIST SET UP AN EXPERIMENT TO
TEST HOW ROAD SALT AFFECTS THE GROWTH OF NEARBY GRASS .
W HAT IS THE DEPENDENT VARIABLE ?
A .
THE AMOUNT OF SALT USED
B .
THE GROWTH OF THE GRASS
C .
THE AREA OF GRASS TREATED WITH SALT
D .
THE DURATION OF THE EXPERIMENT
EQ: H OW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THE MAIN THREE LAYERS OF E ARTH ?
Earth Layer Notes:
8-3.1: Summarize the three layers of Earth – crust, mantle, and core – on the basis of relative position, density, and composition.
• The Earth is made up of 3 main layers: __________________________________________________________
• The Core is broken down into 2 sections: ________________________________________________________
• The core of the Earth is like a _________________ of very ______________________________________.
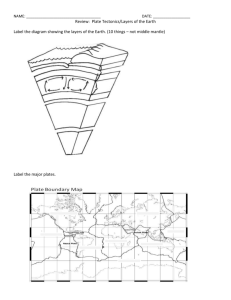
Label the Following Diagram
A
LTHOUGH THE
E
ARTH HAS
3 M
AIN LAYERS
,
IT INLCUDES OTHER LAYERS AS WELL
.
T
HE
E
ARTH HAS
_______
LAYERS OVERALL
.
L
IST THE
6
LAYERS IN ORDER
:
E
ARTH
L
AYERS
D
ESCRIPTION
C
HART
: S
TUDENTS
S
HOULD COMPLETE THE CHART
Layer
Crust
Location/Relative
Position
Composition or State of
Matter
Important Facts
Lithosphere
The layer we Live on
2 types of crust:
Continental Crust (contains
_____________________ rock and is the thickest crust) and
Oceanic (contains
______________________ rock and is the thinnest crust but is the most dense and the youngest because it’s being recycled through subduction.
Composed of ________________ plates or
_____________________plates
The plates floats on top of the
_______________________
The
____________________________ plates moves or floats on top of the asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
Mantle The mantle is located between the asthenosphere and the outer core.
Outer Core
The rocks in the mantle flows because of
___________________________.
Convection currents in the mantle moves the
____________________ layer that moves the
____________________plates
Inner Core
Between the
Mantle and Inner
Core
Density
Dense
Dense
Gets denser as you move down from the upper mantle to the lower mantle
Denser than the mantle
Thickness
Thin
Thin
Thick
Thick
FF:
W HY IS THE INNER CORE A SOLID AND NOT A LIQUID ?
EQ: H OW WOULD YOU EXPLAIN INDEPENDENT AND DEPENDENT VARIABLE IN YOUR OWN WORDS ?
Tuesday: Continuation of Earth Layers: Students will Create an Earth Layer Foldable. Students should use this mock foldable to be a guide for their actual foldable.
OCEAN WATER/ LIGHT BLUE
CONTINENTAL CRUST/LIGHT BROWN ------OCEANIC CRUST (2) DARK BROWN
LITHOSPHERE/BLACK (YOU WILL HAVE TO CREATE YOUR OWN LITHOSPHERE AREA
ASTHENOSPHERE (UPPER MANTLE) / LIGHT ORANGE
MANTLE/ORANGE (COLOR THE MANTLE AND THE LOWER MANTLE THE SAME COLOR)
(MAKE SURE YOU LABEL THE CONVECTION CURRENT SYMBOLS)
OUTER CORE/ LIGHT RED OR PINK
INNER CORE/ RED
NOTE: MAKE SURE YOU USE YOUR EARTH LAYER DESCRIPTION CHART TO FILL IN THE INFORMATION.
TUESDAY HOMEWORK:
DIRECTIONS: ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ON ANOTHER SHEET OF PAPER.
1.
WHAT ARE THE 3 MAIN EARTH LAYERS?
2.
WHICH EARTH LAYER IS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE MAGNETIC FIELD?
3.
WHICH EARTH LAYER IS LIES BETWEEN THE CRUST AND THE UPPER MANTEL?
4.
WHICH LAYER IS THE ONLY LIQUID LAYER?
5.
WHY IS THE INNER CORE A SOLID AND NOT A LIQUID?
6.
WHAT ALLOWS THE SOFT ROCKS TO FLOW IN THE MANTLE?
7.
WHAT IS THE UPPER MANTLE CALLED?
8.
WHICH LAYER IS THE LITHOSPHERIC OR TECTONIC PLATES FOUND?
9.
WHICH LAYER IS THE MOST DENSE LAYER?
10.
WHICH LAYER IS THE THINNEST AND WHICH LAYER IS THE THICKEST LAYER?
11.
WHICH LAYER CONTAINS THE MOST MASS?
12.
WHAT IS THE LAYER WE LIVE ON?
13.
THE CORE IS KNOWN AS WHAT?
14.
WHAT 3 LAYERS ARE TRUE SOLIDS AND WHICH 3 LAYERS ARE NOT TRUE SOLIDS?
15.
THE LITHOSPHERIC OR TECTONIC PLATES FLOATS ON TOP OF WHICH LAYER?
16-20. CREATE A CHART LISTING THE 4 DIFFERENCES AMONG THE CONTINENTAL AND OCEANIC CRUST.
8-3.6
Explain how the theory of plate tectonics accounts for the motion of the lithospheric plates, the geologic activities at the plate boundaries, and the changes in landform areas over geologic time.
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
The theory of plate tectonics explains why and how large sections of Earth’s crust, called lithospheric plates, move. A hypothesis of continental drift was developed before the present theory of plate tectonics. It was based on ___________________________________________________________________________________.
This hypothesis later led to the theory of plate tectonics when evidence was found as to why the plates could move.
Plate tectonics explains how many _______________________________________________.
Changes in Landform areas over Geologic Time
•
__________________________________________ within the mantle have broken the layer below the crust into blocks, called plates, which slowly move around, colliding to build mountains or rifting/spliting apart to form new seafloor.
Except in the crust, the interior of the Earth _________________________ be studied by drilling holes to take samples. Instead, scientists map the interior by watching how ______________________________ from
_____________________ are bent, reflected, sped up, or delayed by the various layers.
The Earth’s crust is divided into _________________major plates, which are moved in various directions.
Plates move at very _____________________ rates – from about _________ to _________ centimeters per year;
At one time in geologic history the ____________________________ were ____________________together in one large landmass that was called __________________________.
As the plates continued to move and split apart , ______________________were formed, _____________________ collided and split apart until the Earth’s landmasses came to be in the positions they are now;
Evidence of these landmass collisions and splits comes from
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Landmass changes can occur at ______________________ (volcanoes) within ____________________ plates;
Earth’s landmasses will continue to move and change during the geologic time of the future.
Motion of the Lithospheric Plates
Plates float on the _____________________________ of the mantle.
_________________________________________ can cause the asthenosphere to flow slowly carrying with it the plates of the lithosphere .
This movement of plates changes the sizes, shapes, and positions of Earth’s ___________________ and
_________________.
“Plates” of lithosphere are moved around by the underlying hot mantle convection cells
Wednesday Homework: Define the following words in your glossary: crust, continental crust, oceanic crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, convection currents, outer core, inner core, tectonic plates, Pangaea, and the theory of plate tectonics.
THURSDAY: STUDENTS WILL COMPLETE THE PLATE BOUNDARIES DESCRIPTION CHART AND NOTES.
FF: THE ORDER OF THE LAYERS OF THE EARTH FROM THE THICKEST TO THINNEST IS _______.
EQ: HOW WOULD YOU EXPLAIN WHAT IS HAPPENING AT THE 3 TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARIES?
PLATE BOUNDARIES
WHAT ARE THE 3 TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARIES? _______________________________________________
WHAT ARE THE KEY WORDS FOR THE 3 TYPES OF BOUNDARIES?
BOUNDARY KEYWORD ARROWS
DIVERGENT
CONVERGENT
TRANSFORM
Divergent Boundary Convergent Boundary
2 Plates spread or move
______________
most located along
______________________
___________ (sea-floor spreading
or a line of
__________________on the bottom of the ocean)
_________________ forms because
____________ pushes up and hardens between separating plating
Continental Crust forms
____________ (on land)
Oceanic Crust Forms
____________ (in oceans)
Can cause
_______________Activity
2 Plates come together and _____________
activity depends upon the types of
________________________________
more dense ________________ plate slides under less dense
__________________________ plate or another
____________________ plate which is called the
___________________.
Has 3 types of collisions
Continental –Continental (CC): forms
________________________: two continental plates converge, both plates buckle and push up into mountain ranges
Continental-Oceanic (CO): Has a
___________________________ and can cause
_____________________ activity
Oceanic-Oceanic (OO) : Has a subduction zone and can cause volcanic activity and can also form
________________________
Subduction is a way of recycling the oceanic crust .
Eventually the subducting slab sinks down into the mantle to be recycled. It is for this reason that the oceanic crust is much younger than the continental crust which is not recycled.
Transform
Boundary
Where 2 Plates
______________
______________
_____________
crust is neither created nor destroyed
________________ occur frequently along this type of boundary
______________
______________