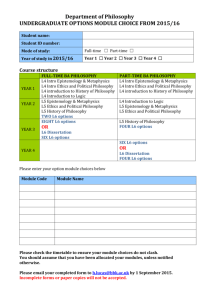
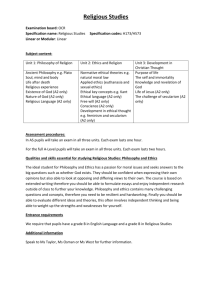
File
advertisement

Understating by Design Draft Grade: 12 Subject: Philosophy Topic: Foundations of Jewish Philosophy Stage 1 Desired Results Established Goal(s): Introduction to Philosophy (PHTU12) this course addresses the main areas of philosophy: metaphysics, logic, epistemology, and ethics. The students will learn critical-thinking skills, the main ideas expressed by philosophers from a variety of the worlds traditions, how to develop and explain their own philosophical ideas, and how to apply those ideas to contemporary social issues and experiences. Understanding(s): Students will know Contrast & Comparison of Foundations of Jewish Philosophy. Students will be able to identify and understand the Introduction to Philosophy both Jewish and secular perspectives. Essential Question(s) Demonstrate an understanding of some of the main questions in Foundations of Jewish Philosophy. Is there a difference between Jewish and secular philosophy? Are their drastic and similarities between both Jewish and secular philosophers? Students will: Summarize the main questions, concepts, and theories about the Introduction to Philosophy. Evaluate the strength and weakness of responses to some of the main 1 questions of Introduction to Philosophy defended by some major philosophers and schools of philosophy. Demonstrate the relevance the Introduction to Philosophical questions and theories to every day life. Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task(s) & Other Evidence: I will ask the students whether they found learning the Introduction to Philosophy to be difficult? I will ask them various questions on the fundamental foundations on the Introduction to Philosophy in all facets for their better understanding. I will assign Oral and/or written response to one of the essential Questions monthly. Stage 3 – Learning Plan Learning Activities: One of the many learning activities I would initiate is by using a smart board in order to engage the students so they can attain the learning goal. I will first show on the smart board each topic and explaining verbally in class then they will have to conduct research on their smart phones to further research on a basic understanding of the introduction to philosophy. Furthermore I would also ask students questions orally and ‘directly’ in class. This will ultimately check for understanding if they really understood the content. _________________________________________________________ 2 Grade: 12 Stage 1 Subject: Philosophy Topic: Metaphysics Desired Results Established Goal(s): Metaphysics (PHTU12) this course addresses the main areas that deals with the first principles of things, including abstract concepts such as being, knowing, substance, cause, identity, time, and space. Understanding(s): Students will be able to identify and understand the fundamentals of Metaphysics. Essential Question(s) Demonstrate an understanding of some of the main questions in metaphysics i.e. What are the ultimate constituents of reality? Does g-d exist? What is Being? What is the relation of mind to matter? What is the self? What is personal identity? Are human actions free? What is the meaning of life? Evaluate the positions of some of the major philosophers and schools of philosophy on some of the main metaphysical questions. Formulate their own clear and cogent responses to some of the fundamental questions of metaphysics Explain with references some classical texts how different metaphysical theories. 3 Demonstrate an understanding of the influence that some metaphysical ideas about topics such as causality, space and time, and the infinite have on other disciplines, such as physics and astronomy. Students will: Summarize the main questions, concepts, and theories about Metaphysics. Determine the relevance Metaphysics questions and theories to every day life. Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task(s) & Other Evidence: I will ask the students whether they found Metaphysics to be difficult? I will assign Oral and/or written response to one of the essential Questions monthly. Stage 3 – Learning Plan Learning Activities: I would assign a reading and oral response followed by a group presentation on metaphysics. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the responses to some questions of natural and social sciences defended by some of the major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. Demonstrate an understanding of the main questions in logic (e.g., What is a valid argument?). 4 Grade: 12 Subject: Philosophy Topic: Logic & the Philosophy of Science Stage 1 Desired Results Established Goal(s): Logic & the Philosophy of Science (PHTU12) this section addresses the main areas of philosophy, which is concerned with the foundations, methods, and implications of science. Understanding(s): Students will be able to identify and understand the fundamentals of Logic & the Philosophy of Science. Essential Question(s) Demonstrate an understating of some main questions in logic e.g. What is a valid argument? What is a logical misconception? Distinguish valid from invalid arguments? The students will demonstrate an understanding of some main questions in the philosophy of science. What differentiates science from non-science? What constitutes a law-like explanation? Students will: Summarize the main questions, concepts, and theories about Metaphysics. Determine the relevance Logic & the Philosophy of Science questions and theories to every day life. 5 The students will evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the responses given by some of the major philosophical theories of science. Such as: What is the relationship between theory and observation? The students will formulate and defend their own responses to some of the fundamental questions in the philosophy of science. What makes a scientific theory true? The students will explain how philosophical theories have influenced the development of the natural and social sciences. Identify the main questions in formal and informal logic, and in the philosophy of science. Apply logical and critical thinking skills in practical contexts, and in detecting logical fallacies Demonstrate an understanding of how philosophical questions apply to disciplines of natural and social sciences defended by some of the major philosophers and schools of philosophy and defend their own responses. Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task(s) & Other Evidence: I will ask the students whether they found Logic & the Philosophy of Science to be difficult? I will assign Oral and/or written response to one of the essential Questions monthly. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the responses to some questions of natural and social sciences defended by some of the major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. Stage 3 – Learning Plan 6 Learning Activities: I would assign a reading and oral response followed by a group presentation on Logic & the Philosophy of Science. _________________________________________________________ Grade: 12 Subject: Philosophy Topic: Epistemology Stage 1 Desired Results Established Goal(s): Epistemology (PHTU12) this course addresses the main areas of the theory of knowledge, especially with regard to its methods, validity, and scope. Understanding(s): Students will be able to identify and understand the fundamentals of Epistemology. Identify the main questions, concepts, and theories of epistemology. Demonstrate an understanding of the main philosophical questions of epistemology (e.g., What is human knowledge? Are there some things that we know with absolute certainty?). Essential Question(s) • The students will demonstrate an understanding of the main philosophical questions of epistemology. What is human knowledge? Can humans know what the world really is? 7 Are there some things that humans can never know? Are there some things that we know with absolute certainty? Students will: The students will identify the main questions, concepts and theories of epistemology. The students will evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of responses to some of the main questions of epistemology defended by some major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. The students will demonstrate the relevance of philosophical theories of epistemology to concrete problems in everyday life. The students will explain how different epistemological theories apply to subject areas such as psychology. The students will evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the responses given by some of the major philosophers and major schools of epistemology to some of the main epistemological questions. Is human knowledge based entirely on sensory perception? What counts as a justification in claiming to know something? The students will formulate their own ideas about some of the main questions of epistemology, and explain and defend those ideas in philosophical exchanges with others. The students will describe instances in which philosophical problems of knowledge occur in everyday contexts, and can be clarified and analysed using philosophical theories of epistemology. The students will explain how theories of knowledge are adopted and applied in subject areas such as psychology. 8 Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task(s) & Other Evidence: I will ask the students whether they found epistemology to be difficult? I will assign Oral and/or written response to one of the essential Questions monthly. Stage 3 – Learning Plan Learning Activities: I would assign a reading and oral response followed by a group presentation on epistemology. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the responses to some questions of natural and social sciences defended by some of the major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. Demonstrate an understanding of the main questions in logic (e.g., What is a valid argument?). _________________________________________________________ Grade: 12 Subject: Philosophy Topic: Ethics Stage 1 Desired Results Established Goal(s): Ethics (PHTU12) this course addresses the main areas of the branch of knowledge that deals with moral principles. Understanding(s): 9 Illustrate the relevance of philosophical theories of ethics to concrete moral problems in everyday life. Identify the main questions of ethics (e.g., What is integrity? Why be moral? What obligations do people have to one another?). Evaluate the responses given by some of the major philosophers (e.g., Maimonides, Kant) and major schools of ethics (e.g., utilitarianism) Essential Question(s) The students will demonstrate an understanding of the main questions, concepts, and theories of ethics. The students will evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of responses to ethical questions and moral problems defended by some major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. The students will illustrate the relevance of philosophical theories of ethics to concrete moral problems in everyday life. The students will demonstrate an understanding of how philosophical theories of ethics are implicit in other subjects. Students will: The students will identify the main questions of ethics. What are good and evil? What is the good life? What is virtue? Why be moral? What obligations do people have to one another? The students will evaluate the responses given by some of the major philosophers and major schools of ethics to some of the main ethical questions 10 Are moral values objective? On what grounds should the rightness and wrongness of actions be determined? The students will use critical and logical thinking skills to defend their own ideas about ethical issues and to anticipate counter-arguments to their ideas. The students will demonstrate how the moral problems and dilemmas that occur in everyday contexts can be effectively analysed using a variety of different philosophical theories. The students will describe how problems in ethics and the theories that address them may be illustrated in novels and drama, and in religious stories and parables. Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task(s) & Other Evidence: I will ask the students whether they found ethics to be difficult? I will assign Oral and/or written response to one of the essential Questions monthly. Stage 3 – Learning Plan Learning Activities: The following would be assigned as a reading and oral response followed by a group presentation on ethics. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the responses to some questions of natural and social sciences defended by some of the major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. Demonstrate an understanding of the main questions in logic (e.g., What is a valid argument?). The students will demonstrate an understanding of the main questions, concepts, and theories of ethics. 11 The students will evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of responses to ethical questions and moral problems defended by some major philosophers and schools of philosophy, and defend their own responses. The students will illustrate the relevance of philosophical theories of ethics to concrete moral problems in everyday life. The students will demonstrate an understanding of how philosophical theories of ethics are implicit in other subjects. 12