Volumetric Analysis Test
advertisement

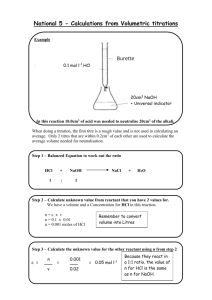
Unit 3 Chemistry Name:_______________ Volumetric Analysis Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For a substance to be suitable as a primary standard in a volumetric analysis, it should have: A a known formula with a low molar mass B a very low melting point C no tendency to absorb moisture from the air D no acid–base or redox properties. 2. In a volumetric analysis of vinegar to determine the concentration of ethanoic acid present, a pair of students obtained the following results: Initial burette reading (mL) 0.10 0.15 0.00 0.25 0.30 Final burette reading (mL) 22.70 22.60 22.50 22.73 22.60 The mean titre is: A 22.60 mL B 22.48 mL C 22.477 mL D 22.47 mL 3. Which one of the following substances is not suitable for use as a primary standard in volumetric analysis? A Sulfuric acid B Potassium hydrogen phthalate C Oxalic acid D Anhydrous sodium carbonate 4. What term is used to describe a substance that, when exposed to air, absorbs so much water from the air that it eventually forms a solution? A Hydrated B Efflorescent C Hygroscopic D Deliquescent 5. The uncertainty of the volume of a solution delivered by a 20.00 mL pipette would be: A 2 mL B 0.2 mL C 0.02 mL D 0.002 mL 6. To standardise a supplied sodium hydroxide solution, a pair of students placed the base in a burette and titrated it against a standard potassium hydrogen phthalate solution, KH(C8H4O4), which was previously prepared using a 250-mL volumetric flask. Which items of equipment should the students have rinsed out with several amounts of de-ionised water just before use, and with no other chemicals, during this procedure? A The volumetric flask and reaction flask only B The pipette and burette only C The reaction flask only D All of the equipment 7. One reason that sodium hydroxide is not suitable as a primary standard is that: A it is highly soluble in water. B it is deliquescent. C it is dangerous to handle. D its solution is colourless. 8. A sample of commercial brick cleaner was analysed against a 20.00 mL aliquot of a solution of the primary standard anhydrous sodium carbonate, of concentration 0.05342 mol L-1. The equation for the titration reaction was: 2HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) The pH of the reaction mixture at the equivalence point should be: A exactly 7, since this is a neutralisation reaction. B less than 7, since some of the CO2 will remain in solution. C greater than 7, since some of the CO2 will remain in solution. D less than 7, since the amount of acid reacting is twice that of the base. 9. Following is the pH curve obtained for a particular volumetric analysis. This curve shows that in all probability in this titration: A a strong acid was being added to a solution of a weak base. B a solution of a weak base was being added to a strong acid. C a weak acid was being added to a solution of a strong base. D a solution of a strong base was being added to a strong acid. 10. Following is the pH curve obtained for another particular volumetric analysis. Of the following list of acid-base indicators, which would be the most suitable indicator to use for this titration? A Alizarin yellow R, which changes colour over the pH range 10.1–12.0 B Bromothymol blue, which changes colour over the pH range 6.0–7.6 C Methyl red, which changes colour over the pH range 4.8–6.0 D Phenolphthalein, which changes colour over the pH range 8.2–10.0 11. To what volume of water must 5.0 mL of nitric acid of concentration 10 mol L-1 be added to produce a solution of pH zero? A 5.0 mL B 45.0 mL C 50.0 mL D 95.0 mL 12. A group of students was given the task of standardising solutions of ammonia (a weak base), sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide (strong bases), using hydrochloric acid (a strong acid). It was known that the concentration of each base was approximately 0.1 mol L-1. In each case the students pipetted 20.00 mL of the base into a reaction flask and then delivered the acid by burette. The concentration of the acid used was the same in each case. If the indicator used in each was chosen so that it only changed colour when the reaction was complete, which statement (about the volume of acid required) is CORRECT? A All three bases should require the same amount of acid. B NH3 should require less acid than NaOH or Ca(OH)2. C NH3 and NaOH should require about half the amount of acid as Ca(OH)2. D NH3 and NaOH should require about twice the amount of acid as Ca(OH)2. 13. To determine the concentration of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, in a sample of vinegar, a 10.00 mL aliquot of the vinegar was made up to 100.00 mL in a volumetric flask then titrated against 20.00 mL aliquots of sodium hydroxide solution of concentration 0.09950 mol L-1. The equation for the titration is: CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) If the mean titre was 19.45 mL, the concentration of ethanoic acid in the vinegar was: A 0.09676 mol L-1 B 0.1023 mol L-1 C 0.9676 mol L-1 D 1.023 mol L-1 14. The active ingredient in a certain toilet cleaner that claims to ‘remove lime scale and rust’ is hydrochloric acid of approximate concentration 3 mol L-1. To analyse this toilet cleaner, a quality control chemist first delivered a 10.00 mL aliquot of the toilet cleaner into a 250-mL volumetric flask, then made up the diluted solution. She then titrated a 20.00 mL aliquot of this diluted solution against standard sodium hydroxide solution of concentration 0.1044 mol L-1. The expected titre would be approximately: A 14.4 mL B 17.4 mL C 23.0 mL D 28.7 mL 15. An analyst was commissioned to determine the concentration of substance X present in a solution. He was provided with some data about X and as a result decided that a simple volumetric analysis would not yield a very accurate result. Which one of the following properties of X may have influenced this decision? A Weak reductant B Soluble in water C Highly volatile D Colourless 16. Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, C6H8O6, is classified as an antioxidant. To determine the percentage by mass of Vitamin C in a tablet, a student weighed one tablet into a conical flask and then crushed it in deionised water. The Vitamin C solution was then titrated against iodine solution of concentration 0.1620 mol L-1. The equation for the reaction is: C6H8O6(aq) + I2(aq) C6H6O6(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2I- (aq) Given the titre was 27.40 mL and the mass of the tablet was 1.335 g, what was the percentage of Vitamin C in the tablet? A 29.26 % B 58.52 % C 78.12 % D 84.39 % 17. An experimental value for the concentration of hydrochloric acid in a sample of brick cleaner was obtained by titrating a diluted solution of the brick cleaner against a standard solution of anhydrous sodium carbonate. This experimental value was found to be lower than that claimed by the manufacturer. Which one of the following explanations offered by different students could reasonably account for this difference? A Some HCl gas evaporated from solution during the analysis. B The brick cleaner may have absorbed carbon dioxide out of the air. C The Na2CO3 used contained some water of hydration. D The pipette was rinsed out with water instead of Na2CO3 solution. 18. The alcohol content of a certain low alcohol beer was determined using volumetric analysis. In this analysis, a 10.00-mL sample of the beer was pipetted into a 100-mL volumetric flask and the solution was made up to the mark. Then 20.00 mL aliquots of this solution were titrated against acidified potassium dichromate solution, K2Cr2O7 of concentration 0.0500 mol L-1. A mean titre of 16.35 mL was obtained. The equation for the analysis is: 2Cr2O72-(aq) + 3C2H5OH(aq) + 16H+(aq) 4Cr3+(aq) + 3CH3COOH(aq) + 11H2O(l) What was the molarity of the alcohol in the beer? A 0.0273 mol L-1 B 0.0613 mol L-1 C 0.273 mol L-1 D 0.613 mol L-1 19. Two pairs of VCE students were analysing the same sodium hydroxide solution by titrating 20.00 mL aliquots against the same standard solution of potassium hydrogen phthalate. The first pair obtained a mean titre of 21.45 mL while the second pair obtained a mean titre of 21.80 mL. Which of the following might explain the difference in the mean titres? A The first pair rinsed their burette with only water and not acid. B The second pair rinsed their burette with only water and not acid. C The NaOH used by the second pair had absorbed more CO2 out of the air. D The first pair blew the last drop of base out of their pipette. 20. An impure sample of anhydrous sodium carbonate was analysed as follows. Several 1.000 g samples of the impure mixture were weighed out into separate conical flasks and about 20 mL of distilled water was added to each. The mixtures were stirred and then 4 drops of an acid–base indicator were added to each flask. These were then standardised against hydrochloric acid of concentration 0.1542 mol L-1, according to the reaction: Na2CO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Three concordant results were obtained for the titres: 21.25 mL, 21.29 mL and 21.30 mL. The percentage purity of the sodium carbonate was: A 8.696% B 17.39% C 17.90% D 34.78%