Mesopotamia Unit Plan: Geography, Civilization, Empires
advertisement

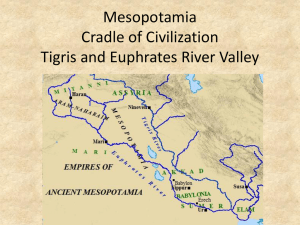
Mesopotamia The Ancient World By Megan Foster & Carolyn DiSalvatore The purpose of this unit plan is to introduce students to the civilizations of Mesopotamia. This will include the geography and how it effects human settlement and development; civilization and how artifacts can lead to conclusions about history of a civilization; and empires and how and why different accomplishments lead to the rise and fall of empires. Students will be introduced to the content through a variety of primary source analysis, both visual and written documents. Students will be asked to think critically about the information they are presented with. At the conclusion of the unit, student groups will create ABC books about Mesopotamia. It is assumed heading into this unit that students will be knowledgeable about emerging societies of people in the ancient world, as well as the themes of geography. This unit is designed to provide students with the framework for understanding the most essential aspects of Mesopotamia. Stage 1 Desired Results ESTABLISHED GOALS Transfer Goals Students will be able to independently use their learning to… History Frameworks: G 7.6 Identify the characteristics of civilizations. (H,G,E) The presence of geographic boundaries and political institutions An economy that produces food surpluses A concentration of a population in distinct areas or cities The existence of social classes Developed systems of religion, learning, art, and architecture A system of record keeping Identify polytheism as the religious belief of the people in Mesopotamian civilizations. (H) 7.7 On a historical map, locate the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers and identify Sumer, Babylon, and Assyria as successive civilizations and empires in this region, and explain why the region is sometimes called “the Fertile Crescent.” On a modern map of western Asia, identify the modern countries in the region (Iraq, Iran, and Turkey). (H, G, E) Understand how recurring patterns in history can inform judgments about current events and other issues. Understand how physical and human geography can inform responsible interactions with environment. Critically appraise historical and contemporary claims/decisions. T Meaning UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that… U U1…people must solve geographic challenges in their environment to live there successfully. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Q E1. Would city-states/civilizations have developed in Mesopotamia without agriculture and new agricultural techniques (irrigation, levees, dams, reservoirs)? E2. Why are these characteristics U2…a society is considered a civilization necessary for a society to be considered a when a complex set of characteristics exist civilization? Must all the characteristics be in the community. present in a society for it to be called a civilization? Can one be missing? U3…strong political and military forces will allow for the rise of empires, however, E3. Which achievement was the most important to the rise and success of empires? What is the most important 7.9 Describe how irrigation, metalsmithing, slavery, the domestication of animals, and inventions such as the wheel, the sail, and the plow contributed to the growth of Mesopotamian civilizations. (H,E) 7.10 Describe important Mesopotamian achievements. (H,C,E) Its system of writing (and its importance in the record keeping and tax collection) Monumental architecture (the ziggurat) Art (large relief sculptures, mosaics, and cylinder seals) 7.11 Describe who Hammurabi was and explain the basic principle of justice in Hammurabi’s Code (“an eye for an eye”). (H, C, E) ELA & Literacy Frameworks: problems within often lead to the fall of these empires. cause for the failure of empires? E4. Why has Mesopotamia changed from the cradle of civilization to a war torn country? How has farming, government, culture, writing, technology effected the civilization? Students will know… Acquisition K Students will be skilled at… K1. Key Terms: Mesopotamia, Tigris River, Euphrates River, Sumer, irrigation, levee, silt, city-state, complex, maintain, culture, civilization, social structure, technology, status, chariot, scribe, ziggurat, lyre , Standard of Ur, polytheism, arch, cuneiform, pictograph, empire, Akkadian Empire, Babylonian Empire, Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire, capital, tribute, stele, Hammurabi’s Code of Laws, economy, siege, strategy, aqueduct, basrelief, invader, unify S Map Skill: interpret maps to explain relationships between landforms, water features, climatic characteristics, and historical events. Critical Thinking: analyzing geographic problems ancient Mesopotamians and evaluating potential solutions. Primary Source Analysis: examine artifacts to discover the history of a civilization; write hypotheses and support opinions with detailed evidence. K2. Mesopotamia was located between Note Taking Skills: determine main idea W. 1. Write arguments to support claims with the Tigris and Euphrates River. Mesopotamians faced and solved a variety and supporting details in describing the clear reasons and relevant evidence. history of an empire. of geographic challenges as they developed into city-states. SL. 1. Engage effectively in a range of Compare and Contrast: identify the collaborative discussions with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts and issues, building on K3. Sumer had the seven characteristics of similarities and differences between each others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. a civilization present: stable food supply, empires success and failures. R. 1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. social structure, government, religion, culture, technology, and writing. Vocabulary: use content based vocabulary in order to communicate understanding of key concepts. K4. Mesopotamia had a variety of political, military and cultural achievements during the height of these empires: Akkadian Empire, Babylonian Empire, Assyrian Empire, and Neo-Babylonian Empire. Stage 2 – Evidence Evaluative Criteria Historically Accurate Well Crafted Revealing and informative Good Detail Mechanically sound Historically Accurate Well Crafted Revealing and informative Good Detail Mechanically sound Assessment Evidence CURRICULUM EMBEDED PERFOMANCE ASSESSMENT (PERFORMANCE TASKS) PT Small groups of students will create Mesopotamia ABC Booklets. Please see attached for directions and rubric. OTHER EVIDENCE: OE Create a map of a Sumerian city-state Analyze the Standard of Ur in an “I See it Means” Analysis and ranking of empires in “Empire Report Card” Chapter Tests Stage 3 – Learning Plan Summary of Key Learning Events and Instruction Lesson 1: Introduction and Preview to Mesopotamia- In this lesson, students will preview the geography of Mesopotamia and the major themes of the unit. Map: History Alive! Geography Challenge: Interactive Notebook pg 4-7 Vocabulary Preview: Mesopotamia Wordle Lesson 2: Geography & Development of Mesopotamia- In this lesson, students will analyze problems faced by early Sumerians and evaluate possible solutions. Critical Thinking: Analysis of four geography based problems in Mesopotamia and student created solutions (History Alive Chapter 4 lesson) Map Skill: Create a map of a Sumerian city-state that labels and details the “solutions” to geographic problems. Lesson 3: Characteristics of a Civilization- In this lesson, students will identify civilization and decide if Sumerian city-states qualify as a civilization. Vocabulary: Frayer Model- civilization, city-state Primary Source Analysis: Analysis of Sumerian artifacts to determine whether Sumerian city-states had the characteristics of a civilization. Visual Analysis: I See, It Means- Standard of Ur Lesson 4: Empires of Mesopotamia- In this lesson, students will identify empire and be able to describe and detail the four empires of Mesopotamia. Vocabulary: Frayer Model- empire Content/ Response Notes: identify the accomplishments(details) of the Akkadian Empire, Babylonian Empire, Assyrian Empire and NeoBabylonian Empire, accompanied by a summary of the empire (main idea). Lesson 5: Empires of Mesopotamia II- In this lesson, students will analyze and rank the accomplishments of the empires. Primary Source Analysis: Hammurabi’s Code Compare & Contrast: Rank the accomplishments of each empire using an Empire Report Card. Critical Thinking: Discussion of empires and what causes empires to rise and fall, also introduce the effects. Lesson 6: ABC of Mesopotamia- In this lesson, students will work in groups of four to write a children’s book on Mesopotamia in an ABC format. Mesopotamia Unit CEPA – ABC Mesopotamian Booklet Objective – Working as part of a group, students will create an A B C Booklet using facts about Mesopotamia. Each booklet will contain 26 facts (one per letter, per page) about various topics like geography, religion, technology, empires and achievements. Each group will consist of an Artistic Director, a Historian and Publisher. Artistic Director – Responsible for creating the visuals Historian – Responsible for the content (facts) Publisher – Presentation – Remember that you are all in this together you can and should be helping each other out. -This should be written for a younger audience. Make sure its easy to understand. - Certain letters may present a problem (q or x). Be creative and use complex language. Requirements ARTISTISTIC DIRECTOR (visuals) ___ Choice of relevant symbols, illustrations. ___ carefully/skillfully drawn, shows thought and effort. ___ colorful ___ used space effectively ___ Participation HISTORIAN (Content) ___ one fact for each letter. ___ accurate information ___ adequate explanation (2 sentences) ___ topic variety ___ Participation PUBLISHER (Ready for Print) ___ attractive Cover Page/Names/Title ___ pages are bound together/in correct order ___ all pages neat/presentable ___ Essential Question answered (on cover) ___ Participation Rubric 3: Ready for the museum 2: Ready for the Refrigerator 1: Ready for the Recycling Bin Presentation Neat Colorful Somewhat neat Some use of color Messy or sloppy No color Information Accurate Clear All important details included Attempts to be accurate Somewhat clear Some important details included Inaccurate information Not clear Missing important details Requirements All requirements included Most requirements included Many requirements missing Participation Active member of the group Always helped others, listened to group and used class time Somewhat active member of the group Sometimes helped others, tried to listen to other members, usually used class time Inactive member of the group Prevented other group members from completing their work, did not use time appropriately