Academic Vocabulary
advertisement
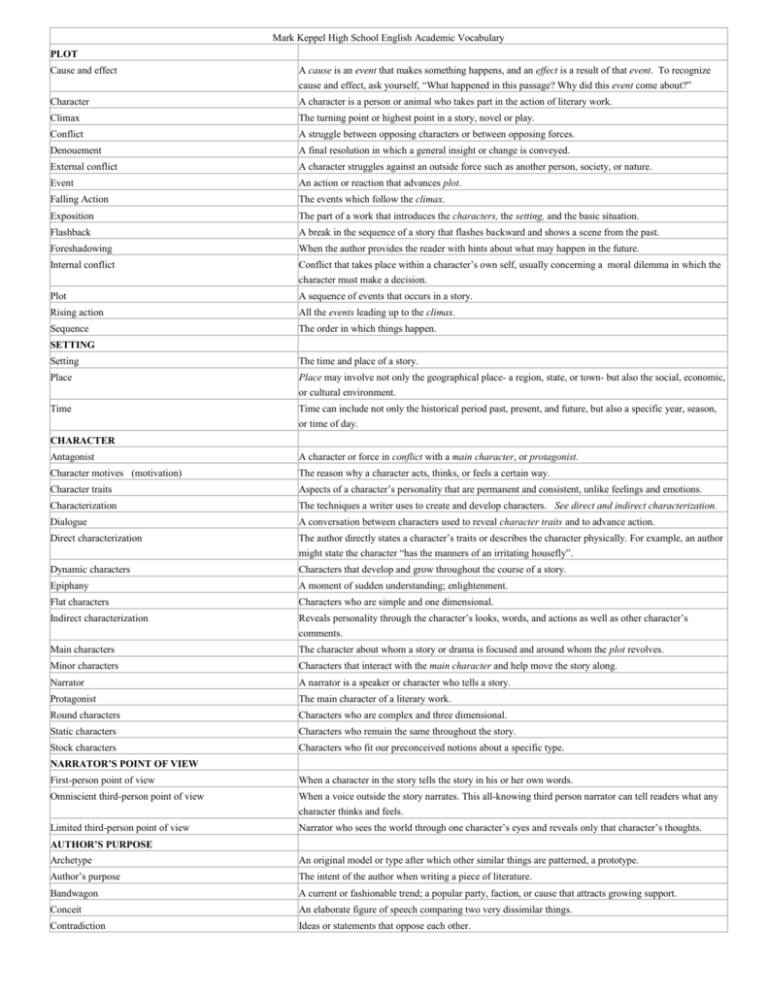
Mark Keppel High School English Academic Vocabulary PLOT Cause and effect A cause is an event that makes something happens, and an effect is a result of that event. To recognize cause and effect, ask yourself, “What happened in this passage? Why did this event come about?” Character A character is a person or animal who takes part in the action of literary work. Climax The turning point or highest point in a story, novel or play. Conflict A struggle between opposing characters or between opposing forces. Denouement A final resolution in which a general insight or change is conveyed. External conflict A character struggles against an outside force such as another person, society, or nature. Event An action or reaction that advances plot. Falling Action The events which follow the climax. Exposition The part of a work that introduces the characters, the setting, and the basic situation. Flashback A break in the sequence of a story that flashes backward and shows a scene from the past. Foreshadowing When the author provides the reader with hints about what may happen in the future. Internal conflict Conflict that takes place within a character’s own self, usually concerning a moral dilemma in which the character must make a decision. Plot A sequence of events that occurs in a story. Rising action All the events leading up to the climax. Sequence The order in which things happen. SETTING Setting The time and place of a story. Place Place may involve not only the geographical place- a region, state, or town- but also the social, economic, or cultural environment. Time Time can include not only the historical period past, present, and future, but also a specific year, season, or time of day. CHARACTER Antagonist A character or force in conflict with a main character, or protagonist. Character motives (motivation) The reason why a character acts, thinks, or feels a certain way. Character traits Aspects of a character’s personality that are permanent and consistent, unlike feelings and emotions. Characterization The techniques a writer uses to create and develop characters. See direct and indirect characterization. Dialogue A conversation between characters used to reveal character traits and to advance action. Direct characterization The author directly states a character’s traits or describes the character physically. For example, an author might state the character “has the manners of an irritating housefly”. Dynamic characters Characters that develop and grow throughout the course of a story. Epiphany A moment of sudden understanding; enlightenment. Flat characters Characters who are simple and one dimensional. Indirect characterization Reveals personality through the character’s looks, words, and actions as well as other character’s comments. Main characters The character about whom a story or drama is focused and around whom the plot revolves. Minor characters Characters that interact with the main character and help move the story along. Narrator A narrator is a speaker or character who tells a story. Protagonist The main character of a literary work. Round characters Characters who are complex and three dimensional. Static characters Characters who remain the same throughout the story. Stock characters Characters who fit our preconceived notions about a specific type. NARRATOR’S POINT OF VIEW First-person point of view When a character in the story tells the story in his or her own words. Omniscient third-person point of view When a voice outside the story narrates. This all-knowing third person narrator can tell readers what any character thinks and feels. Limited third-person point of view Narrator who sees the world through one character’s eyes and reveals only that character’s thoughts. AUTHOR’S PURPOSE Archetype An original model or type after which other similar things are patterned, a prototype. Author’s purpose The intent of the author when writing a piece of literature. Bandwagon A current or fashionable trend; a popular party, faction, or cause that attracts growing support. Conceit An elaborate figure of speech comparing two very dissimilar things. Contradiction Ideas or statements that oppose each other. Credible information/fact Information that is believable, reliable, and worthy of confidence. Entertain When the author’s purpose is to amuse. Express an opinion When the author’s purpose is to influence or convince. Generalization A broad, sweeping statement. Inform When the author’s purpose is to tell about something or give information. Intent Having the mind or will concentrated on something. Irony An intentional contrast between what is expected and what occurs. Parody A humorous imitation of another work or type of work. Persuade When the author’s purpose is to influence or convince. MOOD/TONE/THEME Descriptive words Words that express quality, kind, or condition. Details Small elements that collectively make up a work. Dialect The form of a language to create vivid word pictures that appeal to the senses. Imagery The use of descriptive language to create a vivid word pictures that appeal to the senses. Irony An intentional contrast between what is expected and what occurs. Mood The atmosphere or feeling the writer creates for the reader. Theme The controlling/main idea of a work of literature. Usually a general statement about life. Tone A writer’s attitude toward his or her subject. Word Choice Specific words an author uses to convey mood or tone. GENRE Allegory A story in which the characters represent general qualities, or symbolize abstract ideas or principles. Autobiography/ autobiographical narrative A narrative or story based on an event in the author’s life. Ballad A specific type of narrative poem based on the ancient custom of telling stories in songs; uses repetition, and elaborate language. Biography/ biographical narrative A narrative or story based on an event in a real person’s life. Comedy Literary works that end happily. Concrete poem A poem whose words are arranged on the page to make a shape that suggests the topic of the poem. Descriptive essay/writing A descriptive essay that seeks to convey an impression about a person, place, or object. Dramatic literature/ drama Literature that is acted out or performed; theater. Elegy A solemn and formal lyric poem about death. Epic A long narrative poem about the deeds of gods or heroes in war or travel. Epigram A brief statement in prose or verse. An essay may be written in epigrammatic style. Essay A short nonfiction work about a particular subject. Expository Essay An essay that gives information, discusses ideas, or explains a process. Fable A type of folktale that teaches a lesson. Functional document A document that fives how-to information. Haiku A short poem with a distinct structure that originated in Japan. Line 1 has 5 syllables; line 2 has 7 syllables; line 3 has 5 syllables. Journal/ diary A daily account of what has happened. Letter A written message from one person to another. Lyric poem Musical verse that expresses personal thoughts and feelings. Myth A fictional tale, originally with religious significance, that explains the actions of gods and heroes, the causes of natural phenomena, or both. Narrative essay A narrative essay tells a true story. Narrative poetry A narrative poem tells a true story. Nonfiction Writing that deals with real people and events. Novel An extended work of fiction that often has a complicated plot, many major and minor characters, a unifying theme, and several settings. Ode A single, unified strain of exalted verse with a single purpose and dealing with a single theme. Oral histories The stories and histories kept alive by the spoken word rather than the written word. Parable A short, simple story from which a moral or religious lesson can be drawn. Persuasive essay A persuasive essay tries to convince readers to do something or to accept the writer’s point of view. Response to literature Demonstrates understanding and insight into a work of literature. Satire Writing that ridicules or holds up to contempt the faults of individuals or groups. Sonnet A poem that follows a specified rhyme theme. All sonnets have 14 lines and are in iambic pentameter. Tragedy Literary works that end unhappily. Work place documents Documents that provide information to employees. LITERARY DEVICES Alliteration The repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words. Allusion A reference to a well-known person, place, event, literary work. or work of art. Analogy A comparison that points out a resemblance between two seemingly dissimilar things. Assonance The repetition of vowel sounds other than in rhyme. Consonance The repetition of final consonant sounds in stressed syllables containing dissimilar vowel sounds. Couplet Two successive rhyming lines. Connotation The implied or personal definition of a word. Example: That is a bad looking cat with those sweet chrome wheels. Denotation The dictionary definition of a word. Epithet An inscription written on a tomb of a burial place. Euphemism The use of a word or phrase that is less expressive or direct but considered less distasteful, less offensive. Figurative language Language that is not meant to be taken literally. Hyperbole Exaggeration for the sake of emphasis. Imagery The use of descriptive language to create vivid word pictures that appeal to the senses. Irony An intentional contrast between what is expected and what occurs. Literary devices Any one of a variety of tools a writer may use to achieve the tone or communicate the purpose or theme intended. Metaphor A comparison between basically dissimilar things that does not use the words as, like, than, or resembles. Metonymy A figure of speech that substitutes something closely related for the thing actually meant. Onomatopoeia The use of words that imitate sounds. Oxymoron A figure of speech that fuses two contradictory ideas. Paradox A statement that seems to be contradictory but that actually represents a truth. Parallelism Parallel structure- when a piece of writing has the same grammatical pattern. Parallel example: I enjoy skiing, boating, and hiking. Non-parallel example- I enjoy skiing, boating, and I like to hike. Personification Giving human qualities to inhuman things such as animals or objects. Red herring A distracter that draws attention away from the real issue. Repetition Using the same sounds, word, or phrase more than once. Rhetorical question A question not made to answer but to inspire thought- provoking discussion and analysis. Simile A comparison between two basically dissimilar things that uses the word like, as, than, or resembles. Symbol Objects, persons, or ideas that stand for something beyond themselves. LITERARY CRITICISM Clarify A method of identifying an author’s purpose by simplifying and making clear. Monitor A method of identifying an author’s purpose by checking or observing. Evaluate A method of identifying an author’s purpose by measuring, judging, or assessing. Aesthetic approach A means of analyzing or evaluating literature that focuses on the stylistic elements of the piece. Ambiguity Uncertain interpretation; lack of precise, definite meeting. Analyze/analysis A method of identifying an author’s purpose by breaking the subject into parts and explaining the various parts. Biographical approach A means of analyzing or evaluating literature that focuses on the life of the author. Diction An author’s careful choice of words to create a desired effect. Historical approach A means of analyzing or evaluating literature based on the time in which it is set or the environment in which it was written. Historical investigation The techniques used by historians to reconstruct and interpret the past. Incongruity Elements or details that defy conventional reason or do not agree. Infer/Inference To make a judgment based on reasoning rather than on direct statement. Literal Meaning The use of words in their strict meanings. Literary Analysis The study of a literary work by a critic, student, or scholar; a careful, detailed reading and report thereof. Literary criticism The analysis and judgment of a work of fiction. Main idea The central idea throughout a passage. Mood The atmosphere or feeling the writer creates for the reader, Theme The controlling/main idea of a work of literature. Usually a general statement about life. Tone A writer’s attitude toward his or her project. Voice A writer’s unique way of speaking, writing, and sounding. DRAMA Act One part of a larger work, sometimes divided into scenes. Several acts make up a drama. Aside A line of dialogue or a speech in which the character addresses the audience, rather than the other characters in the play. An aside can also take place when two characters converse without the other characters on stage hearing. Dialogue The words the actors say. Monologue A speech by one character in a play, story, or poem. Props An article or object used in a play or motion picture. A prop can be an ordinary item but can also take on greater significance by its relationship to the characters. Scene The smaller unit of an act of a play. Soliloquy A long speech expressing the thoughts of a character alone on stage. Stage directions The author’s comments on how and where the action of a play takes place. Dramatic irony In dramatic irony, a contradiction exists between what a character thinks and what the audience knows to be true. Situational irony In irony of situation, an event occurs that directly contradicts the expectations of the characters, the reader, or the audience. Verbal irony In verbal irony, words are used to suggest the opposite of what is meant. POETRY Poetic purpose The intention of a poem. An ode, an elegy, and an epic, are written to achieve different poetic purposes. Stanza A group of lines that are meant to be read as a unit. Couplet A pair of rhyming lines. Free verse Poetry that has no regular patterns. Speaker The person “saying” the poem, it can be the poet or an imaginary character created by the poet. Sound devices Elements such as rhyme, rhythm, alliteration, and onomatopoeia that give poetry a musical quality. Rhyme Using the same vowel sound and consonant sound at the end of two words. Rhythm Pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables. Blank verse Unrhymed poetry usually written in iambic pentameter. Rhythm scheme A regular pattern of rhyming words in a poem or stanza. Poetic devices See literary devices. AMERICAN LITERATURE TERMS Archetypal literary element Patterns in literature founds across the world. For instance, the occurrence of events in threes is an archetypal element of fairy tales. Classicism An approach to the literature and the other arts that stresses reason, balance, clarity, ideal beauty, and orderly form in imitation of the arts of ancient Greece and Rome. This is often contrasted with romanticism. Gothic The use of primitive medieval, wild, or mysterious elements in literature. Gothic novels feature places like mysterious and gloomy castles, where horrifying, supernatural events take place. Grotesque characters characters who have become ludicrous or bizarre through their obsession with an idea or value, or as a result of an emotional problem. Idyll A poem or part of a poem that describes and idealizes country life. Harlem renaissance Occurring during the 1920’s, was a time of African American artistic creativity centered in Harlem, in New York City. Imagism Flourishing between 1912 and 1927. these poems that used ordinary language and free verse to create sharp, exact, concentrated pictures. Journal A daily autobiographical account of events and personal reactions. Legend A traditional story that often deals with a particular person- a hero, a saint, or a national leader. Letters A written message or communication addressed to a reader and is generally sent by mail. Letters may be private or public, depending on the intended audience. Local color The use of characters and details unique to a particular geographic area. Local color can be created by the use of dialect and by descriptions of customs, clothing, manners, attitudes, scenery, and landscape. Naturalism A literary movement among novelists at the end of the nineteenth century and during the early decades of the twentieth century. The Naturalists tended to view people as hapless victims of immutable natural laws. Oral tradition The passing of songs, stories, and poems from generation to generation by word of mouth. The oral tradition in America has been preserved in Native American myths and legends, spirituals, folk ballads, and other works. Plain Style Type of writing in which uncomplicated sentences and ordinary words are used to make simple direct statements. This style was favored by the Puritans who wanted to express themselves clearly. Regionalism Like local color writing, regionalists tended to write about specific geographical areas; however, these writers went beyond a mere presentation of cultural characteristics and instead tried to display a sophisticated sociological or anthropological treatment of the culture of a region. Romanticism A literary and artistic movement of the nineteenth century that placed emphasis on the imagination, emotion, nature, individualist, and exotica. Stream of consciousness Narrative technique that presents thought as if they were coming directly from a character’s mind. Transcendentalism An American literary and philosophical movement of the nineteenth century that promoted the belief that intuition and the individual conscience “transcend” experience and thus are better guides to truth than are the senses and logical reason. WRITING PROCESS Active voice A verb form in which the subject of the verb carries out some action. Annotated bibliography The inclusion of additional comments in the works listed in the standard bibliography. Audience Those people for whom you are writing. Prewriting The stage in which you plan out the work to be done. You prepare to write by exploring ideas, gathering information, and working out an organization plan. PREWRITING STEPS Clustering A brainstorm technique to help you freely associate ideas around a key word or phrase, thus forming a group of related concepts. Brainstorm The listing of possible ideas from a cluster to use in your paper. Not all of your ideas will be useful or suitable. You will need to evaluate them later. Consultation Speaking informally with other who may suggest an idea or an approach. Questioning When your brainstorm list is complete, make a list of questions about your topic, then find answers to your questions. Research Do research. Your topic may require information that you do not have, so you will need to go to other sources to find information. Outlining A detailed list of all your ideas and information presented in an organized manner. Drafting From your outline, create a rough plan that presents your ideas in sentences and paragraphs. Body Paragraphs The presentation of your information and ideas, which elaborate on you main idea, or thesis. Elaboration of your main idea can use the following kinds of details: textual evidence (facts) and statistics, sensory details, explanations and definitions, anecdotes, examples, and/or questions. PARAGRAPH ORGANIZATION Cause and effect order The means of organizing a written work that shows the reasons for results of events or incidents. Chronological order Events are presented in the order in which they occurred. This organization works best for presenting narrative material or explaining in a “how-to” format. Main idea and details order This logical organization works well to support an idea or opinion. Present each main idea, and back it up with appropriate support (see body paragraphs). Order of importance This order helps readers to see the relative importance of ideas. You present ideas from the most important to least important or from the least to most important. Spatial order In spatial order, details are presented as seen in space; for example, from the left to right, top to bottom, or from foreground to background. This order is good for descriptive writing. EDITING Looking more closely at the language you have used to ensure that the way you expressed your ideas is the most effective. Editing techniques Replace dull language with vivid, precise words. Cut or change unnecessary repetition. Cut empty words and phrases that do not add anything to the writing. Check passive voice. Usually, active voice is more effective. Replace wordy expressions with short, more precise ones. Graphics Charts, tables, or visual elements such as illustrations within a text. Headers Subtitles within a text that indicates the sections of a text. Introduction The first paragraph of an essay. The introduction should engage the reader’s attention and let them know the purpose of your paper. You may use the following strategies: startle your reader, use an anecdote, take a stand, and/or provide and insight. Conclusion The ending of your essay, which gives the final impression that you have pulled everything together. Following are some effective ways to end your paper: summarize and restate, state an opinion, call for action, ask a question, tell an anecdote, and/or provide an insight. Main idea The central idea throughout a passage. Paraphrase Restating the information from a source in your own words, and mentioning the source. Passive voice A verb form in which the subject of the verb is the receiver of some action or state indicated by the verb. Primary source An information source that arises from direct participation with the subject. Proofread After you finish your final draft, correct errors in grammar and usage, punctuation and capitalization, and spelling. It is best to have several other readers proofread your drafts as well. Publishing and presenting When your final draft has been proofread by you and several others, it is ready to be shared with classmates, family, instructor, or a wider audience. Reference books Dictionaries, encyclopedias, thesauruses. Revising After your paper has been proofread, make changes based on your reader’s evaluation in terms of concept, organization, style, and appropriateness to purpose and audience. Rubric A scale of grading standards in which your work will be judged based on specific criteria. Secondary source An information source produced by someone who did not directly participate in or personally observe the events described. Structure Organization. (See body paragraphs) Summary The main points and details in a text in condensed form, leaving out unimportant information. Synthesize To connect information or ideas from various sources. Textual evidence (facts) Convincing factual support from a variety of outside sources, including direct quotations whose sources are credited. Antithesis The opposite of the original controlling idea (Thesis), the discovery of a contradiction in the original thesis, or proposition. Synthesis The formulation of a third thesis, or proposition, being the combination of the original idea and the contradiction to it. Topic The general category or class of idea, often stated as a word or phrase, to which the ideas of a passage as a whole being. Topic Sentence A sentence that clearly states what a paragraph is about. Transition Words or ideas that connect one idea to another, making paragraphs flow freely. Unity When your introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion are directly related, highly organized, and carefully written, you will achieve a unified or cohesive paper that fully explores your main idea. READING VOCABULARY Cause What makes something happen. Effect What happens as a result of a cause. Connotation The emotional impression that a word conveys. Context clues The word clues surrounding an unknown word or phrase that help clarify its meaning. Denotation The literal meaning of a word. BIOLOGY ROOT A AEROAMPHIBIARTH ASTER AUTO BI BIO CARPCAUD CENTI CEPHA CHLORO CHONDRO CHRYS COEL, COELO CYAN CYTO DERM DI ECTERYTHRO GEN GYN HEMO HEMI HEMO HEPAT HERB HETERO HOMO HYDRO HYPER HYPO HYPER ICHTHY INTER ISO IT IS KILO LEPI LEPTO LYSIS MACRO MESO META MILLI MYCO OCUL SOURCE A AER AMPHI ARTHRON ASTRAUTOS BIS BIOS CAUDA CENTUM CEPHALE CHLORO CHONDROS CHRYSOS KOILOS CYANOS CYTO DERMA DIS ERYTHROS GENOS GYNE HEM HEMI HAIMA HETEROS HOMOIS HYDOR HYPER HYPO HYPER ICH INTER ISOS ITIS LEPIS LEPTOS LYS MAKROS MESO META MEANING OR ASSOCIATION SOME EXAMPLES WITHOUT OR NOT ASEXUAL, ASYMETRICAL AIR AEROBIC LEADING A DOUBLE LIFE AMPHIBIAN JOINT ARTHROPOD STAR ASTEROID SELF AUTO-OXIDATION, AUTOLYSIS TWICE, DOUBLE BISULFATE LIFE, LIVING BIOCHEMISTRY, BIOLOGY FRUIT PERICARP TAIL CAUDAL FIN (FISH) HUNDRED CENTIMETER HEAD CEPHALIC GREEN CHLOROPLAST CARTILAGE CHONDROBLAST GOLDEN-YELLOW CHRYSOBERYL, CHRYSANTHEMUM HOLLOW, CAVITY COELOBLAST, COELUM DEEP BLUE CYANIDE, HEMOCYANIN CELL CYTOLOGY SKIN DERMATITIS TWICE, DOUBLE DISACCARADE OUTSIDE, WITHOUT ECTODERM RED ERYTHRODEXTRIN BIRTH, BEGINNING GENESIS, OOGENESIS WOMAN GYNDOICECIOUS, POLYGAMY BLOOD HEMOLYSIS A HALF HEMIHYDRATE BLOOD HEMOCYANIN LIVER HEPATITIS GRASS HERBARIUM OTHER, DIFFERENT HETEROCYCLIC SAME HOMOCERCA; HOMOLOGOUS WATER HYDRATE, HYDROGEN EXCESSIVE HYPERTHYROIDISM UNDER, LOWER HYPOCHLOROUS, THYROID ABOVE HYPERLASIA, HYPERTHYROIDISM FISH ICHTHYICHES BETWEEN INTERNODE SIMILAR ISOTONIC INFLAMATION ARTHRITIS THOUSAND KILOMETER SCALE LEPIDOPETRA SLENDER LEPTOPHYLLUS DECOMPOSE LYSOSOME, LSYSIS LARGE MACROMOLECULE MIDDLE MESOGLEA, METAPHASE BETWEEN METAPHASE THOUSANDTH MILLIMETER FUNGUS, THREADLIKE MYCELUIM EYE OCULAR OSTIPHILPHOBIA PHYTE POLY PSEUDO PTER SEPTIC PHYT POLY PSEUDES PTERYX SPERM SYMTELE THERMTROPH- SPERMA ZYGO ZYGON TELEOS BONE OSTEOPOROSIS LOVING, FOND OF HYDROPHILIC EXCESSIVE FEAR OF HYDROPHOBIC PLANT GAMETOPHYTE MANY, SEVERAL POLYANDRY FALSE, DECEPTIVE PSEUDOPOD WING PTERIDOPHYTE PUTREFACTION, ASPETIC INFECTION SEED SPERMATOCYTE TOGETHER SYMBIOTIC COMPLETE TELOPHASE HEAT THERMOSTATIC ONE WHO FEEDS, AUTOTROPH WELL FED YOKE ZYGOTE CHEMISTRY VOCABULARY Word Alloy Ambient Temperature Boiling vs. Evaporating Cease to Evaporate Compress Condensation Decreasing order Diatomic vs. Monatomic Diffusion vs. Effusion Direct vs. Inverse Relationship Distinctive Color Electronic Probe Electrostatic Forces Emit Light Extrapolate Formula Units Increasing Order Intermolecular vs. Intramolecular Forces Interpolate Lattice Structure Macromolecules- Subunits Polar vs. Non-Polar Ppm Precipitate Reactants vs. Products Reagent Repulsion Spectra Vacuum Yield Definition Mixture of two or more metals. Temperature of your surroundings, room temperature. Boiling and evaporating are both changes from liquid to gas state but evaporating happens at many temperatures and only on the surface of the liquid. Boiling happens only at the boiling temperature within the body of the liquid. Stops changing from liquid state to gas state on the surface of a liquid. If you squeeze a pillow made of foam, you compress it. Molecules change from gas to liquid. Increasing order: put items in order from the largest value to the smallest value. Two atoms will make a diatomic molecule; one molecule makes a monatomic molecule. Diffusion is movement of one material through another while effusion is when a gas escapes through a tiny opening. Direct: when one value goes up, so will the other one; indirect, when one value goes up, the other one goes down. Main color; The distinctive color of a banana is yellow. Device that measures data, i.e. temperature, pH, pressure. Attraction between cations (positive ions) and anions (negative ions). To release or give off. A combustion reaction emits light and heat. Extend and estimate best fit line. Ionic bonded “molecule”. Increasing order; put items in order from smallest value to highest value. Intermolecular is attractions between molecules; intramolecular is bonding between atoms like covalent or ionic bonds. Best fit line Crystal pattern made from ionic compounds. Very large molecules are made from smaller pieces. Proteins are macromolecules made from amino acid subunits. Polar bonds have uneven charge, nonpolar charges are equal. Parts per million: measure of concentration. Multiple values to make denominator 1,000,000 parts. Solid formed from solutions, will settle as a powder. Reactants are the starting material, products are what is formed. Reactants make products! Another name for a chemical used in a reaction. Separation caused by same charges. You cannot put like ends of a magnet together because of repulsion. Series of colors given off by energizing elements. Empty space, absence of matter To produce. PHYSICS VOCABULARY Motion & Forces Word Acceleration Average Velocity Centripetal Acceleration Centripetal Force Density Displacement Equilibrium Force Friction Gravity Inertia Mass Normal Force Projectile Resultant Speed Vector Weight Energy & Momentum Word Elastic Collision Elastic Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Energy Impulse Inelastic Collisions Kinetic Energy Momentum Power Work Definition The rate at which the velocity changes over time; an object accelerates if its speed, direction, or both change. The total displacement divided by the time interval during which the displacement. An acceleration directed to the center of a circle. The necessary net force exerted perpendicular to the tangential velocity to cause centripetal acceleration. The concentration of matter of an object, measured as the mass per unit volume of a substance. The change in position of an object The state in which the net force on an object is zero. An action exerted on an object which may change the object’s state of rest or motion; force has magnitude and direction. A non-conservative force that resists the relative motion of surfaces in contact with each other. Attractive force directly proportional to the product of the masses of and inversely proportional to the distance between two objects. The tendency of an object to resist being moved or, if the object is moving, to resist a change in speed or direction. The property of matter (measured in kilograms in the metric system) which determines its inertia and the gravitational forces it exerts. A force that acts on a surface in a direction perpendicular to the surface. An object with independent vertical and horizontal motion that moves through the air only under the force of gravity after an initial thrust. A vector that represents the sum of two or more vectors. Distance traveled divided by the time. A physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object; its value can change with the location of the object in the universe. Definition A collision in which the total momentum and total kinetic energy are conserved. The energy available for use when an elastic body returns to its original configuration. The potential energy stored in the gravitational fiends of interacting bodies. The product of the force and time over which the force acts on an object. A collision in which total momentum is conserved, but total kinetic energy decreases. The energy of an object that is due to the object’s motion. A quantity defined as the product of the mass and velocity of an object. A quantity that measures the rate at which work is done or energy is transformed. The product of the component of a force along the direction of displacement and the magnitude of the displacement. Waves Word Diffraction Doppler Effect Definition A change in the direction of a wave when the wave encounters an obstacle, and opening, or an edge. An observed change in the frequency when there is relative motion between the source of waves and an observer. Electromagnetic Wave Frequency Interference Longitudinal Wave Mechanical Wave Period Reflection Refraction Superposition Principle Transverse Wave Wavelength Heat and Thermodynamics Word Entropy Heat Engine Work Electricity and Magnetism Word Electric Current Electric Field Electric Potential Magnetic Field Parallel Circuit Plasma Resistance Series Circuit Transistor A wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which radiate outward from the source at the speed of light. The number of cycles or vibrations per unit time; also the number of waves produced per unit of time. Constructive interference is a superposition of two or more waves in which individual displacements on the same side of the equilibrium position are added together to form the resultant wave. Destructive interference is a superposition of two or more waves in which individual displacements on opposite sides of the equilibrium, position are added together to form the resultant wave. A wave whose particles vibrate parallel to the direction the wave is traveling. A wave that requires a medium through which to travel. The time that it takes a complete cycle or wave oscillation to occur. The turning back of an electromagnetic wave at a surface. The bending of a wavefront as the wavefront passes between two substances in which the speed of the wave differs. The displacement of any point due to the superposition of waves is equal to the sum of the displacements of the individual waves at that point. A wave whose particles vibrate perpendicularly to the direction the wave is traveling. The distance between two adjacent similar points of a wave, such as from crest to crest or from trough to trough. Definition A measure of the randomness or disorder of system. A device that uses heat to do mechanical work. The process of changing the energy of a system by means of forces. Definition The rate at which charges pass through a given area. A region where an electric force on a test charge can be detected. The work that must be performed against electric forces to move a charge from a reference point to the point in question divided by the charge. A region where a magnetic force can be detected. A circuit with several current paths, whose total current equals the sum of the currents in its branches. The gas-like state of matter made up of positively charged ions or negatively charged electrons or a mixture of them. The opposition presented to electric current by a material or device. A circuit in which current passes through each device, one after another. A semiconductor device that can amplify current and that is used in amplifiers, oscillators, and switches. EARTH SCIENCE WORD PART OR ROOT MEANING APPLICATION a- Not,without Abiotic Astr-, aster- Star Astronomy Bar-, baro- Weight, pressure Barometer Batho-, bathy- Depth Batholiths, bathysphere Circum- Around Circum-Pacific, circumpolar -cline Lean, slope Anticline, syncline -duct- To lead, draw Conduction Eco- Environment Ecology, ecosystem Epi- On Epicenter Ex-, exo- Out, outside of Exosphere, exfoliation, extrusion Geo- Earth Geode, geology, geomagnetic -graph Write, writing Seismograph Hydro- Water Hydrosphere Hypo- Under Hypothesis Iso- Equal Isoscope, isostasy, isotope -lith, -lithic Stone Neolithic, regolith -log- Study Ecology, geology, meteorology Magn- Great, large Magnitude Mar- Sea Marine Meta- Among, change Metamorphic, metamorphism -meter To measure Thermometer, spectrometer Micro- Small Microquake -morph, -morphic Form, shape Metamorphic Nebula- Mist, cloud Neolithic Paleo- Old Paleontology, Paleozoic Ped-, pedo- Ground, soil Pediment Per- Through Permeable Peri- Around Perigee, perihelion Seism-, seismo- Shake, earthquake Seismic, seismograph Sol- Sun Solar, solstice Spectro- Look at, examine Spectroscope, spectrum -sphere Ball, globe Geosphere, lithosphere Strati-, strato- Spread, layer Stratification, stratovolcano terra- Earth, land Terracing, terrane Thermo- Heat Thermosphere, thermometer Top-, topo- Place Topographic Trop-, tropo- Turn, respond to Tropopause, troposphere ANATOMY VOCABULARY Word Definition Acne Sebaceous gland inflammation cause by an accumulation of secretions. Arthritis Rheumatic diseases that affect synovial joints. Arthritis always involves damage to the articular cartilages, but the specific cause can vary. Athsma An acute repository disorder characterized by unusually sensitive, irritated conducting airways. Benign Tumor A mass or swelling in which the cells usually remain within a connective tissue capsule, rarely life threatening. Biopsy The removal and examination of tissue from the bodey for the diagnosis of disease. Cancer An illness characterized by gene mutations leading to the formation of malignant tumors and metastatis. Carcinogen An environmental factor that stimulates the conversion of a normal cell to a cancer cell. CAT SCAN Computerized axial tomography: an imaging technique that uses X-rays to reconstruct the body’s threedimensional structure. Cholesterol A steroid and an important component of cellular membranes; in high concentrations it increases the risk of heart disease. Disease A malfunction of organs or organ systems resulting from a failure in homeostatic regulation. Fracture A crack or break in a bone. Gallstones Deposits of minerals, bile salts, and cholesterol that form if bile becomes too concentrated. Genetic Engineering The research on and techniques for changing the genetic makeup (DNA ) of an organism. Hernia A condition involving an organ or a body part that protrudes through an abnormal opening in the wall of a body cavity. Histology The study of tissues. Malignant Tumor A mass or swelling in which the cells no longer respond to normal control mechanisms but divide rapidly and spread. Pnemonia A respiratory disorder characterized by fluid leakage into the alveoli and/or swelling and constriction of the respiratory bronchioles. Regeneration The repair of injured tissues following inflammation. Tendinitis Inflammation of the connective tissue surrounding a tendon. Tracheostomy The insertion of a tube directly into the trachea to bypass a blocked or damaged larynx. Tumor (neoplasm) A mass or swelling produced by abnormal cell growth and division. Ulcer A localized shrededing of an epithelium. Varicose Veins Sagging, swollen veins distorted by gravity and by the failure of the venous valves. SOCIAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY All Courses Word Agrarian Allies Anti-Trust Capitalism Checks and Balances Civilian Communism Constitution Demand Despot Dictator Discrimination Domestic Due Process Clause Economic System Emigrant Entrepreneur Executive Branch Exploitation Export Factors of Production Federal Reserve Federalism Feudalism Hierarchy Ideology Immigrant Import Industrialism Inflation Interest Groups Judicial Branch Jurisdiction Labor Labor Union Laissez-Faire Legislative Branch Legislature Definition Relating to the land and its ownership, cultivation, and tenure. Groups or countries that side with each other diplomatically or militarily; friends. Prevention of illegal grouping of companies that discourage competition; antimonopoly. An economic system in which the means of production and distribution are privately or corporately owned. System that prevents a branch or person in government from having too much power. A person following the pursuits of a civil life, not a member of the armed forces. A system of government in which the state controls the economy, claiming that all goods are equally shared. System of fundamental laws and principles that prescribes the nature, functions, and limits of a government. The desire to posses a commodity or make use of a service, combined with the ability to purchase it. A ruler with absolute power. An absolute ruler. Treatment or consideration based on class or category rather than individual merit. Indigenous to or products made within one’s own country; not foreign; native. A clause in a constitution prohibiting the government from depriving a person of life, liberty, or property. The system of production and distribution and consumption. A person who emigrates, as from his or her native country or region. A person who organizes and manages any enterprise. The branch of the United States government that is responsible for carrying out the laws. Selfish utilization. To ship (commodities) to other countries or places for sale, exchange. Land, labor, capital, entrepreneurs; necessities for production to occur. The central bank of the United States; 12 Federal Reserve branch banks. The federal principle of government. The feudal system, or its principles and practices. An organized body of ecclesiastical officials in successive ranks or orders. Such a body of doctrine, myth, etc., with reference to some political and social plan. A person who migrates to another country, usually for permanent residence. To bring in (merchandise, commodities, workers, etc) from a foreign country for use, sale, processing, etc. An economic society built largely on mechanized industry rather than agriculture, craftsmanship, or value of currency. A persistent, substantial rise in the general level of prices resulting in the loss of value of currency. A group of people drawn or acting together in support of a common interest or to voice a common concern. The branch of the United States government responsible for the administration of justice. The right, power, or authority to administer justice by hearing and determining controversies. The body of persons engaged in such activities, esp., those working for wages. An organization of wage earners or salaried employees for mutual aid and protection. Theory of believing that government should intervene as little as possible in the direction of economic affairs. The branch of the United States government that has the power of legislating. The branch of the United States government that has the power of legislating. The branch of government having the power to make laws. Liberal Liberalism Liberty Mercantilism Monarch Oppression Proletariat Propaganda Public Works Radical Rebellion Refugee Regime Representation Republic Revolution Rural Scarcity Segregation Socialism Sovereignty Suffrage Tolerance Total War Unions Urban Veto U.S Courses Word ACLU Amendment ARVN Bessemer Domino Theory Editorial Electoral College Geneva Accord Noting or pertaining to a political party advocating measures of progressive reform. Philosophy advocating the freedom of the individual, government, nonviolent modification of liberties. Freedom from external or foreign rule; independence. Economic policy; nations tried to increase wealth/power by obtaining amounts of gold/silver and selling more goods than they bought. A person who rules a kingdom or empire, the succession of a monarchy is usually hereditary. Unjust or cruel exercise of authority or power. In Marxist theory, the group of workers who would overthrow the czar and come to rule Russia. A kind of biased communication designed to influence people’s thoughts and actions. Goods or services provided by the government through tax dollars. In the first half of the 19th century, a European who favored drastic change to extend democracy to all people. Open, organized, and armed resistance to one’s government or ruler. A person who leaves his or her country to move to another to find safety. The period during which a particular government or ruling system is in power. The state, fact, or right of being represented by delegates having a voice in legislation or government. A government in which the citizens rule through elected representatives. The overthrow or renunciation of one’s government or ruler and the substitution of anther by the governed. Of or relating to the country or countryside, often involving agricultural production. Limited quantities of resources meet unlimited wants. The legal or social separation of people of different races. An economic system in which the factors of production are owned by the public and operate for the welfare of all. Supreme and independent power or authority in government as possessed or claimed by state or community. The right to vote. A fair, objective, and permissive attitude toward those whose opinions, practices, race, religion, and nationality differ from one’s own. A conflict in which the participating countries devote all of their resources to the war effort. An association of workers, formed to bargain for better working conditions and higher wages. A migration of people from cities to the surrounding suburbs. Power vested in one branch of the government to cancel the decisions of another branch, esp. the right of a president to reject bills passed by the leg. Definition American Civil Liberties Union; an organization devoted to upholding constitutional rights. Within the context of the US Constitution, a formal change in the Constitution; requires ratification by ¾ of states. S. Vietnamese soldiers with whom U.S. troops fought against communism and forces in the North during the Vietnam War. A cheap and efficient process for making steel, developed around 1850. The idea that if a nation falls under communist control, nearby nations will also fall under communist control. Newspaper or magazine article that gives the opinions of the editors or publishers. Representatives from each state who formally cast ballots for the president and vice president. A 1954 peace agreement that divided Vietnam into Communist North Vietnam and non-Communist South Vietnam. Gilded Age Harlem Renaissance Internment Camp Lend Lease Act Manhattan Project Manifest Destiny Marbury v. Madison Mass Culture Melting Pot Monroe Doctrine Muckracker My Lai NAACP Nativism Palmer Raids Populist Progressive Red Scare Social Gospel Tariff Tet Offensive Tonkin Gulf Vietcong Vietnamization Vietminh War Powers Act W/U.S. Courses Word Annexation Anti-Semitism Appeasement Brinkmanship Colonies Containment Democratic Détente Local and national political corruption in the 19th century that led to calls for reform. A flowering of African-American artistic creativity during the 1920’s, centered in the Harlem community of New York City. Confinement or a restriction in movement, especially in wartime conditions. Law passed in 1941 that allowed the U.S. to ship arms and other supplies to nations fighting the Axis powers. The U.S. program to develop an atomic bomb for use in World War II. 19th century belief that the United States would inevitably expand westward to the Pacific Ocean and into Mexican Territory. 1803 case, Supreme Court ruled it had the power to abolish legislative acts by declaring them unconstitutional (judicial review). The production of works of art and entertainment designed to appeal to a large audience. Mixture of people from different cultures and races who blend together by abandoning their native languages and cultures. A policy of U.S. opposition to any European interference in the affairs of the Western Hemisphere. One of the magazine journalists who exposed the corrupt side of business and public life in the early 1900’s. A village in northern Southern Vietnam where more than 200 unarmed civilians were killed by U.S. troops (May 1968). The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People. An organization founded in 1909 to promote racial equality. Favoring the interests of native-born people over foreign-born people. Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer, authorized to target communists, socialists and anarchists, often violating people’s rights. Political movement demanding people to have a greater voice in government and seeking to advance the interests of farmers/laborers. Early 20th century reform movement seeking to return control of the government to the people, restore the economy, and correct injustices. A panic that began after Russia’s Bolshevik Revolution based on a fear that communists were taking over the country. 19th century reform movement; belief that Christians have a responsibility to help improve working conditions and poverty. A tax on imported goods. A massive surprise attack by the Viet Cong on South Vietnamese towns and cities early in 1968. A resolution adopted by Congress in 1964, giving the president broad powers to wage war in Vietnam. South Vietnamese Communists who, with N. Vietnamese support, fought against the gov. of South Vietnam in the Vietnam War. President Nixon’s strategy for ending U.S. involvment in the Vietnam War. Org. of Vietnamese Communists and other nationalist groups between 19461954 fought for Viet. Independence from French. A law enacted in 1973, limiting a president’s right to send troops into battle without consulting Congress. Definition The adding of a region to the territory of an existing political unit. Prejudice against Jews. The making of concessions to an aggressor in order to avoid war. A policy of threatening to go to war in response to any enemy aggression. Land controlled by another nation. U.S. foreign policy, in which the U.S. tried to stop the spread of communism by creating alliances and helping weak countries. A government that uses aspects of democracy, or rule by the people. A policy of reducing Cold War tensions that was adopted by the United States during the presidency of Richard Nixon. Empire Fascism Genocide Hiroshima Imperialism Isolation League of Nations Militarism Nationalism Neutrality Nuremburg Trials Roosevelt Corollary Self-Discrimination Totalitarianism Trench Warfare Truman Doctrine World Courses Word Abdicate Armistice Authoritarianism Bourgeoisie Boxer Rebellion Conservative Divine Right Fall of the Bastille Geopolitical Glasnost Government Great Purge Industrial Revolution John Locke Lost Generation Marxism Mobilize Monotheism A number of territories or peoples under a single sovereign authority, usually an emperor. Political movement that promotes an extreme form of nationalism, a denial of individual rights, and a dictatorial one-party rule. The systematic killing of an entire people. Japanese port city struck by the first dropping of an atomic bomb on August 6, 1945. A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, economically, or socially. Policy of avoiding political or military involvement with other countries. An international association formed after World War I with the goal of keeping peace among nations. A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war. The belief that people should be loyal mainly to their nation rather than a king or empire. To remain neutral or uninvolved in a conflict. A series of court proceedings held in Nuremburg, Germany, after WWII, in which Nazi Leaders were tried. Extension of the Monroe Doctrine, in which the U.S. had the right to exercise “police power” throughout Western Hemisphere. The freedom of a people to decide under what form of government they wish to live. Government control over every aspect of public and private life. A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield. A U.S. policy giving economic and military aid to free nations threatened by internal or external opponents. Definition To step down from a throne or high office. An agreement to stop fighting. The concentration of political power in a leader or elite not constitutionally responsible to the people. The French word for middle class. In pre-revolutionary France, the bourgeoisie had little political power but was taxed heavily. A 1900 revolt in China, aimed at ending foreign military influence in the country. First half of the 19th century, a European mainly wealthy landowners and nobles that wanted to keep the traditional monarchies. The idea that monarchs are God’s representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God. Seizure of a royal prison in Paris by Parisians that became a symbol of revolutionary activity; Bastille Day is July 14th. A foreign policy based on consideration of the strategic locations or products of other lands. Gorbachev’s policy of “openness”; churches reopened, dissidents released from prison; and people could voice criticisms. The continuous exercise of authority over the performance of functions for a political unit. Campaign of terror in the Soviet Union; Joseph Stalin sough to eliminate Communists and whoever threatened his power. The shift, beginning in England during the 18th century, from making goods by hand to making them machine. Political thinker who believed that a government’s power comes from the people; also supported natural rights (see below). American writers, musicians, and painters who left the U.S. for Europe and were disillusioned after WWI. Ideas created by The Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx and Freidrich Engels promoting the overthrow of capitalism by workers. To prepare a country’s military forces for deployment or use. A religious belief in one god. NATO Natural Rights Non-Aggression Treaty Perestroika Philosopher Kings Pogrom Renaissance Romanticism Schlieffen Plan Separation of Powers Simon Bolivar Social Contract Social Darwinism Taiping Rebellion Tennis Court Oath Theocracy Treaty of Versailles Trench Warfare Triple Alliance Triple Entente Tyranny Ultimatum Yalta Conference North Atlantic Treaty Organization: A Cold War military alliance formed among western European nations, the U.S., and Canada. From John Locke: life, liberty, and property. A government should protect people’s natural rights. Signed by Hitler and Stalin before WWII. It also planned for the partition of Poland. Mikhail Gorbachev’s policy of economic restructuring communism for greater efficiency and higher production. According to Plato in The Republic: they should rule; have the spirit and power of philosophy, political greatness and wisdom. An organized massacre of helpless people. A period of European history, about 1300-1600, renewed interest in classical culture led to changes in art and learning. An early 19th century movement in art and thought, which focused on emotion and nature rather than reason and society. Germany’s military plan at the outbreak of WWI, which Germany would rapidly defeat France and then attack Russia. An idea championed by Montesquieu during the enlightenment in which the government is divided into 3 separate branches. Venezuelan general who achieved Independence from Spain for Venezuela and then other South American colonies. The agreement by which people define and limit their individual rights, thus creating an organized society or government. The application of Charles Darwin’s ideas about evolution and “survival of the the fittest” to human societies. A Mid-19th century rebellion against the Qing Dynasty in China, led by Hong Xiuquan. At the Estates General, the pledge by members of the Third Estate to meet until they had written a constitution for France. Government of a state by immediate divine guidance or by officials who are regarded as divinely guided. The peace treaty between the Allies and Germany to end WWI. It punished Germany, created new nations and mandates. A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield. Prior to WWI, the military alliance comprised to Germany, Austra-Hungary and Italy. Prior to WWI, the military alliance comprised of Russia, Britain and France. A government in which absolute power is vested in a signal ruler. A final proposition, condition, or demand. Meeting during the end of WWII between Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin about planning the postwar world. MATH VOCABULARY Word Binomials Commutative Property Counterexample Data Distributive Property Domain Equations Equivalent Expression Expression Evaluated Fraction Function Functions Expressions Graphing Equations Horizontal Axis Inequality Intercept Linear Equations Linear Function Multiplication Property Multiplicative Inverse Number Properties Operations Ordered Pairs Parallel Perimeter Perpendicular Points on a Graph Polynomials Prime Factorization Product Quadratic Equation Quadratics Quantity Rational Expressions Real Number Reciprocal Slope Solution Statement System of Inequalities Systems of Linear Equations Value Vertical Axis Zero Product Property Definition A polynomial of two terms. a+b=b+a Any example that proves a statement false. Individual facts, statisitics, or items of information. For every real number a, b, and c: a(b+c) = ab + ac (b+c) a= ab +ac The domain of a relation is the set of all inputs, or x-coordinates, of the ordered pairs. A mathematical sentence that uses an equal sign. Equations that have the same solution. A symbol or a combination of symbols representing a value, relation, or the like. Simplifying an expression. A number usually expressed in the form a/b. A relation that assigns exactly one value in the range to each value of the domain. Or function notation, to write a rule in function notation, you use the symbol f(x) in place of y. Use slope intercept form, y = mx + b. Lines that lie on the x axis. A mathematical sentence that compares the values of two expressions using an inequality symbol. To mark off or include, as between two points or lines. An equation whose graph forms a straight line. An equation whose graph forms a straight line. If a = b then a x c = b x c. Given a nonzero rational number a/b, the multiplicative inverse, or the reciprocal, is b/a, the product of a nonzero number and its multiplicative inverse is 1. Commutative, Associate, and Distributive. PEMDAS- parenthesis, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and substraction. Two numbers that identify the location of a point. Two lines that never intersect. The space or area within a shape. Lines that intersect to form right angles. Two lines are perpendicular if the product of their slopes is -1. A point that is a line or on the graph. A sum of one or more monomials. A quotient with a variable in the denominator is not a polynomial. The process of decomposing a number into its constituent prime numbers. The result obtained by multiplying two or more quantities together. An equation you can write together in the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a does not equal 0. It’s to the second power. The amount of something. A ratio of two polynomials. The value of the variable cannot make denominator equal to zero. A number that is either rational or irrational. Is the inverse of a fraction. If you have 2/3 then reciprocal is 3/2. The ratio of the vertical change to the horizontal change. The set of all solutions. Something stated. Two or more linear inequalities using the same variables. A “system” of equations is a set or collection of equations that you deal with all together at once. Magnitude, quality, number by a figure, symbol, or the like. Lines that lie on the y axis. For all real numbers a and b, if ab=0 , then a =0 or b = 0.









