Write Up Assignment 1
advertisement

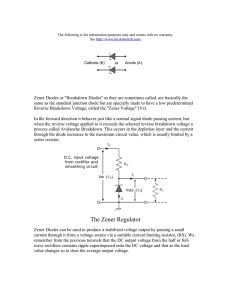
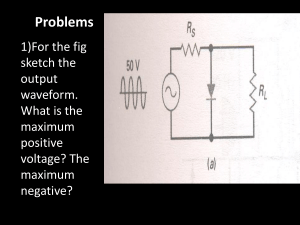
Write Up Assignment 1 (Chapter2) 1. Draw the output voltage waveform included the voltage drop and determines the peak inverse voltage for each circuit. Fig. 1(a) Fig. 1(b) 2. For fig.2, determine: (a) the peak output voltage (b) peak inverse voltage. 1:2 +100V RL = 2 kΩ -100V Fig. 2 3. For fig.3, determine: (a) the voltage waveform for each half of secondary winding (b) voltage across RL (c) PIV 2: 1 +120V Vin 12 kΩ -120V Fig. 3 4. Figure 4 shows the full-wave rectifier (practical model) with the transformer have a 110Vrms for input voltage. (a) Sketch Vsec (b) Calculate Vp(rect), Vr(pp) and Vdc. (c) Calculate percent of ripple of the circuit (b) What PIV rating required for each diode? Figure 4 5. A certain full wave rectifier has a peak output voltage of 50V with capacitor filter input = 70µF. Calculate: (a) peak to peak ripple and (b) dc output voltage across 700Ω load resistance. 6. Determine the output voltage waveform for the diode limiter in figure below? +12V -12V 7. Sketch the output voltage waveform as shown in the circuit combining a positive limiter with negative limiter in Figure below (Chapter3) 1. Zener diode has two types of reverse breakdown. State and explain these reverse breakdown. 2. An 7.5 V zener diode (7.5 V at 30 0C) has a positive temperature coefficient of 0.05 %/0C. What is the zener voltage at 60 0C? 3. Determine the minimum and the maximum input voltages that can be regulated by the zener diode in Figure below. 4. Determine the minimum and the maximum load currents for which the zener diode in Figure will maintain regulation. What is the minimum RL that can be used? VZ = 12V, IZK = 1 mA, and IZM = 50 mA. Assume ZZ = 0 Ω and VZ remains a constant 12 V over the range of current values, for simplicity 5. Determine the output voltage for each zener limiting circuit in Figure below. +10V 4.7V -10V 6.8V 6. Briefly explain the basic operation of LED.