QB - mohd javed khan

Question Bank of Communication Engineering (EC 605)
Unit 1:
1. What do you mean by information rate?
2. State shannon’s Hartley law of information capacity.
3. Define the Entropy.
4. Consider a discrete memoryless source with a source alphabet A = { so, s1, s2} with respective probs. p0 = ¼, p1 = ¼, p2 = ½. Find the entropy of the source.
5. Differentiate bit rate and baud rate.
6. An analog signal is band limited to B Hz, sampled at the Nyquist rate, and the samples are quantized into 4-levels. The quantization levels Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4
(messages) are assumed independent and occur with probs. P1 = P2 =1/ 8 and P3 = P4 = 3/8 . Find the information rate of the source.
7. What is the need of modulation?
8. Give the general block diagram of a communication system.
9. Define standard form amplitude modulation and explain each term.
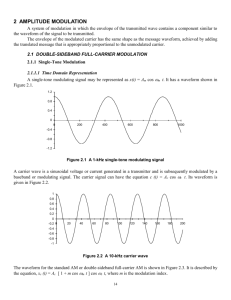
10. Describe AM both in time and frequency domain ..
11.. Explain how you generate AM using a. square law and b. Switching modulators.
12. Explain with the help of a neat sketch, how square law modulator is used to generate
AM.
13. Write a short note on envelop detector.
14. Explain the generation of AM wave using switching modulator with relevant equations, waveform and spectrum before and after filtering process.
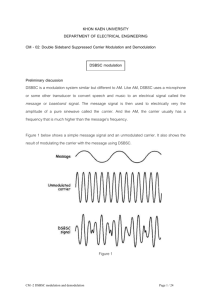
15. What is DSBSC modulation? What are the advantages and limitations of DSBSC as compared to standard AM?
16. Explain SSB wave generation with relevant diagrams and equations.
17. Explain detection process of FM signals ..
18. Give the description of FM in time and frequency domain.
19. Differentiate between FM and AM.
20. Obtain the expression for an FM wave. Also write the different waveforms.
21. Explain the following terms: a) Direct generation of FM b) Indirect generation of FM
22. Write a short note on Armstrong method of generating FM.
23. Define angle modulation.. Describe with the help of block diagrams, schemes for generating a) FM wave using PM b)PM wave using FM.
24. Explain the demodulation of FM wave ..
25. Derive the equation for FM waves. Define modulation index, maximum deviation and bandwidth of a FM signal.
26. Define angle modulation. Describe with the help of block diagrams, schemes for generating i) FM wave using PM ii) PM wave using FM
27.Explain different types of noise.
28. Define Noise figure, Noise temperature and Noise equivalent BW.
29. Define modulation index for AM
30. What is the relation between total power and carrier power?
31. What is the need for modulation?
32. The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 8A when only carrier is sent. It increases to
8.93A when the carrier is modulated by a single sine wave. Find the percentage modulation.
33. A 400W carrier is modulated to a depth of 75 %. Calculate the total power in the modulated wave
34. For 100% modulation what is the relationship between the voltage amplitudes of the side band frequencies and the carrier?
35. Draw The Amplitude Modulation Wave Forms With Modulation Index (m) =1, m<1, m>1.
36. The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 8A when only carrier is sent. It increases to
8.93A when The carrier is modulated by a single sine wave. Find the percentage modulation.
37. Compare FM with AM.
Unit 2:
1.What is sampling ? describe the type of sampling?
2.
3.
4. Differentiate among PAM, PWM and PPM.
5.Explain the Aliasing Effect.
6.Explain the signal reconstruction .
7.What is the Base band Signal ? Explain it’s characteristic.
8.Explain the generation of PAM.
9.Explain the generation of PWM.
10.Explain the generation of PPM.
Unit 3:
1. Explain in detail the PCM.
2. Explain the bandwidth requirement of PCM.
3.Explain the Delta Modulation.
4.Explain the TDM.
5.Explain the type of Digital Modulation Techniques .
6.Explain the differences among ASK,PSK and FSK.
7. Describe the generation of ASK.
8. Describe the generation of PSK.
9. Describe the generation of FSK.
10.
Unit 4 & 5:
1. Write a short notes on
a.Wire Telephone System b. Public Telephonic Networks
2.Explain the application of Radar also explain the Pulse Radar in Details.
3.Differentiate the TDMA , FDMA and CDMA techniques.
4.What are the different applications of satellite systems?
5.Mention the different services of satellite systems.
6.Define Polar-orbiting Satellites.
7.StateKepeler’s second law.
8.Write short notes on attitude control system.
9.Write the expression for the refractive index in graded index fibers.
10.Define Numerical aperture of a step index fiber.
11.What is Snell’s law?
12.What is the necessity of cladding for an optical fiber?
13.What are the uses of optical fibers?
14.What is the principle used in the working of fibers as light guides?
15.what are step index and graded index fibers?
16.Why do we prefer step index single mode fiber for long distance communication?
17.What are the conditions for total internal reflection?
18.Define cutoff wavelength of the fiber.
19. What is Intra Modal Dispersion?
20. What are the causes of intra modal dispersion?
21.What is material dispersion?
22.What is waveguide dispersion?
23.What is group velocity?
24.What is polarization?
25.What is intermodal dispersion?
26.What are the advantages of optical communication?
27.Define direct band gap materials and indirect band gap materials
28.What are the advantages of LED?
29.What are the two types of LED configurations?
30.What are the three requirements of Laser action?
31.What are splices? What are the requirements of splices?
32.What are connectors? What are the types of connectors?
33.Explain the advantages of fiber optics communication in detail.
34.Name the basic principle of light propagation in optical fiber. Explain in detail.
35.Explain step index and graded index fiber in detail.
36.Differentiate multimode and single mode fibers.
37.What do you mean by dispersion in fiber. How it is related to bit rate of system?
38.What are the requirements of optical sources? Explain any one type of source in detail.
39.Give the advantages of LED over LASER.