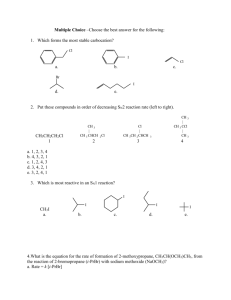
Ethotoin Phenobarbital Methsuximide Mephenytoin Carbamazepine
advertisement

Ethotoin Methsuximide Mephenytoin Phenobarbital Carbamazepine Diazepam If we have a look at all structures, first four are similar in terms of having two amide functional groups being more polar compared to 5 and 6 compounds have single substituted amide functional group. So that’s the reason first 4 elute in smaller difference of elution times while 5 and 6 being less polar elute a little later. Back pressure differs depending on species of organic solvents and mixing ratio. Back pressure of acetonitrile is lower than that of methanol at the same concentration. Mobile phase given is water:CH3-C≡N in the ratio of 40:60 indicating that more of acetonitrile whose back pressure impact is all the more due to its higher proportion. Water is polar Inorganic solvent and hence can elute only polar inorganic impurities along with it during elution, while Acetonitrile is a polar solvent and hence polar organic compounds would elute faster with the higher proportion of acetonitrile, moreover its back pressure being more than that water. Changing this ratio [say, lowering the percentage of acetonitrile and increasing the percentage of water] would effect the polarity of the mobile phase and it may alter the elution pattern drastically. Less polar compounds out of the given [5 and 6] having single substituted amide group might elute first since the polarity of the mobile phase in this new proportion is less, and hence polar compounds 1-4 would elute later. If the proportion or mixing of two solvents water and acetonitrile is too extreme say [water: 20 and acetonitrile: 80], this may effect the elution pattern too since the mobile pahse now would be too polar than required, where first 4 compounds would equally compete with this high polar solvent all of them, might be eluted almost at same elution times giving less difference in the graph and might pose problem in their separation and purification later. Elution time difference between 5 and 6 might decrease drastically too. Hence the ratio of 40:60 for water:acetonitrile is chosen efficiently based on the functional groups of the compounds present in the mixture such that their elution pattern is distinct enough to isolate them.