IME 101 Intro to Industrial and Manufacturing Eng
advertisement

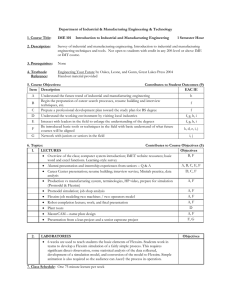
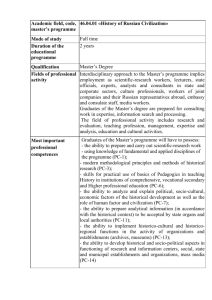
Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering & Technology 1. Course Title: IME 101 Introduction to Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering 2. Description: 3. Prerequisites: Survey of industrial and manufacturing engineering. Introduction to industrial and manufacturing engineering techniques and tools. Not open to students with credit in any 200-level or above IME or IMT course. None 4. Textbook: Reference: Engineering Your Future by Oakes, Leone, and Gunn, Great Lakes Press 2004 Handout material provided 5. Course Objectives: 1 Semester Hour Contributes to Student Outcomes Item Description EAC MFE A Understand the future trend of industrial and manufacturing engineering a, c B Begin the preparation of career search processes, resume building and interview techniques, etc b, d, k C Prepare a professional development plan toward the study plan for BS degree k D Understand the working environment by visiting local industries g, i, k E Interact with leaders in the field to enlarge the understanding of the degrees g, , i F Be introduced basic tools or techniques in the field with basic understand of what future courses will be aligned b, c, d, e, i, j, k G Network with juniors or seniors in the field i, j 6. Topics: Contributes to Course Objectives (5. 1. LECTURES Objectives B, F Overview of the class; computer system introduction; IMET website resources; basic word and excel functions. Learning-style survey A, B, C, E, F Alumni presentation and internship experiences from seniors – Q & A D, C, F Career Center presentation; resume building; interview service; Minitab practice, data analysis A, F Production vs manufacturing system, terminologies, HP video, prepare for simulation (Promodel & Flexsim) 2. Promodel simulation; job shop analysis A, F Flexsim-job modeling two machines / two operators model Robot completion lecture; work; and final presentation Plant tours A, F A, F D MasterCAM – name plate design A, F Presentation from a lean project and a senior capstone project F, G LABORATORIES 6 weeks are used to teach students the basic elements of Flexsim. Students work in teams to develop a Flexsim simulation of a fairly simple process. This requires significant direct observation, some statistical analysis of the data collected, development of a simulation model, and conversion of the model to Objectives Flexsim. Simple animation is also required so the audience can Asee@ the process in operation. 7. Class Schedule: One 75 minute lecture per week 8. Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: Mathematics and Basic Science Engineering Topics, Engineering Sciences, Engineering Design General Education 0 hrs 1 hrs 0 hrs 9. Relationship of Course to MFE Student Outcomes: (based on 1 to 5 scales, 5 denotes very strong continuation to the student outcome and blank cell denotes that the course does not continue the related student outcome) Code a b c d e f g h i j k 10. Student Outcomes, A Graduate from the Program Will Have: Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics and science to manufacturing processes, materials, and design of manufacturing systems Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to design and conduct experiments, and to analyze and interpret data related to manufacturing processes, materials evaluation, and manufacturing systems Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to design, select, implement, and control a manufacturing system and its components or processes to meet desired needs Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to function on multidisciplinary teams and the ability to apply a concurrent approach and project management to process and product development Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to identify, formulate, and solve manufacturing engineering problems through a hands-on approach that considers constraints, costs, benefits, and comparative processes and materials Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the professional and ethical responsibilities of a manufacturing engineer Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to effectively communicate technical concepts through appropriate methods Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the impact of manufacturing engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have a recognition of the need to engage in lifelong learning Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have a knowledge of contemporary issues facing manufacturing engineers Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to use the proper techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for manufacturing engineering practice utilizing supporting technologies Prepared by: Joseph Chen, 2/2014 Contribution Reviewed by: Curriculum Committee 1 1.29 1 2.14 1 — 2 — 1.17 — 1.25