Eighth Grade Social Studies
advertisement
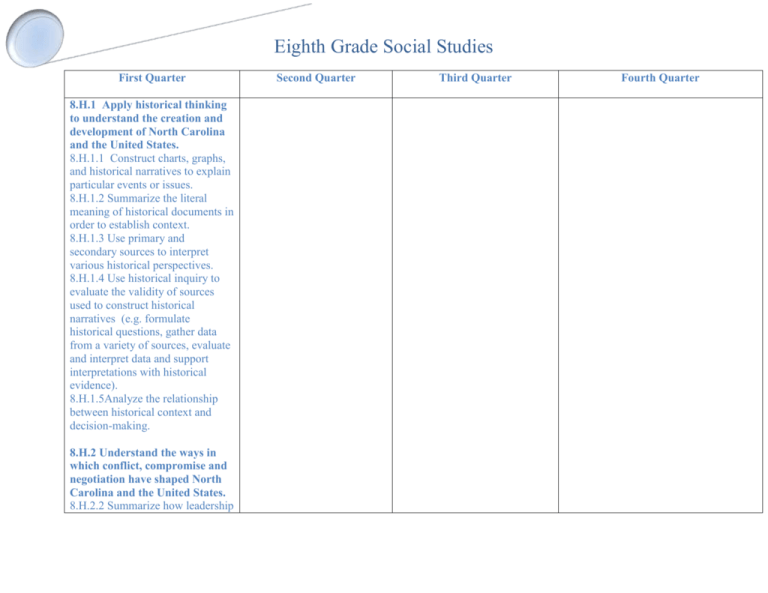
Eighth Grade Social Studies First Quarter 8.H.1 Apply historical thinking to understand the creation and development of North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.1.1 Construct charts, graphs, and historical narratives to explain particular events or issues. 8.H.1.2 Summarize the literal meaning of historical documents in order to establish context. 8.H.1.3 Use primary and secondary sources to interpret various historical perspectives. 8.H.1.4 Use historical inquiry to evaluate the validity of sources used to construct historical narratives (e.g. formulate historical questions, gather data from a variety of sources, evaluate and interpret data and support interpretations with historical evidence). 8.H.1.5Analyze the relationship between historical context and decision-making. 8.H.2 Understand the ways in which conflict, compromise and negotiation have shaped North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.2.2 Summarize how leadership Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter Eighth Grade Social Studies and citizen actions (e.g. the founding fathers, the Regulators, the Greensboro Four, and participants of the Wilmington Race Riots, 1898) influenced the outcome of key conflicts in North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.2.3 Summarize the role of debate, compromise, and negotiation during significant periods in the history of North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.3 Understand the factors that contribute to change and continuity in North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.3.3 Explain how individuals and groups have influenced economic, political and social change in North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.3.4 Compare historical and contemporary issues to understand continuity and change in the development of North Carolina and the United States. 8.C and G.1 Analyze how democratic ideals shaped government in North Carolina and the United States. 8.C and G.1.1 Summarize Eighth Grade Social Studies democratic ideals expressed in local, state, and national government (e.g. limited government, popular sovereignty, separation of powers, republicanism, federalism and individual rights). 8.C and G. 1.4 Analyze access to democratic rights and freedoms among various groups in North Carolina and the United States (e.g. enslaved people, women, wage earners, landless farmers, American Indians, African Americans and other ethnic groups). First Quarter Cartographer Loam Era Circa Anthropologist BD AD CE BCE Timeline Narrative Archaeologist Climate Barrier Islands Coastal Plain Piedmont Mountains Outer Banks Tidewater Geographic Region Declaration of Independence Constitution Primary Source Articles of Confederation Mecklenburg Resolves Halifax Resolves Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter Eighth Grade Social Studies The Great Compromise 3/5’s Compromise Propaganda Bill of Rights Bias Primary Sources Secondary Sources Historical Perspective Bibliography Validity Evaluate Back Country Cash Crop Racism Arsenal Protest Appeasement British Rule Townshend Acts Sugar Act Battle of Gettysburg 54th Massachusetts Battle of Midway Torpedo Junction Gen. Douglas MacArthur Desert Storm Iran-Contrat Boycott Treason Tariff Session Sectionalism Neutrality French and Indian War Intolerable Acts Sons of Liberty March to the Sea Fort Fisher Hiroshima Lusitania NAFTA al Qaeda Terrorism Anti-Bellum Confederacy Slavery Progressive Prohibition Propaganda Albany Plan of Union Edenton Tea Party Fort Sumter Total War Political Alliance Eighth Grade Social Studies Pearl Harbor Isolationism Watergate OPEC Social Reform Consumerism Recession Gross Domestic Product Proclamation of 1763 Boston Tea Party Hunley Battle of Vicksburg Axis Powers Manhattan Project Adolf Hitler 9/11 Middle East Unemployment Inflation Concentration Camp Holocaust Imperialism Quartering Act Parent Country Appomattox Courthouse Allied Powers Island Hopping United Nations War on Terror Patriot Act Genocide Nationalism D-Day Andrew Jackson Carpetbaggers Scalawag Boston Massacre Iraq Way Battle of Iwo Jima Dwight Eisenhower ADA Magna-Carta Minuteman Loyalists Patriot Arsenal Revolution Framers Reconstruction Impeach Fascism Civil Rights Suburb Segregation Incumbent Eighth Grade Social Studies Electoral College Liberal Conservative Hessian Continental Congress Zebulon Pike War Hawks Lord Proprietors Sacagawea Andrew Jackson Battle of New Orleans Nathaniel Green Napoleon Bonaparte Westward Expansion Dolly Madison George Washington War with Mexico Trail of Tears Benjamin Franklin Texas Independence Daniel Boone Wilmington Sit-In Thomas Paine Civil Rights Missouri Compromise Underground Railroad Dred Scott Confederate States of America Fort Sumter Cotton Farming Abolition Domino Theory Compromise of 1877 Great Compromise Temperance Emancipation Draft Sharecropping Tenant Farming Monopoly Acid Rain Infrastructure Research Triangle Park Space Race Eighth Grade Social Studies Internet Canal System Cotton Gin Westward Expansion Wilmington Race Riot Literacy Tests Poll Tax Ellis Island Angel Island Grandfather Clause Quota System Robert E. Lee Ulysses S. Grant Jefferson Davis Abraham Lincoln CSA Anaconda Plan Proclamation Albany Plan of Union NAACP Federalist Anti-Federalist Regionalism Liberal Conservative McCarthyism Bill of Rights Landless Farmers Wage Earners Segregation Korean War Refugee Cold War Truman Doctrine 38th Parallel Containment Tet Offensive Viet Nam War Marshall Plan War Powers Act Mikhail Gorbachev Ronald Regan Glasnost Vietnamization Cuban Missile Crisis Gulf of Tonkin Eighth Grade Social Studies Suffrage Resources Communists Writing Task Is a democracy always democratic? Given what you know about the history of American Indians in North Carolina and the United States, write an essay explaining the extent to which you believe American Indians were adequately included in the democratic process. Be sure to cite specific examples in your essay. Updated 8/31/2013