Electrochemistry questions for midterm or semi
advertisement

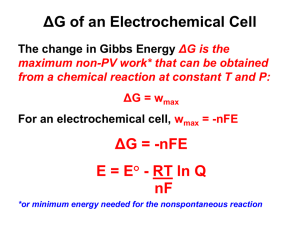
Q inelectrochemistry 2015 Sample questions for midterms and semi final exams In your answer explain the meaning of all parameters you used. E.g. C = capacitance, R = universal gas constant. Electrochemistry of ion activity 1.Chemical potential of a 1:1electrolitegiveninterms of activities, activitycoefficients 2.The mean activity coefficient, geometric mean. 3.Example activity: MgCl2. 4.Relationship between Ka and Km, in other words: the equilibrium constant given in terms of activities and activity coefficients 5.Ionic strength, a definition . 6. Mean activity coefficient determination via calculation 7. Debye-Hückel extended and limiting Law Conductivity and transportnumber 1.Base definitions: electric resistance, e. conductance, e. conductivity, e. molar conductivity 2. The molar conductivity vs. electrolyte concentration dependence of a strong electrolite. Use figure for explanation. 3. Strong electrolite: Kohlrausch’s law ( Λm f (c) . Use figure for explanation. 4. Determination of limiting molar conductivity. 5. Independent migration of ions. Electrolyte Λm0 KCl 149.79 KI 150.31 ½ K2SO4 153.48 Electrolyte NaCl NaI ½ Na2SO4 Λm0 126.39 126.88 130.1 Difference 23.4 23.4 23.4 Using this table explain the meaning of independent migration of ions. 6. Weak electrolites: the degree of ionization given in terms of molar conductivities. Λm0 7. Ostwald’s dilution law ( f (K a ) Λm 8. Ostwald’s dilution law: determination of 0m . 9. The condition for mechanical equilibrium of transporting ion, ionic mobility. 10. The ion flux 11. u zF , explain the meaning of parameters and variables. c 12. Transport number, a definition. Galvanic cells 1.Anode, cathode ,liquid liquid junction – their description and working principle. 2.Galvanic cell, electrolisyscell –the spontaneous direction of electrode processes. 3. Cell diagram usingDaniell cell as example cell. How to make sure the cellreaction potential to be positive? 4. Cell reaction potential, electromotive force – their definitions, conditions of measurement Ecell. 5.The Nernst equation – the activity dependence of Ecell 6.Electrode potentials, possibility of determination of individual electrode potentials 7. The structure of electric double layer 0 8. Eqilibrium constant determination from Ecell data. 9. Electrolyte concentration cells: the cell diagram, the cell reaction, Nernst equation. 10. Metal metal-ion electrode: the cell diagram, the cell reaction, Nernst equation. 11. Metal insoluble salt electrodes: the cell diagram, the cell reaction, Nernst equation. 12. The properties of reference electrodes. 13. Ion – ion (redox) electrode: the cell diagram, the cell reaction, Nernst equation. 14. The hydrogen gas electrode: the cell diagram, the cell reaction, Nernst equation. 15. The electrochemical potential scale, the standard hydrogen elctrode. 16. The electrochemical determination of pH. 17. The electrode reaction potential, formal potential 18. Temperature dependence of Ecell, EMF Electrochemical kinetics (This lecture is the theme of semi-final exam only) 1.The rate of reactions at phase boundary. 2. The reaction rate given in terms of current density. (diff. equation is needed) 3.Polarization, overvoltage, exchange current density. 4.Compare the current vs. polarization potential curve of an ideal polarizable and ideal nonpolarizable electrodes. (two graphs are needed). 5. Forward and backward rate of reversible process: Fe3+ + e ↔ Fe2+ (kinetic equation for reduction and oxidation direction). Ex01. What molality of CuSO4 has the same ionic strength as a 1 mol/kg molality solution of KCl? Ex02. Calculate ionic strength for a solution that is 0.2 molal in KCl and 0.6molal in K2Cr2O7.