oxide films deposited by CBD
advertisement

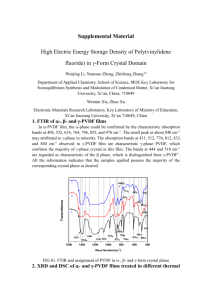
Effect of solution molarity on structural and optical properties of nickel hydroxide/ oxide films deposited by CBD T. Taşköprü 1, 2*, E. Turan 1, M. Zor 1 1 2 Department of Physics, Anadolu University, Eskişehir 26470, Turkey Department of Physics, Çankırı Karatekin University, Çankırı 18100, Turkey Abstract In this work, nickel hydroxide samples at different molarities (0.1M, 0.3M, and 0.5M) have been successfully deposited using nickel nitrate as precursor in a mixed solution of ammonia onto glass substrate by chemical bath deposition (CBD) method. The structural and optical properties of the films have been investigated using XRD, SEM, and UV-Visible spectroscopy. XRD patterns show that as-deposited films were β- Ni(OH)2 (Theophrastite, JCPDS 14-0117) have (001) preferred orientation with 4.615Å interlayer spacing. Ni(OH)2 were annealed at 400°C for 1 h in air to obtain NiO. The XRD results showed that all annealed films were polycrystalline in nature with face centerd cubic structure (Bunsenite, JCSPD 47-1049) and preferred orientation along (111) plane. The SEM images reveal that the surface morphologies of nickel hydroxide / oxide samples were affected by the solution molarity. The deposited samples with 0.1 M is in the form of network structured nanoflakes. The increase in molarity leads to change the nanoflake structure to nanosheet formation. The absorbance and transmittance spectra of nickel hydroxide / oxide samples were recorded by using Shimadzu Solid Spec 3700 UV-VIS-NIR Spectrophotometer in the wavelength range of 200– 3300 nm in order to study the optical properties. The optical band gap of the NiO films have been evaluated using Tauc’s equation. The band gap energy of NiO samples were found to be in the range 3.72 and 3.80 eV depending on the solution molarity.