Probabilistic_analysis_handout
advertisement

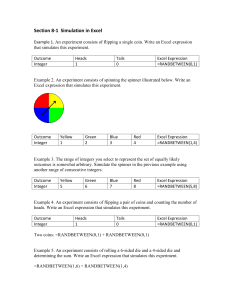
Probabilistic Analysis Handout Important excel functions =randbetween(bottom, top) might require analysis tool pack add-in = rand() =norminv(probability, mean, standard deviation) =if(logical test, value if true, value if false) =vlookup(lookup value, table array, column number) =countif(range, “criteria”) =count(range) F9 to execute the rand() and randbetween() functions Table 1: Using excel to get a random “draw” from a distribution Common Excel functions to call a Examples distributions random value uniform =randbetween(min, max) uniform between 2,000 and 3,000 $400 at 25% $500 at 25% $600 at 25% $700 at 25% normal =norminv(rand(),mean,std) normal dist. with mean = $500 and std = $200 discrete (2 =if(rand()<=lower bound, 15 yrs 30% possibilities) lower outcome, higher 16 yrs 70% outcome) discrete =vlookup(rand(),lookup table, $120 at 10% (more than 2 column) $160 at 30% possibilities) $180 at 60% Example Excel code =randbetween(2,000,3,000) =randbetween(4,7)*100 =norminv(rand(),500,200) =if(rand()<=.3,15, 16) lookup table range Lower value bound 0-0.1 0 $120 0.1-0.4 0.1 $160 0.4-1.0 0.4 $180 Note: lower bound sorted low to high Installation of the MCSim add in 1. Get MCSim.xla from the class website or directly from its creators at this address: http://www3.wabash.edu/econometrics/EconometricsBook/Basic%20Tools/ExcelAddIns/MCSim.htm 2. In excel, go to Excel Options/Add-Ins. Hit “Go” at the bottom. Browse to location. 3. You will from now on see the button for it in the “Add-In” tab of excel. **1. Do not run the addin from the zip folder. You need to "extract" or "unzip" the folder first. **2. Do not click on the addin and open it up directly. You must open a separate excel file, and then: File/Options/Addins/Go/Browse. 1 Generate 1,000 simulation runs and calculate (1) mean, (2) standard deviation, (3) and prob. of loss. Example 1 [This problem is easier than the next two.] Initial investment = $150,000 Annual revenues are uniformly distributed between $200,000 and $300,000. Annual costs are uniformly distributed between $175,000 and $275,000. Salvage value has a 75% chance of being $40,000 and 25% chance of being $80,000. n=8 MARR = 10% Example 2 [This problem is more advanced because the annual costs have a constraint that requires additional coding in excel.] Initial investment = $150,00 Annual revenues are uniformly distributed between $65,000 and $98,000. Annual costs are normally distributed with a mean of $35,200 and standard deviation of $14,500 (annual costs can only be negative, so make positive values =0). Salvage value = $60,000. n=8 MARR = 10% Example 3 [This problem is more advanced because the salvage value has a discrete distribution that requires a vlookup table in excel. The annual revenue also has a discrete distribution but it can be dealt with using =randbetween().] Initial investment = $80,000 Annual revenues have an equal chance of being $30,000, $40,000, or $50,000. Annual costs are uniformly distributed between $27000 and $38,500. Salvage value could be: $30,000 (60% chance), $50,000 (20% chance), or $75,000 (20% chance). n=8 MARR = 10% Example 4 [This problem is more advanced because (1) the useful life has a discrete distribution that requires additional “dependency” coding in excel and (2) the salvage value depends on useful life so requires an if statement.] Calculate IRR for the following business venture: Initial investment = $45,000 Annual sales are uniformly distributed between 100 and 900. Annual revenues = $85*(annual sales) Annual costs are uniformly distributed between $20,000 and $40,000. Salvage value is $35,000 if n = 9 years and $20,000 if n = 10 years Useful life, n, has a 80% chance of being 9 years and a 20% chance of being 10 years. 2